Abstract
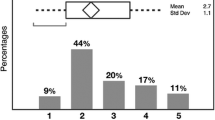
Arsenic existing in the soil and ground water worldwide is known as a neurotoxic that affects the peripheral nervous system. The peripheral neuropathy caused by chronic or sub acute arsenic exposure by inhalation or oral route is well documented. However, the effects of arsenic, especially chronic low-level exposure, on the central nervous system have been rarely reported. The present result highlights the direct interference of arsenic in the cognitive level of the school of children. The arsenic level in drinking water ranges from 0.0507 to 0.084 ppm with mean, SD, and SE are 0.0506, ±0.0196, and 0.0018, respectively. Mean IQ level in the contaminated area varies between 76 and 120 and two-sample t test results show significance difference (p < 0.000) with control. The multiple regression analysis suggests strong negative regression coefficient (−308.2) of IQ with water borne arsenic (WAs). Almost similar negative regression coefficient (−6.513) is also recorded with memory power. Results also suggest the inconsistency with urine arsenic and drinking water arsenic. On the other hand, drinking water manganese level also demonstrates weak relation with IQ.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amador DR, Navarro M, Trejo-Acevedo A, Carrizales L, Pe’rez-Maldonado I, Dı’az Barriga F, Caldero’n J (2009) Use of the Rey–Osterrieth complex figure test for neurotoxicity evaluation of mixtures in children. NeuroToxicol 30:1149–1154
American Public Health Association (APHA) (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 21st edn. APHA, Washington, DC
Asadullaha MN, Chaudhury N (2011) Poisoning the mind: arsenic contamination of drinking water wells and children’s educational achievement in rural Bangladesh. Econ Edu Rev 30:873–888
Baldissarelli AL, Capiotti KM, Bogo MR, Ghisleni G, Bonan CD (2012) Arsenic alters behavioral parameters and brain ectonucleotidase activities in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Compar Biochem Physiol-Part C Toxicol Pharmacol 155:566–572
Bellinger DC (2004) Lead. Pediatrics 113(Suppl. 1):1016–1022
Bellinger DC (2009) Interpreting epidemiologic studies of developmental neurotoxicity:conceptual and analytic issues. Neurotoxicol Teratol 31:267–274
Bhattacharyya P, Tripathy S, Kim K, Kim SH (2008) Arsenic fractions and enzymeactivities in arsenic-contaminated soils by groundwater irrigation in West Bengal. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 71:149–156
Biswas B (2010) Geomorphic controls of arsenic in ground water Purbasthali I & II blocks of Burdwan district, West Bengal, India. Int J Environ Sci 1(4):429–439
Bouchard MF, Sauve S, Barbeau B, Legrand M, Brodeur ME, Bouffard T (2011) Intellectual impairment in school-age children exposed to Manganese from drinking water. Environ Health Perspect 119:138–143
Calderon J, Navarro ME, Jimenez-Capdeville ME, Santos-Diaz MA, Golden A, Rodriguez-Leyva I, Borja-Aburto V, DmHaz-Barriga F (2001) Exposure to arsenic and Lead and neuropsychological development in Mexican children. Environ Res 85:69–76
Chakraborti D, Rahman MM, Das B, Murrill M, Dey S, Mukherjee SC, Dhar RK, Biswas BK, Chowdhury UK, Roy S, Sorif S, Selim M, Rahman M, Quamruzzaman Q (2010) Status of groundwater arsenic contamination in Bangladesh: a 14-year study report. Water Res 44:5789–5802
Chandra AV, Ali MM, Saxena DK, Murthy RC (1981) Behavioral and neurochemical changes in rats simultaneously exposed to manganese and lead. Arch Toxicol 49:49–56
Chiba M, Kikuchi M (1984) The in vitro effects of zinc and manganese on delta aminolevulinic acid dehydratase activity inhibited by lead or tin. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 73:388–394
Crinella FM, Cordova EJ, Ericson J (1998) Manganese, aggression, and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (abstract). Neurotoxicol 19:468–469
Das AK (2008) Bioinorganic chemistry, 1st edn. Book and Allied (P) Ltd, Kolkata, pp 351–359
De AK (2008) Environmental chemistry, 1st edn. New Age International Publishers, New Delhi, pp 222–247
Duker AA, Carranza EJM, Hale M (2005) Arsenic geochemistry and health. Environ Inter 31(5):631–641
Garai R, Chakraborty AK, Dey SB, Saha KC (1984) Chronic arsenic poisoning from tube well water. J Ind Medical Asso 82:34–35
