Abstract
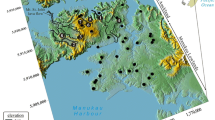
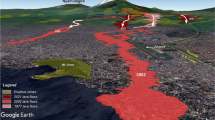
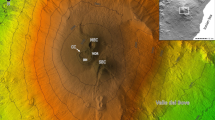
Energy cone is a unique but characteristic slope that describes the extent of deposits left around a volcano by various flowage phenomena, usually regarded as the boundary of pyroclastic and the source region of lahar. The energy cone value is determined as 0.07 by the energy-line model combined with the parameters of plume height and gradient, and the energy cone spread extent is defined by the numerical simulation method LAHARZ to simulate with this value based on the 1: 50 000 digital elevation model of Tianchi (天池) Volcano, and the source region profiles in the north and south slope can prove the correctness of this threshold. This energy cone threshold and extent can be used as the reference of pyroclastic flow and lahar simulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References Cited
Alfred, S. M. E., Michael, C. M., 1989. Dynamics of Mount St. Helens’ 1980 Pyroclastic Flows, Rockslide-Avalanche, Lahars, and Blast. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 37(3–4): 205–231
Cui, T. R., Jing, D. C., Jin, Y. J., et al., 2005. Distribution and Characteristic of Lahars in Tumen River. The Fourth Volcano Seminar of China, Beihai. 10–12 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Iverson, R. M., 1997. The Physics of Debris Flow. Reviews of Geophysics, 35(3): 245–296
Lee, S., 1984. Large Volcanic Debris Avalanches: Characteristics of Source Areas, Deposits, and Associated Eruptions. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 22(3–4): 163–197
Liu, X., 2005. Sequence and Distribution of the Pyroclastic Deposits of the Greatest Eruption of Changbaishan Volcano during the Period of History. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 36(3): 313–318 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Michael, C. M., Michael, F. S., 1982. Computre-Assisted Mapping of Pyroclastic Surge. Science, 217(4560): 637–640
Munoz, S. E., Renschler, C. S., Palacios, D., 2009. A GIS-Based Method to Determine the Volume of Lahars: Popocatépetl Volcano, Mexico. Geomorphology, 111: 61–69
Nie, B. F., Liu, Y. S., Peng, N., 2009. The Characteristics of Lahar Deposits at Tianchi Volcano. Journal of Capital Normal University (Natural Sciences Edition), 30(1): 70–75 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Richard, M. I., Steven, P. S., James, W. V., 1998. Objective Delineation of Lahar-Inundation Hazard Zones. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 110(8): 972–984
Vallance, J. W., Schilling, S. P., Devoll, G., 2001a. Lahar Hazard at Mombacho Volcano, Nicaragua. U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report, 1-455
Vallance, J. W., Schilling, S. P., Devoll, G., et al., 2001b. Lahar Hazard at Concepcion Volcano, Nicaragua. U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report, 1-457
Walker, G. P. L., Hayashi, J. N., Self, S., 1995. Travel of Pyroclastic Flows as Transient Waves: Implications for the Energy Line Concept and Particle-Concentration Assessment. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 66(1–4): 265–282
Wei, H. Q., Jing, B. L., Liu, Y. S., 2004. Some Advances in the Study of Volcanic Geology and a Hazards Analysis of Tianchi Volcano. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 23(4): 306–312 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Wilson, L., Sparks, R. S. J., Huang, T. C., et al., 1978. The Control of Volcanic Column Heights by Eruption Energetics and Dynamics. Journal of Geophysical Research, 83(B4): 1829–1836
Xu, J. D., 2006. The Major Types of Potential Volcanic Hazard of China and Hazard Mapping Technique. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 1(3): 266–272 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Yang, Q. F., Bo, J. S., 2007. Status Quo and Prospects for Research on Tianchi Volcano in Changbai Mountain. Journal of Natural Disasters, 16(6): 133–139 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Yang, Q. F., Shi, L. B., Chen, X. D., et al., 2006. Characteristics of Recent Ejecta of the Changbaishan Tianchi Volcano, China. Seismology and Geology, 28(1): 71–82 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Yang, Q. F., Liu, R. X., Wei, H. Q., et al., 2003. Countermeasure for Deduce the Damage in Changbai Mountain Tianchi Volcano. Journal of Seismological Research, 26(2): 183–189 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Yang, Q. F., Liu, R. X., Wei, H. Q., et al., 1999. Comment on Potential Volcano Disaster of Changbai Mountain Tianchi Volcano. Geological Review, 45(Suppl.): 215–220 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 40972209) and the Special Projects of the Fundamental Scientific Research of the Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration (No. IGCEA1103).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wan, Y., Xu, J. & Pan, B. Define the energy cone threshold and extent of Tianchi volcano. J. Earth Sci. 23, 768–774 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-012-0283-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-012-0283-0