Abstract
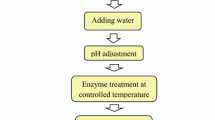
The present study was aimed at optimizing the enzyme assisted aqueous extraction (EAAE) process for extraction of maize germ oil. The different EAAE process parameter viz., pH of the slurry, seed to water ratio, the temperature of incubation and time of hydrolysis were optimized for improving oil recovery and oil quality. The combined effect of independent variables on recovery of oil, time taken for oil extraction and various quality parameters were studied using response surface methodology. The designed experimental runs were conducted to obtain the optimal conditions as 5.85 pH of slurry, 1:6.92 seed to water ratio, 45.12 °C temperature of incubation and 1 h time of hydrolysis. Oil extracted under these conditions was light yellowish in color and had a pleasant nutty taste, with maximum oil recovery of 70 %. The extraction variables viz., pH of slurry, seed to water ratio, the temperature of incubation had a significant effect on recovery of oil and various quality characteristics, however the time of hydrolysis had a non significant effect.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdulkadir M, Abubakar GI (2011) Production and refining of corn oil from hominy feed a by-product of dehulling operation. ARPN J Eng Appl Sci 6:4
Abdulkarim SM, Long K, Lai OM, Muhammad SKS, Ghazali HM (2005) Some physico-chemical properties of Moringa oleifera seed oil extracted using solvent and aqueous enzymatic methods. Food Chem 93:253–263
Abdulkarim SM, Long K, Lai OM, Muhammad SKS, Ghazali HM (2007) Frying quality and stability of high-oleic Moringa oleifera seed oil in comparison with other vegetable oils. Food Chem 105:1382–1389
Anonymous (2012) Directorate of Maize Research: Annual Report (2011-2012). Online source culled from http://www.maizeindia.org
Anonymous (2013a) Punjab produces record wheat rice and maize Crop. Online source culled from http://www.agricorner.com. Assessed 3 Feb
Anonymous (2013b) Saponification. Online source culled from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Saponification. Assessed 25 Feb
Anonymous (2014) Sukhjit starch and chemicals limited, Maize by-products. Online source culled from http://www.sukhjitgroup.com/maize-by-product.html#germ. Assessed 2 July
AOCS (1997) Official and recommended practices of the American oil chemists society, 5th edn. AOCS Press, Champaign
Bocevska M, Karlovic D, Turkulov J, Pericin D (1993) Quality of corn germ oil obtained by aqueous enzymatic extraction. J Am Oil Chem Soc 70:1273–1277
Chaovanalikit A, Wrolstad RE (2004) Total anthocyanins and total phenolics of fresh and processed cherries and their antioxidant properties. Food Chem Toxicol 69:67–72
Concha J, Soto C, Chamy R, Zuniga ME (2004) Enzymatic pretreatment on Rose-Hip oil extraction: hydrolysis and pressing conditions. J Am Oil Chem Soc 81:549–552
Deiana MR, Cao CF, Pirisi FM, Bandino G, Dessi MA (2002) Novel approach to study oxidative stability of extra virgin oils: importance of α—tocopherol concentration. J Agric Food Chem 50:4342–4346
Eckhoff SR, Rausch KD, Fox EJ, Tso CC, Wu X, Pan Z, Buriak P (1993) A laboratory wet-milling procedure to increase reproducibility and accuracy of product yields. Cereal Chem 70:723–727
EPA (2001) National emissions standards for hazardous air pollutants: solvent extraction for vegetable oil production; 40 CFR Part 63. Environmental Protection Agency. Final Rule Fed Regist 66:19005–19026
Farhoosh R, Kafrani MHT, Sharif A (2011) Antioxidant activity of the fractions separated from the unsaponifiable matter of bene hull oil. Food Chem 126:583–589
FSSAI (2012) Manual of methods of analysis of foods, oils and fats. Food safety and standard authority of India, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, GOI, New Delhi
Karlovic DJ, Bocevska M, Jakolevic J, Turkulov J (1994) Corn germ oil extraction by a new enzymatic process. Acta Aliment 23:389–400
Khan HN, Khan JS, Ali S, Hussain K, Alam MS, Habib A (2011) Vegetable oil blends after frying and sample stored in different storage packs. Curr Bot 2(5):20–25
