Abstract
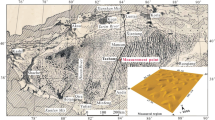
Planation surfaces (PS) play a major role in reconstruction of the evolutionary history of landforms in local areas. Thus, objective and consistent mapping of planation surfaces from remotely sensed data (e.g., satellite imagery, digital elevation models (DEMs)) is paramount for interpreting the geomorphological evolution. Due to the lack of dated sedimentary covers and the difficulties of comprehensive field work, the number and age of planation surfaces in the Southwest Hubei (湖北) Province of China are still controversial. In order to map the PS in the study area, four data visualization techniques including ETM+ false color composite, grey-scale DEM, shaded relief model (SRM) and painted relief model (PRM) were examined. It is found that the PRM is the most optimal technique for planation surface mapping. The study area was successfully mapped by visual interpretation of a PRM derived from ASTER GDEM. The mapped PS was divided into five classes in terms of elevation according to previous studies, varying from 1 700–2 000 (PS1), 1 300–1 500 (PS2), 1 000–1 200 (PS3), 800–900 (PS4) to 500–600 (PS5) m. The results were partially compared with the published works. It is revealed that this method of mapping enjoys a higher accuracy and can reduce the time and effort required in the traditional mapping to a large extent. The results also demonstrated that the PRM is an effective tool for geomorphological feature mapping with considerable accuracy. The preliminary results can serve to facilitate locating representative samples for the planation surfaces dating, thus to determine the ages of PS in the study areas.
Similar content being viewed by others
References Cited
Barbour, G. B., 1935. The Physiographic Period of Yangtze Valley. Geol. Soc. China Bull., 14: 1–15
Blackwelder, E., 1912. The Old Erosion Surface in Idaho: A Criticism. The Journal of Geology, 20(5): 410–414
Davis, W. M., 1901. Peneplains of Central France and Brittany. Bull. Geol. Soc. Amer., 12: 481–483
Hillier, J. K., Smith, M., 2008. Residual Relief Separation: Digital Elevation Model Enhancement for Geomorphological Mapping. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 33(14): 2266–2276, doi: 10.1002/esp.1659.
Jenson, S. K., Domingue, J. O., 1988. Extracting Topographic Structure from Digital Elevation Data for Geographic Information System Analysis. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 54: 1593–1600
Johansson, M., 1999. Analysis of Digital Elevation Data for Palaeosurfaces in South-Western Sweden. Geomorphology, 26: 279–295
Keller, E. A., Pinter, N., 1996. Active Tectonics: Earthquakes, Uplift and Landscapes. Prentice Hall, New Jersey
King, L. C., 1949. On the Ages of African Land-Surfaces. Geol. Soc. London Quart. Jour., 104: 439–453, doi: 10.1144/GSL.JGS.1948.104.01-04.20
Li, J. J., Xie, S. Y., Kuang, M. S., 2001. Geomorphic Evolution of the Yangtze Gorges and the Time of Their Formation. Geomorphology, 41(2-3): 125–135
Lidmar, B. K., Elvhage, C., Ringberg, B., 1991. Landforms in Skane, South Sweden. Geografiska Annaler, 73A: 61–91
Liu, X. S., 1983. Quternary of Sichuan Basin. Sichuan Science and Technology Press, Chengdu. 158 (in Chinese)
Loisios, D. N., Tzelepis, N., Nakos, B., 2007. A Methodology for Creating Analytical Hill-Shading by Combining Different Lighting Directions. Proceedings of 23rd International Cartographic Conference, Moscow
Martz, L. W., Garbrecht, J., 1998. The Treatment of Flat Areas and Depressions in Automated Drainage Analysis of Raster Digital Elevation Models. Hydrol. Process, 12: 843–855
Onorati, G., Poscolieri, M., Ventura, R., et al., 1992. The Digital Elevation Model of Italy for Geomorphology and Structural Geology. Catena, 19(2): 147–178
Pike, R. J., 1992. Machine Visualization of Synoptic Topography by Digital Image Processing. U.S. Geological Survey Bulletin, 2016: B1–B12
Raharimahefa, T., Kusky, T. M., 2006. Structural and Remote Sensing Studies of the Southern Betsisimarka Suture, Madagascar. Gondwana Research, 10: 186–197
Rowberry, M., Brewer, P., Macklin, M., 2007. The Number, Form and Origin of Subhorizontal Surfaces in North Ceredigion, Wales, U. K.. Norwegian Journal of Geology, 87: 207–222
Shen, Y. C., 1965. The Valley Landform of the Upper Yangtze. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Singh, A. K., Parkash, B., Choudhury, P. R., 2007. Integrated Use of SRM, Landsat ETM+ Data and 3D Perspective Views to Identify the Tectonic Geomorphology of Dehradun Valley, India. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 28(11): 2403–2414, doi: 10.1080/01431160600993397
Smith, M. J., Clark, C. D., 2005. Methods for the Visualization of Digital Elevation Models for Landform Mapping. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 30: 885–900, doi: 10.1002/esp.1210
Smith, M. J., Clark, C. D., Wise, S. M., 2005. Mapping Glacial Lineaments from Satellite Imagery: An Assessment of the Problems and Development of Best Procedure. Slovak Geological Magazine, 7: 263–274
Smith, M. J., Rose, J., Booth, S., 2006. Geomorphological Mapping of Glacial Landforms from Remotely Sensed Data: An Evaluation of the Principal Data Sources and an Assessment of Their Quality. Geomorphology, 76: 148–165, doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2005.11.001
Tian, L. J., Li, P. Z., Luo, Y., 1996. Valley Development History of Three Gorges of Yangtze River. Press of Southwest Jiaotong University, Chengdu (in Chinese)
Wang, Z. L., Niu, Z. J., Zhao, X. M, et al., 2010. Study of Characteristics of Layered Landforms Depositions and Geomorphic Evolution in the Qingjiang River Basin. Yangtze River, 41(8): 18–35 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Wang, Z. Y., Shen, J. F., Xu, R. C., et al., 1995. Karst Landscapes and Their Evolution in Reaches of the Qingjiang River, Western Hubei. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 20(4): 439–444 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Wayland, E. J., 1934. Peneplains and Some Other Erosional Platforms. Ann. Rep. Bull. Protectorate of Uganda Geological Survey Dept. Notes, 74(1): 376–377
Wu, S. R., Shi, L., Wang, R. J., et al., 2001. Zonation of the Landslide Hazards in the Forereservoir Region of the Three Gorges Project on the Yangtze River. Engineering Geology, 59: 51–58
Xie, S. Y., Yuan, D. X., Wang, J. L., et al., 2006. Features of the Planation Surface in the Surrounding Area of the Three Gorges of Yangtze. Carsologica Sinica, 25(1): 40–45 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Zhang, K., 2008. Planation Surfaces in China: One Hundred Years of Investigation. In: Grapes, R. H., Oldroyd, D. R., Grigelis, A., eds., History of Geomorphology and Quaternary Geology. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 301: 171–178
Zhao, H. Z., Li, Y. L., Yang, J. C., et al., 2009. Geomorphic Characteristics of Northern Tianshan Mountains Based on DEM Data. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 29(3): 445–449 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2011CB710600), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China University of Geosciences (Wuhan) (No. CUGL100211), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 91014002).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Huang, X., Deng, Q. et al. Mapping of planation surfaces in the southwest region of Hubei Province, China—Using the DEM-derived painted relief model. J. Earth Sci. 23, 719–730 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-012-0290-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-012-0290-1