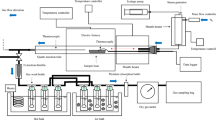
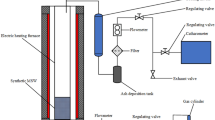
Abstract
Tar derived from municipal solid waste (MSW) will block and foul process equipment. To better understand its formation mechanism during the pyrolysis process, key MSW components including polyethylene (PE), paper pulp, and bamboo (chopsticks) were selected and analytical pyrolysis-gas chromatography/mass spectrometry investigations were performed to examine their tar formation characteristics. Increasing the heating rate had no impact on the composition of pyrolysis product from bamboo, paper pulp, and PE pyrolysis, excluding the naphthalene generated from bamboo. Its content rose as the heating rate increased. Increasing the final temperature could reduce the total yield of tar. However, some compounds derived from bamboo, such as naphthalene, would increase as the final temperature rose. The tar chemical composition from paper pulp pyrolysis would get changed and the contents of some compounds, such as styrene and naphthalene, from PE pyrolysis would rise as the final temperature ascended. This work described here favors us control the tar production in the MSW pyrolysis process.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Malkow, T.: Novel and innovative pyrolysis and gasification technologies for energy efficient and environmentally sound MSW disposal. Waste Manage. 4(1), 53–79 (2004)
Chen, D.Z., Yin, L.J., Wang, H., He, P.J.: Pyrolysis technologies for municipal solid waste: a review. Waste Manage. 34(12), 2466–2486 (2014)
Zhou, H., Long, Y.Q., Meng, A.H., Li, Q.H., Zhang, Y.G.: The pyrolysis simulation of five biomass species by hemi-cellulose, cellulose and lignin based on thermogravimetric curves. Thermochim. Acta 566, 36–43 (2013)
Ren, Q.Q., Zhao, C.S., Wu, X., Liang, C., Cheng, X.P., Shen, J.Z., Tang, G.Y., Wang, Z.: TG-FTIR study on co-pyrolysis of municipal solid waste with biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 100(17), 4054–4057 (2009)
Zhou, H., Meng, A.H., Long, Y.Q., Li, Q.H., Zhang, Y.G.: Interactions of municipal solid waste components during pyrolysis: a TG-FTIR study. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 108, 19–25 (2014)
del Río, J.C., Gutiérrez, A., Hernando, M., Landín, P., Romero, J., Martínez, A.T.: Determining the influence of eucalypt lignin composition on paper pulp yield using Py-GC/MS. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 74(1–2), 110–115 (2005)
Maschio, G., Koufopanos, C., Lucchesi, A.: Pyrolysis, a promising route for biomass utilization. Bioresour. Technol. 42(3), 219–231 (1992)
Li, S.D., He, J.D., Yu, P.H., Cheung, M.K.: Thermal degradation of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) and poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) as studied by TG, TG-FTIR, and Py-GC/MS. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 89(6), 1530–1536 (2003)
Li, X.H., Meng, Y.Z., Zhu, Q., Tjong, S.C.: Thermal decomposition characteristics of poly(propylene carbonate) using TG/IR and Py-GC/MS techniques. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 81(1), 157–165 (2003)
Perng, L.H.: Thermal degradation mechanism of poly(ether imide) by stepwise Py-GC/MS. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 79(7), 1151–1161 (2001)
Perng, L.H.: Thermal decomposition characteristics of poly(phenylene sulfide) by stepwise Py-GC/MS and TG/MS techniques. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 69(3), 323–332 (2000)
Dizhbite, T., Telysheva, G., Dobele, G., Arshanitsa, A., Bikovens, O., Andersone, A., Kampars, V.: Py-GC/MS for characterization of non-hydrolyzed residues from bioethanol production from softwood. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 90(2), 126–132 (2011)
Azeez, A.M., Meier, D., Odermatt, J., Willner, T.: Fast pyrolysis of African and European lignocellulosic biomasses using Py-GC/MS and fluidized bed reactor. Energy Fuels 24, 2078–2085 (2010)
