Abstract
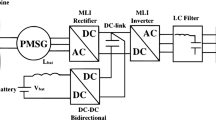
This paper presents a simple control structure using rotor flux oriented vector technique for a stand-alone permanent magnet synchronous generator (PMSG) associated to PWM rectifier, PWM DC–DC converter and PWM inverter. The DC–DC converter feeding an electronic load is controlled to maintain the dc-bus voltage at a desired constant value. The isolated PMSG is assumed to be driven by a variable speed wind turbine. A sliding mode control strategy has been developed to regulate the direct axis current, ensure maximum power tracking issue as well dc-bus voltage regulation. The online estimation of the rotor flux using sliding mode concept is provided. The control and estimator stability analysis is based on Lyapunov theory. Simulation results, carried out in Matlab/Simulink software, are presented to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed control method when the control system operates under load variations and parameters uncertainties. The proposed adaptive control can be used in remote area where wind speed is low.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sniders A, Straume I (2008) Simulation of electrical machine system with permanent magnet synchronous generator. Eng Rural Dev 29:97–102
Dambur L, Bezrukov V, Pugachev V, Johanson U (1994) On the use of the permanent magnet motor as a generator for the wind-power plant (WPP). Latv J Phys Tech Sci 5:63–67
Chang L (2002) Systèmes de conversion de l’énergie éolienne. IEEE Canadian Review 1–5
Messaoud M, Abdessamed R (2011) Modeling and optimization of wind turbine driving permanent magnet synchronous generator. Jordan J Mech Ind Eng 6:489–494
Belakehal S, Bentounsi A, Merzoug M, Benalla H (2010) Modélisation et commande d’une génératrice synchrone à aimants permanents dédiée à la production de l’énergie éolienne. Revue des Energies Renouvelables 13:149–161
Chennoufi H, Lamri L, Nemmour AL, Khezzar A, (2010) Contrôle d’une génératrice synchrone à aimants permanents dédiée à la conversion de l’énergie éolienne par la commande directe du couple. Revue des Energies Renouvelables SMEE’10 Bou Ismail Tipaza, 115–124
Merzoug MS, Benalla H, Louze L (2011) Nonlinear control of permanent magnet synchronous generators ( PMSG) using feedback linearization. Revue des Energies Renouvelables 14:357–367
Utkin VI (1993) Sliding mode control design principles and applications to electric drives. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 40:26–36
Utkin VI, Guldner J, Shi J (1999) Sliding mode control in electromechanical systems. CRC Press LLC, New York
Kenné G, Ahmed-Ali T, Nkwawo H, Lamnabhi-Lagarrigue F (2005) Robust rotor flux and speed control of induction motors using on-line time-varying rotor resistance adaptation. Proceeding of the 44th IEEE conference on decision and control, and European control conference,CDC-ECC’05, Seville, Spain
Kenné G, Ahmed-Ali T, Lamnabhi-Lagarrigue F, Arzande A (2007) Real-time implementation of rotor flux and speed control of induction motors using on-line rotor resistance and load torque adaptation. Book of the selected papers of the joint CTS-HYCON Workshop, 15:341–362 Paris, France, July 2006, Ed. by ISTE Publishing Knowledge, ISBN: 978 1 905209 65 1
Bekakra Y, Ben Attous D (2014) DFIG sliding mode control fed by back-to-back PWM converter with DC-link voltage control for variable speed wind turbine. Front Energy 8:345–354
Merzoug MS, Benalla H, Louze L (2012) Sliding mode control (SMC) of permanent magnet synchronous generators (PMSG). Energy Procedia 18:43–52
Hostettler J, Wang X (2015) Sliding mode control of a permanent magnet synchronous generator for variable speed wind energy conversion systems. Syst Sci Control Eng 3:453–459
Ciampichetti S, Corradini ML, Ippoliti G, Orlando G, (2011) Sliding mode control of permanent magnet synchronous generators for wind turbines. IEEE IECON, 37th annual conference on IEEE industrial electronics society 740–745
Li-Xia S, Zhe W, Feng-Ling H, Feng Y (2014) A chattering-free terminal sliding mode control of direct-drive PWM for wind generation system. IEEE IECON, 4th annual IEEE international conference on cyber technology in automation, control and intelligent systems, 296–301
Benelghali SE, Benbouzid MEH, Charpentier JF, Ahmed-Ali I, Munteanu T (2011) Experimental validation of a marine current turbine simulator: application to a permanent magnet synchronous generator-based system. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 58:118–126
Valenciaga F, Puleston PF (2008) High-order sliding control for a wind energy conversion system based on a permanent magnet synchronous generator. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 23:860–867
Heier S (1998) Grid integration of wind energy conversion systems. Wiley, Hoboken
Hadri-Hamida A, Zerouali S, Allag A (2013) Toward a nonlinear control of an AC-DC-PWM converter dedicated to induction heating. Front Energy 7:140–145
Thongam JS, Bouchard P, Beguenane R, Okou AF, Merabet A, (2011) Control of variable speed wind energy conversion system using a wind speed sensorless optimum speed MPPT control cethod. IEEE IECON. 37th annual conference of the IEEE industrial electronics 855–860
Lin CH (2013) Recurrent modified elman neural network control of permanent magnet synchronous generator system based on wind turbine emulator. AIP J Renew Sustain Energy 5:053103
Deraz SA, Abdel Kader FE (2013) A new control strategy for a stand-alone self-excited induction generator driven by a variable speed wind turbine. Renew Energy 51:263–273
Beltran B, Ahmed Ali T, Hachemi Benbouzid ME (2009) High-order sliding-mode control of variable-speed wind turbines. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 56:3314–3321
Slotine JJ, Li W (1991) Applied nonlinear control. Prentice Hall, New york
Utkin VI (1992) Sliding modes in optimization and control. Springer, Berlin
Haque ME, Muttaqi KM, Sayeef S, Negnevitsky MM (2008) Control of a stand alone variable speed wind turbine with a permanent magnet synchronous generator. IEEE IECON. Energy society general meeting. Pittsburgh, pp. 1–9
Mancilla-David F, Ortega R (2012) Adaptive passivity-based control for maximum power extraction of stand-alone windmill systems. Control Eng Pract 20:173–181
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kenne, G., Douanla, R.M. & Pelap, F.B. An adaptive nonlinear control strategy for a stand-alone permanent magnet synchronous generator driven by a variable speed wind turbine. Int. J. Dynam. Control 5, 1103–1113 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40435-016-0257-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40435-016-0257-7