Abstract
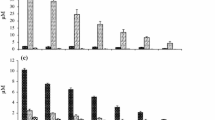
The population growth pattern and related changes in both the nitrogen and phosphorus contents in the cell of the dinoflagellate Peridinium penardii (Lemm.) Lemm., which formed a freshwater red tide in a reservoir, were studied in situ. An exponential increase with time in population density was found. A specific growth rate of 0.25 d−1 was observed. The cellular content of phosphorus per cell decreased from 6.0 × 10−5 µg to 9.2 × 10−6 µg along with an increase in population density from 8.0 × 102 cells ml−1 to 2.5 × 104 cells ml−1. A prominent change in the cellular nitrogen did not occur. Decreasing cell content and continuous uptake of phosphorus were advantageous for P. penardii to form a freshwater red tide under P-limited conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA-AWWA-WPCF (ed.), 1975. Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (14 edn). APHA, Washington.
Elgavish, A., G. A. Elgavish & M. Halmann, 1980. Phosphorus utilization and storage in batch cultures on the dinoflagellate Peridinium cinctum f. westii. J. Phycol. 16: 626–633.
Elgavish, A., M. Halmann & T. Berman, 1982. A comparative study of phosphorus utilization and storage in batch cultures of Peridinium cinctum, Pediastrum duplex and Cosmarium sp., from Lake Kinneret (Israel). Phycol. 21: 47–54.
Grasshoff, K., M. Ehrhardt & K. Kremling (eds), 1976. Methods of Seawater Analysis. Verlag Chemie.
Halmann, M. & A. Elgavish, 1979. An indication to the role of intracellular phosphorus for the development of the dinoflagellate Peridinium bloom in Lake Kinneret. Wat. Res 13: 585–588.
Hashimoto, Y., T. Okaichi, L. D. Dang & T. Noguchi, 1968. Glenodine, an ichthyotoxic substance produced by a dinoflagellate, Peridinium poplonicum. Bull. Jap. Soc. Sci. Fish. 34: 528–534.
Hata, Y., 1983. Peridinium red tide in the Nagase Reservoir. Res. Data Natl. Inst. Envir. Stud. Japan 24: 15–28 (in Japanese).
Healey, F. P., 1973. Characteristics of phosphorus deficiency in Anabaena. J. Phycol. 9: 383–394.
Healey, F. P. & L. L. Hendzel, 1979. Indicators of phosphorus and nitrogen deficiency in five algae in culture. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 36: 1364–1369.
Herrgesell, P. L., T. H. Sibley & A. W. Knight, 1976. Some observations on dinoflagellate population density during a bloom in a California reservoir. Limnol. Oceanogr. 21: 619–624.
Honjo, T., T. Shimouse & H. Hanaoka, 1978. A red tide occurred at the Hakozaki Fishing Port, Hakata Bay, in 1973 — The growth process and the chlorophyll content. Bull. Plankton Soc. Jap. 25: 7–12.
Horne, A. J., P. Javornicky & C. R. Goldman, 1971. A freshwater ‘red tide’ on Clear Lake, California, Limnol. Oceanogr. 16: 684–689.
Ikeda, T., T. Matsumoto, H. Kisa, Y. Ishida & A. Kawai, 1993. Analysis of growth limiting factors causative of freshwater red tide by dinoflagellate Peridinium bipes f. occulatum. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 54: 179–189 (in Japanese with English summary).
Ito, T., 1979. Occurence of freshwater red tide in western Japan. Bull. Plankton Soc. Jap. 26: 113–116. (In Japanese).
JWWA., 1978. Methods for the examination of water (in Japanese). Jap. Wat. Work Assoc., Tokyo.
Kagawa, H., Y. Iseri & T. Ito, 1984. Environmental conditions at the head of a reservoir where freshwater red tide of Peridinium occurs — In the case of the Ishitegawa Dam Reservoir. Jap. J. Wat. Pollut. Res. 7: 375–383 (in Japanese with English summary).
Kawabata, Z. & M. Ohta, 1989. Cyst distribution and excystment conditions for the dinoflagellate Peridinium penardii (Lemm.) Lemm. in a reservoir. Freshwat. Biol. 21: 437–444.