Boateng, A.A., Mullen, C.A., McMahan, C.M., Whalen, M.C., Cornish, K.: Guayule (Parthenium argentatum) pyrolysis and analysis by PY-GC/MS. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 87(1), 14–23 (2010)
Bridgeman, T.G., Darvell, L.I., Jones, J.M., Williams, P.T., Fahmi, R., Bridgwater, A.V., Barraclough, T., Shield, I., Yates, N., Thain, S.C., Donnison, I.S.: Influence of particle size on the analytical and chemical properties of two energy crops. Fuel 86(1–2), 60–72 (2007)
Cai, G.M., Yu, W.D.: Study on the thermal degradation of high performance fibers by TG/FTIR and Py-GC/MS. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 104(2), 757–763 (2011)
Lou, R., Wu, S.B., Lv, G.J.: Effect of conditions on fast pyrolysis of bamboo lignin. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 89(2), 191–196 (2010)
Shen, D.K., Gu, S., Luo, K.H., Wang, S.R., Fang, M.X.: The pyrolytic degradation of wood-derived lignin from pulping process. Bioresour. Technol. 101(15), 6136–6146 (2010)
Kirubakaran, V., Sivaramakrishnan, V., Nalini, R., Sekar, T., Premalatha, M., Subramanian, P.: A review on gasification of biomass. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 13(1), 168–175 (2009)
Zhang, B.P., Xiong, S.J., Xiao, B., Yu, D.K., Jia, X.Y.: Mechanism of wet sewage sludge pyrolysis in a tubular furnace. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 36(1), 355–363 (2011)
Adrados, A., De Marco, I., Lopez-Urionabarrenechea, A., Solar, J., Caballero, B.: Avoiding tar formation in biocoke production from waste biomass. Biomass Bioenergy 74, 172–179 (2015)
Zhang, Y.L., Wu, W.G., Zhao, S.H., Long, Y.F., Luo, Y.H.: Experimental study on pyrolysis tar removal over rice straw char and inner pore structure evolution of char. Fuel Process. Technol. 134, 333–344 (2015)
Beneroso, D., Bermúdez, J.M., Arenillas, A., de la Peña, F., García, J.L., Prieto, M.A., Menéndez, J.A.: Oil fractions from the pyrolysis of diverse organic wastes: the different effects of conventional and microwave induced pyrolysis. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 114, 256–264 (2015)
Blanco, P.H., Wu, C.F., Onwudili, J.A., Dupont, V., Williams, P.T.: Catalytic pyrolysis/gasification of refuse derived fuel for hydrogen production and tar reduction: influence of nickel to citric acid ratio using Ni/SiO2 catalysts. Waste Biomass Valorization 5(4), 625–636 (2014)
Zhou, H., Meng, A.H., Long, Y.Q., Li, Q.H., Zhang, Y.G.: An overview of characteristics of municipal solid waste fuel in China: physical, chemical composition and heating value. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 36, 107–122 (2014)
Luo, S.Y., Xiao, B., Hu, Z.Q., Liu, S.M.: Effect of particle size on pyrolysis of single-component municipal solid waste in fixed bed reactor. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 35, 93–97 (2010)
Yang, H., Yan, R., Chen, H., Lee, D.H., Zheng, C.: Chracteristics of hemicellulose, cellulose and lignin pyrolysis. Fuel 86, 1781–1788 (2007)
Serrano, D.P., Aguado, J., Escola, J.M., Rodriguez, J.M., San Miguel, G.: An investigation into the catalytic cracking of LDPE using Py-GC/MS. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 74(1–2), 370–378 (2005)
Jess, A.: Mechanisms and kinetics of thermal reactions of aromatic hydrocarbons from pyrolysis of solid fuels. Fuel 75(12), 1441–1448 (1996)
Acknowledgments
The authors appreciate the financial supports from Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (No. 16ZR1422900) and Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (No. 13DZ2260900).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, X., Chen, C., Ying, Z. et al. Py-GC/MS Study on Tar Formation Characteristics of MSW Key Component Pyrolysis. Waste Biomass Valor 8, 313–319 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-016-9596-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-016-9596-z