Abstract
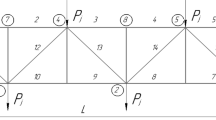
The stable equilibrium configuration of structures is a main goal in structural optimization. This goal may be achieved through minimizing the potential energy function. In the real world, sometimes, the input data and parameters of structural engineering design problems may be considered as fuzzy numbers which lead us to develop structural optimization methods in a fuzzy environment. In this regard, the present paper is intended to propose a fuzzy optimization scheme according to the nonmonotone globalization technique, the Barzilai–Borwein (BB) gradient method and the generalized Hukuhara differentiability (gH-differentiability). In fact, using the best benefits of BB-like methods i.e., simplicity, efficiency and low memory requirements, a modified global Barzilai–Borwein (GBB) gradient method is proposed for obtaining a non-dominated solution of the unconstrained fuzzy optimization related to the two bar asymmetric shallow truss in a fuzzy environment. The global convergence to first-order stationary points is also proved and the R-linear convergence rate is established under suitable assumptions. Furthermore, some numerical examples are given to illustrate the main results.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akaike, H.: On a successive transformation of probability distribution and its application to the analysis of the optimum gradient method. Ann. Inst. Stat. Math. 11, 1–17 (1959)
Amini, K., Ahookhosh, M., Nosratipour, H.: An inexact line search approach using modified nonmonotone strategy for unconstrained optimization. Numer. Algorithm 66, 49–78 (2014)
Ban, A.I., Bede, B.: Properties of the cross product of fuzzy numbers. J. Fuzzy Math. 14, 513–531 (2006)
Barzilai, B., Borwein, J.M.: Methods of conjugate gradients for solving linear systems. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 8, 141–148 (1988)
Ban, A.I., Bede, B.: Properties of the cross product of fuzzy numbers. J. Fuzzy Math. 14, 513–531 (2006)
Bede, B., Stefanini, L.: Generalized differentiability of fuzzy-valued functions. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 230, 119–141 (2013)
Bede, B., Gal, S.G.: Generalizations of the differentiability of fuzzy number valued functions with applications to fuzzy differential equations. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 151, 581–599 (2005)
Bellman, R.E., Zadeh, L.A.: Decision making in a fuzzy environment. Manag. Sci. 17, 141–164 (1970)
Birgin, E.G., Chambouleyron, I., Martinez, J.M.: Estimation of the optical constants and the thickness of thin films using unconstrained optimization. J. Comput. Phys. 151, 862–880 (1999)
Buckley, J.J., Abdalla, A.: Monte Carlo methods in fuzzy queuing theory. Soft Comput. 13, 1027–1033 (2009)
Cadenas, J.M., Verdegay, J.L.: Towards a new strategy for solving fuzzy optimization problems. Fuzzy Optim. Decis. Mak. 8, 231–244 (2009)
Chalco-Cano, Y., Rufián-Lizana, A., Román-Flores, H., Jiménez-Gamero, M.D.: Calculus for interval-valued functions using generalized Hukuhara derivative and applications. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 219, 49–67 (2013)
Chalco-Cano, Y., Silva, G.N., Rufián-Lizana, A.: On the Newton method for solving fuzzy optimization problems. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 272, 60–69 (2015)
Dai, Y.H., Fletcher, R.: New algorithms for singly linearly constrained quadratic programs subject to lower and upper bounds. Math. Prog. 106, 403–421 (2006)
Dai, Y.H.: On the nonmonotone line search. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 112(2), 315–330 (2002)
Dai, Y.H., Liao, L.Z.: R-linear convergence of the Barzilai and Borwein gradient method. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 22, 1–10 (2002)
Diamond, P., Kloeden, P.E.: Meric Spaces of Fuzzy Sets: Theory and Applications. World Scientific, Singapore (1994)
Diamond, P.: Stability and periodicity in fuzzy differential equations. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 8(5), 583–590 (2000)
Fletcher, R.: Low storage methods for unconstrained optimization. Lect. Appl. Math. 26, 165–179 (1999)
Glunt, W., Hayden, T.L., Raydan, M.: Molecular conformations from distance matrices. J. Comput. Chem. 14, 114–120 (1993)
Grippo, L., Lampariello, F., Lucidi, S.: A nonmonotone line search technique for Newton’s method. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 23, 707–716 (1986)
