Abstract
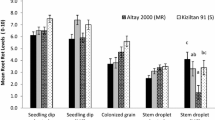
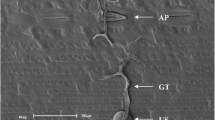
Inoculation of wheat seedlings by the crown rot pathogen Fusarium pseudograminearum is commonly used to screen for resistance based on leaf sheath discolouration. While leaf sheath discolouration is effective for describing disease reactions, the degree to which the pathogen colonises the full range of seedling host tissues is an important aspect of the disease process, which has not been systematically examined. After single point droplet inoculation of the coleoptile, quantitative PCR was used to determine the spread of F. pseudograminearum into different host tissues during crown rot pathogenesis at 14 and 28 days after inoculation. Quantitative PCR and visual assessment indicated that while most seedling tissues (leaf sheath, leaf blade, sub-crown internode, primary root and secondary root) were colonised, the basal portion of leaf sheath tissue supported the highest density of F. pseudograminearum. Other significant sites of colonisation were the upper leaf sheath and sub-crown internode. By comparison, the quantity of mycelium detected in the primary and secondary roots was significantly lower, while the infection of leaf blade tissues was severely restricted.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burgess LW, Backhouse D, Summerell BA, Swan LJ (2001) Crown rot of wheat. In: Summerell B, Leslie J, Backhouse D, Bryden W, Burgess L (eds) Fusarium: Paul E. Nelson memorial symposium. APS Press, St. Paul, pp 271–294
Fowler J, Cohen L, Jarvis P (1998) Practical statistics for field biology. John Wiley and Sons, Chichester
Knight NL, Sutherland MW (2013) Histopathological assessment of wheat seedling tissues infected by Fusarium pseudograminearum. Plant Pathol 62:679–687
Knight NL, Martin A, Sutherland MW, Herde DJ (2013) Assessment of infection by Fusarium pseudograminearum in wheat seedling tissues using quantitative PCR and a visual discoloration scale. Plant Dis 96:1661–1669
Li X, Liu C, Chakraborty S, Manners JM, Kazan K (2008) A simple method for the assessment of crown rot disease severity in wheat seedlings inoculated with Fusarium pseudograminearum. J Phytopathol 156:751–754
Liddell CM (1985) The comparative pathogenicity of Fusarium graminearum group 1, Fusarium culmorum and Fusarium crookwellense as crown, foot and root rot pathogens of wheat. Australas Plant Pathol 14:29–31
Mitter V, Zhang MC, Liu CJ, Ghosh R, Ghosh M, Chakraborty S (2006) A high-throughput glasshouse bioassay to detect crown rot resistance in wheat germplasm. Plant Pathol 55:433–441
Mudge AM, Dill-Macky R, Dong Y, Gardiner DM, White RG, Manners JM (2006) A role for the mycotoxin deoxynivalenol in stem colonisation during crown rot disease of wheat caused by Fusarium graminearum and Fusarium pseudograminearum. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 69:73–85
Murray GM, Brennan JP (2009) Estimating disease losses to the Australian wheat industry. Australas Plant Pathol 38:558–570
Percy CD, Wildemuth GB, Sutherland MW (2012) Symptom development proceeds at different rates in susceptible and partially resistant cereal seedlings infected with Fusarium pseudograminearum. Australas Plant Pathol 41:621–631
Smiley RW, Gourlie JA, Easley SA, Patterson L-M, Whittaker RG (2005) Crop damage estimates for crown rot of wheat and barley in the Pacific Northwest. Plant Dis 89:595–604
Smiley RW, Backhouse D, Lucas P, Paulitz TC (2009) Diseases which challenge global wheat production - root, crown, and culm rots. In: Carver BF (ed) Wheat: science and trade. Wiley-Blackwell, Ames, pp 125–153
Wildermuth GB, McNamara RB (1994) Testing wheat seedlings for resistance to crown rot caused by Fusarium graminearum Group 1. Plant Dis 78:949–953
Yang X, Ma J, Li H, Ma H, Yao J, Liu C (2010) Different genes can be responsible for crown rot resistance at different developmental stages of wheat and barley. Eur J Plant Pathol 128:495–502
Acknowledgments
We thank our colleague Dr Anke Martin for her critical discussions of this research. Financial support for this project was provided in part by the Grains Research and Development Corporation. Noel Knight acknowledges the support of an Australian Postgraduate Award.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Knight, N.L., Sutherland, M.W. Spread of Fusarium pseudograminearum in wheat seedling tissues from a single inoculation point. Australasian Plant Pathol. 42, 609–615 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13313-013-0225-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13313-013-0225-z