Abstract
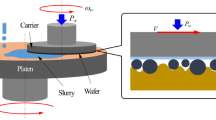
In this paper, effect of ultrafine ceria (UFC) particle of which size is as small as 20 nm on CMP performance was investigated. Compared to conventionally used 100 nm abrasive particle which is made by calcination process, almost 80% scratch reduction was obtained by using UFC. However, a UFC slurry showed unstable material removal rate behavior from less than 200 Å/min to over 2000 Å/min, depending on polishing pad surface characteristics. As pad surface roughness increases, oxide removal rate using UFC drops abruptly to less than 200 Å/min. In order to use UFC for scratch reduction, the pad surface roughness optimization is necessary to avoid a sudden drop in the removal rate. This study gives a possible boundary for pad surface roughness for UFC application for CMP.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. M. Steigerwald, S. P. Muraka, and R. J. Gutmann, Chemical Mechanical Planarization of Microelectronic Materials, p. 1, John Wiley & Sons Inc., New York, USA (1997).
M. R. Oliver (Ed.), Chemical-Mechanical Planarization of Semiconductor Materials, p. 7, Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, Germany (2004).
Y. Li (Ed.), Microelectronic Applications of Chemical Mechanical Planarization, p. 1, John Wiley & Sons Inc., New Jersey, USA (2008).
H. Liang, Tribo. Int. 38 235 (2005).
J. Van Olmen, J. Coenen, W. Dehaene, K. De Meyer, C. Huyghebaert, A. Jourdain, Guruprasad Katti, A. Mercha, M. Rakowski, M. Stucchi, Y. Travaly, E. Beyne, and B. Swinnen, IEEE Int. Conf. on 3D Sys. Integr. p. 1, IEEE, San Francisco, CA, USA (2009).
S. W. Yoon, D. W. Yang, J. H. Koo, M. Padmanathan, and F. Carson, IEEE Int. Conf. on 3D Sys. Integr. p. 28, IEEE, San Francisco, CA, USA (2009).
A. Chandra, P. Karra, A. F. Bastawros, R. Biswas, P. J. Sherman, S. Armini, and D. A. Lucca, CIRP Annals-Manuf. Tech. 57 559 (2008).
N. Saka, T. Eusner, and J.-H. Chun, CIRP Annals-Manuf. Tech. 57 341 (2008).
D. Ryuzaki, Y. Hoshi, Y. Machii, N. Koyama, H. Sakurai, and T. Ashizawa, Proc. Sym. VLSI Tech. p. 168, Jpn. Soc. Appl. Phys., Kyoto, Japan (2009).
H.-J. Kim, B. Kim, B.-U. Yoon, K. Lee, Y. Ko, and C.-J. Kang, Proc. of Int. Conf. on CMP/Planarization Tech., p. 93, AZ, USA (2010).
I.-H. Sung, H. J. Kim, and C. D. Yeo, Appl. Surf. Sci. 258 8298 (2012).
Y. Wang, Y.-W. Zhao, and J. Gu, J. Mater. Proc. Tech. 183 374 (2007).
Y. Lee, Y.-J. Seo, J.-W. Yang, H.-H. Kim, Y. Park, and H. Jeaong, Electron. Mater. Lett. 8 81 (2012).
J.-S. Kim, H.-G. Kang, M. Kanemoto, U. Paik, and J.-G. Park, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 46 7671 (2007).
M.-H. Oh, R. K. Singh, S. Gupta, and S.-B. Cho, Microelec. Eng. 87 2633 (2010).
H.-G. Kang, T. Katoh, and J.-G. Park, J. Kor. Phys. Soc. 47 705 (2005).
S.-K. Kim, U. Paik, and J.-G. Park, J. Cer. Proc. Res. 7 53 (2006).
Y. Lee, Y. J. Seo, and H. Jeong, Electron. Mater. Lett. 8 523 (2012).
S. Raghavan, M. Keswani, and R. Jia, KONA Powder and Particle Journal 26 94 (2008).
J. Park, H. Jung, K. Yoshida, and M. Kinoshita, Jpn J. Appl. Phys. 47 1028 (2008).
X. Liao, Y. Zhuang, L. J. Borucki, S. Theng, X. Wei, T. Ashizawa, and A. Philipossian, Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 14, H201 (2011).
J. Luo and D. A. Dornfeld, IEEE Trans. on Semicon. Manuf. 14 112 (2001).
Y. Sampurno, A. Rice, Y. Zhuang, and A. Philipossian, Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 14, H318 (2011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, S., Kim, H.J., Hong, M.K. et al. Effect of pad surface roughness on material removal rate in chemical mechanical polishing using ultrafine colloidal ceria slurry. Electron. Mater. Lett. 9, 155–159 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-012-2144-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-012-2144-5