Kubo, N., K. Shiota & Y. Kitamura, 1988. Phenomena of red tide in fresh water and environmental conditions in Kazaya Reservoir. Comm. Internat. Grands Barrages: 283–307.
Lang, D. S. & E. J. Brown, 1981. Phosphorus-limited growth of a green alga and a blue green alga. Appl. envir. Microbiol. 42: 1002–1009.
Lund, J. W. G., 1950. Studies on Asterionella formosa Hass. II. Nutrient depletion and the spring maximum. J. Ecol. 38: 1–35.
Nakamoto, N., 1975. A freshwater red tide on a water reservoir. Jap. J. Limnol. 36: 55–64.
Nishibori, N., T. Nishijima, Y. Onoda & Y. Hata, 1991. Effects of light intensity, temperature, pH, and nitrogenous nutrient on the growth of Peridinium bipes fo. occulatum. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 57: 1729–1735 (in Japanese with English).
Oshima, Y., H. Minami, Y. Takano & T. Yasumoto, 1988. Ichthyotoxins in a freshwater dinoflagellate Peridinium polonicum. In T. Okaichi, D. M. Anderson & T. Nemoto (eds), Red Tides: Biology, Environmental Science and Toxicology. Elsevier Science Publishing Co., Inc.; New York: 375–378.
Park, H. D. & H. Hayashi, 1993. Role of encystment and excystment of Peridinium bipes f. occulatum (dinophyceae) in freshwater red tide in Lake Kizaki, Japan. J. Phycol. 29: 435–441.
Pestalozzi, G. H., 1968. Das Phytoplankton des Süßwassers (3 Teil), E. Schweizerbart'sche Verlagsbuchhandlung, Stuttgart.
Pollingher, U. & B. Hickel, 1991. Dinoflagellate associations in a subtropical lake (Lake Kinneret, Israel). Arch. Hydrobiol. 120: 267–285.
Sakshaug, E., K. Anderson, S. Myklestad & Y. Olsen, 1983. Nutrient status of phytoplankton communities in Norwegian waters (marine, brackish, and fresh) as revealed by their chemical composition. J. Plankton Res. 5: 175–196.
Serruya, C. & T. Berman, 1975. Phosphorus nitrogen and the growth of algae in lake Kinneret. J. Phycol. 11: 155–162.
Sibley, T. H., P. L. Herrgesell & A. W. Knight, 1974. Density-dependent vertical migration in the freshwater dinoflagellate Peridinium penardii (Lemm.) Lemm. fo. californicum Javorn. J. Phycol. 10: 475–476.
Sibley, T. H., P. L. Herrgesell & A. W. Knight, 1975. Interactions between population density and water quality parameters during a dinoflagellate bloom. Verh. int. ver. Limnol. 19: 1820–1828.
Watanabe, T., A. Shimizu, T. Ishii & T. Tsubota, 1983. A study on freshwater red tide Peridinium bipes f. occulatum (Lemm.) Lef. Res. Data Natl. Inst. Envir. Stud. 24: 29–48 (in Japanese).
Watanabe, M., 1983. Reservoir environment and a red tide of Peridinium. Res. Data Natl. Inst. Envir. Stud. 24: 123–131 (in Japanese).
Watanabe, M. M., 1983. Studies on growth characteristics of an axenic Peridinium, a freshwater red tide species — establishment of an artificial medium. Res. Data Natl. Inst. Environ. Stud. 24: 111–121 (in Japanese).
Watanabe, Y., H. Park & H. Hayashi, 1990. Effects of Calcium on occurrence of freshwater red tide caused by Peridinium bipes in Lake Kizaki. Rep. Ann. Envir. Sci. Shinshu Univ. 22: 70–77 (in Japanese).
Wynne, D., N. J. Paitni, S. Aaronson & T. Berman, 1982. The relationship between nutrient status and chemical composition of Peridinium cinctum during the bloom in Lake Kinneret. J. Plankton Res. 4: 125–136.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kawabata, Z., Hirano, Y. Growth pattern and cellular nitrogen and phosphorus contents of the dinoflagellate Peridinium penardii (Lemm.) Lemm. causing a freshwater red tide in a reservoir. Hydrobiologia 312, 115–120 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00020767
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00020767