Grippo, L., Sciandrone, M.: Nonmonotone globalization techniques for the Barzilai–Borwein gradient method. Comput. Optim. Appl. 23, 143–169 (2002)
Guo, P. Tanaka, H.: Fuzzy decision in possibility programming problems. In Proceedings of Asian Fuzzy System Symposium, pp. 278–283 (1996)
Hanss, M.: Applied Fuzzy Arithmetic. Springer, New York (2005)
Hestenes, M.R., Stiefel, E.L.: Methods of conjugate gradients for solving linear systems. J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand. 49, 409–436 (1952)
Hukuhara, M.: Integration des applications measurables dont la valeur est un compact convexe. Funkcialaj Ekvacioj 10, 205–223 (1967)
Jung, C.Y., Pulmano, V.A.: Improved fuzzy linear programming model for structural designs. Comput. Struct. 58, 471–477 (1996)
Liu, W.B., Dai, Y.H.: Minimization algorithms based on supervisor and searcher cooperation. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 111, 359–379 (2001)
Lodwick, W.A., Bachman, K.A.: Solving large-scale fuzzy and possibilistic optimization problems. Fuzzy Optim. Decis. Mak. 4(4), 257–278 (2005)
Lodwick, W.A., Jamison, K.D.: Theoretical and semantic distinctions of fuzzy, possibilistic, and mixed fuzzy/possibilistic optimization. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 158(17), 1861–1872 (2007)
Lodwick, W.A.: The relationship between interval, fuzzy and possibilistic optimization. Model. Decis. Artif. Intell. 5861, 55–59 (2009)
Pathak, V.D., Pirzada, U.M.: The optimality conditions for fuzzy optimization problem under the concept of generalized convexity. Adv. Appl. Math. Anal. 1, 23–38 (2010)
Pirzada, U.M., Pathak, V.D.: Newton method for solving the multi-variable fuzzy optimization problem. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 156, 867–881 (2013)
Puri, M.L., Ralescu, D.A.: Differentials of fuzzy functions. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 91, 552–558 (1983)
RamiK, J., Rimanek, J.: Inequality relation between fuzzy numbers and its use in fuzzy optimization. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 16, 123–138 (1985)
Ramik, J., Vlach, M.: Fuzzy mathematical programming: a unified approach based on fuzzy relation. Fuzzy Optim. Decis. Mak. 1, 335–346 (2002)
Rao, S.S.: Description and optimum design of fuzzy mathematical systems. J. Mech. Trans. Autom. Des. 109, 126–132 (1987)
Raydan, M.: The Barzilai and Borwein gradient method for the large scale unconstrained minimization problem. SIAM J. Optim. 7, 26–33 (1997)
Saito, S., Ishii, H.: L-fuzzy optimization problems by parametric representation. IEEE, N Y 1173–1177 (2001). doi:10.1109/ICSMC.2001.973078
Serafini, T., Zanghirati, G., Zanni, L.: Gradient projection methods for quadratic programs and applications in training support vector machines. Optim. Methods Softw. 20, 353–378 (2005)
Wu, H.-C.: An \((\alpha,\beta )\)-optimal solution concept in fuzzy optimization problems. Optimization 53, 203–221 (2004)
Wu, H.-C.: Duality theory in fuzzy optimization problems. Fuzzy Optim. Decis. Mak. 3, 345–365 (2004)
Wu, H.-C.: Fuzzy optimization problemsbased on the embedding theorem and possibility and necessity measures. Math. Comput. Model. 40(3), 329–336 (2004)
Wu, H.-C.: The Karush–Kuhn–Tucker optimality conditions for optimization problems with fuzzy valued objective functions. Math. Methods Oper. Res. 66, 203–224 (2007)
Wu, H.-C.: The optimality conditions for optimization problems with fuzzy-valued objective functions. Optimization 57, 473–489 (2008)
Xu, C.: Fuzzy optimization of structures by the two-phase method. Comput. Struct. 31(4), 575–580 (1989)
Yeh, Y.C., Hsu, D.S.: Structural optimization with fuzzy parameters. Comput. Struct. 37(6), 917–924 (1990)
Zadeh, L.A.: Optimality and non-scalar-valued performance criteria. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. 8, 59–60 (1963)
Zadeh, L.A.: Fuzzy sets. Inf. Control 8, 338–353 (1965)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nosratipour, H., Fard, O.S., Borzabadi, A.H. et al. Stable equilibrium configuration of two bar truss by an efficient nonmonotone global Barzilai–Borwein gradient method in a fuzzy environment. Afr. Mat. 28, 333–356 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13370-016-0451-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13370-016-0451-y
Keywords
- Unconstrained fuzzy optimization
- Truss
- Generalized Hukuhara differentiability
- Nonmonotone line search
- Barzilai–Borwein gradient method