Latif S (2009) Analytical investigations to compare the enzyme-assisted extraction of vegetable oils with conventional methods. M.sc. Thesis, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad
Lee YY, Tang TK, Phuah ET, Karim NAA, Alwi SMM, Lai OM (2015) Palm-based medium-and-long-chain triacylglycerol (P-MLCT): production via enzymatic interesterification and optimization using response surface methodology (RSM). J Food Sci Technol 52(2):685–696. doi:10.1007/s13197-013-1065-0
Li Y, Li D, Qi B, Rokayya S, Ma W, Liang J, Sui X, Zhang Y, Jiang L (2014) Heating quality and stability of aqueous enzymatic extraction of fatty acid-balanced oil in comparison with other blended oils. J Chem 530787:1–8. doi:10.1155/2014/530787
Matill KF, Norris FA, Swern D (1964) Extraction of Fats and oils. In: Swern D (ed) Bailey’s industrial oil and fats products. Wiley, London, pp 637–717
Mcglone OC, Octavio CM, Canales ALM, Carter JV (1986) Coconut oil extraction by new enzymatic process. J Food Sci 51:696–698
Mestrovic T (2015) Oils rich in linoleic acid. Online source culled from http://www.news-medical.net/health/Oils-Rich-in-Linoleic-Acid.aspx
Mishra G, Joshi DC, Mohapatra D (2015) Optimization of pretreatments and process parameters for sorghum popping in microwave oven using response surface methodology. J Food Sci Technol 52(12):7839–7849. doi:10.1007/s13197-015-1898-9
Moreau RA, Johnston DB, Powell MJ, Hicks KB (2004) A comparison of commercial enzymes for the aqueous enzymatic extraction of corn oil from corn germ. J Am Oil Chem Soc 81:11
Olaniyan AM (2007) Development of mechanical expression rig for dry extraction of shea butter from shea kernel. J Food Sci Technol 44(5):465–470
Owusu-Ansah YJ (1997) Enzyme-Assisted Extraction. In: Wan P, Wakelyn PJ (eds) Technology and solvents for extracting oilseeds and nonpetroleum oils. AOCS Press, Champaign, pp 323–332
Qian J, Zhang H, Liao Q (2011) The properties and kinetics of enzymatic reaction in the process of the enzymatic extraction of fish oil. J Food Sci Technol 48(3):280–284
Qiu X, Hong H, Datta N, Reed DW, Truska M, Hu Z, Covello PS, MacKenzie SL (2003) Production of nutraceutical fatty acids in oilseed crops. In: Murata N, Yamada M, Nishida I, Okuyama H, Sekiya J, Hajime W (eds) Advanced research on plant lipids. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, pp 403–406
Rajendran RA, Singh N, Mahajan V, Chaudhary DP, Sapna KumarRS (2012) Corn oil: an emerging industrial product. Directorate of Maize Research, New Delhi. Technol Bul 8:36
Ranalli A, Pollastri L, Contento S, Iannucci E (2003) The glyceridic and nonglyceridic constituents of virgin olive oil after use of a novel method of enzyme extraction. Int J Fd Sci Technol 38:17–27
Rhee KC, Cater CM, Mattil KF (1972) Simultaneous recovery of protein and oil from raw peanuts in an aqueous system. J Food Sci 37:90–93
Rhee KC, Cater CM, Mattil KF (1973) Effect of processing pH on the properties of peanut protein isolates and oil. Cereal Chem 50:395–404
Rosenthal A, Pyle DL, Niranjan K (1996) Aqueous enzymatic processes for edible oil extraction. Enzyme Microb Technol 19:402–420
Shi L, Lu J, Jones G, Loretan PA, Hill WA (1998) Characteristics and composition of peanut oil prepared by an aqueous extraction method. Life Support Biosci 5:225–229
Singh V, Eckhoff SR (1996) Effect of soak time, soak temperature, lactic acid on germ recovery parameters. Am Assoc Cereals Chem Inc, Pub No C-1996-0930-04R
Singh RK, Sarker BC, Kumbhar BK, Agrawal YC, Kulshreshtha MK (1999) Response surface analysis of enzyme-assisted oil extraction factors for sesame, groundnut, and sunflower seeds. J Food Sci Technol 36:511–514
Tuan HQ (2011) Characterization of natural edible oils regarding their quality and safety related constituents. M.Sc. Thesis, University of Natural Resources and Life Sciences, Vienna
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shende, D., Sidhu, G.K. Response surface methodology to optimize enzyme-assisted aqueous extraction of maize germ oil. J Food Sci Technol 53, 3282–3295 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-016-2303-z
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-016-2303-z