He P, Liu D, Zhang G, Su M (1994) Effects of high-level manganese sewage irrigation on children’s neurobehavior. Chin J Preven Med 28:216–218
Hu P, Ouyang Y, Wu L, Shen L, Luo Y, Christie P (2015) Effects of water management on arsenic and cadmium speciation and accumulation in an upland rice cultivar.J. Environ Sci 27:225–231
Hua MS, Huang CC (1991) Chronic occupational exposure to manganese and neurobehavioral function. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 13(4):495–507
Kaplan RM, Saccuzzo DP (2009) Standardized tests in education, civil service, and the military. Psychol Test 7:325–327
Karthikeyan K, Nanthakumar K, Velmurugan P, Tamilarasi S, Lakshmanaperumalsamy P (2010) Prevalence of certain inorganic constituents in groundwater samples of Erode district, Tamil Nadu, India, with special emphasis on fluoride, fluorosis and its remedial measures. Environ Monitor Assess 160(1–4):141–155
Kim Y, Kim BY, Hong YC, Shin MS, Yoo HJ, Kim JW (2009) Co-exposure to environmental lead and manganese affects the intelligence of school-aged children. Neuro Toxicol 30:564–571
Li XS, Zhi JL, Gao RO (1995) Effect of fluoride exposure on intelligence in children. Fluoride 28(4):189–192
Lu Y, Sun ZR, Wu LN, Wang X, Lu W, Liu SS (2000) Effects of high-fluoride water on intelligence in children. Fluoride 33(2):74–78
Mergler D, Baldwin M, Belanger S, Larribe F, Beuter A, Bowler R (1999) Manganeseneurotoxicity, a continuum of dysfunction: results from a community based study. Neuro Toxicol 20:327–342
Mondal NK, Roy P, Das B, Datta JK (2011) Chronic arsenic toxicity and it’s relation with nutritional status: a Case Study in Purbasthali-II, Burdwan, West Bengal, India. Int J Environ Sci 2(2):1103–1118
Mondal NK, Dey U, Ghosh S, Dutta JK (2015) Soil enzyme activity under arsenic stressed area of Purbasthali, West Bengal, India. Arch Agro Soil Sci 61(1):73–87
Ostrowski SR, Wilbur S, Chou CH, Pohl HR, Stevens YW, Allred PM (1999) Agency for toxic substances and disease registry’s 1997 priority list of hazardous substances. Latent effects—carcinogenesis, neurotoxicology, and developmental deficits in humans and animals. Toxicol Indus Health 15:602–644
Rahaman S, Sinha AC, Pati R, Mukhopadhyay D (2013) Arsenic contamination: a potential hazard to the affected areas of West Bengal, India. Environ Geochem Health 35:119–132
Rahman MM, Sengupta MK, Ahamed S, Chudhury UK, Hossain AMd, Lodh D, Saha KC, Pati S, Kaies I, Barua AK, Chakraborti D (2005) Health effects to the inhabitants of the Jalangi—one of the 85 arsenic affected blocks in West Bengal, India. Sci Total Environ 338:189–200
Raven JC, Court JH, Raven J (1983) Manual for Raven’s progressive matrices and vocabulary scales (section 3)-standard progressive matrices. Lewis, London
Riojas-Rodrı´guez H, Solis-Vivanco R, Schillman A, Montes S, Rodriguez S, Rodriguez-Agudelo Y (2011) Intellectual function in Mexican children living in a mining area and environmentally exposed to manganese. Environ Health Perspect 118:1465–1470
Rocha-Amador D, Navarro ME, Carrizales L, Morales R, Calderon J (2007) Decreased intelligence in children and exposure to fluoride and arsenic in drinking water. Cad Saude Publica 23(Suppl 4):S579–S587
Rosado JL, Ronquillo D, Kordas K, Rojas O, Alatorre J, Lopez P (2007) Arsenic exposure and cognitive performance in Mexican school children. Environ Health Perspect 115:1371–1375
Roy A, Kordas K, Lopez P, Rosado J, Cebrian M, GarciaVargas G, Ronquillo D, Stoltzfus R (2011) Association between arsenic exposure and behavior among first-graders from Torreo´ n, Mexico. Environ Res 111:670–676
Roy P, Mondal NK, Das B, Das K (2013) Arsenic contamination in groundwater: a statistical modelling. J Urban Environ Eng 7(1):24–29
Roychowdhury T (2010) Groundwater arsenic contamination in one of the 107 arsenic-affected blocks in West Bengal, India: status, distribution, health effects and factors responsible for arsenic poisoning. Int J Hyg Environ Health 213:414–427
Siripitayakunit P, Visudhiphan M, Pradipasen M, Vorapongsathron T (1999) Association between chronic arsenic exposure and children’s intelligence in Thailand. In: Chappel WR, Abernathy CO (eds) Arsenic expo health effects. Elsevier, New York, pp 141–150
Takser L, Mergler D, Hellier G, Sahuquillo J, Huel G (2003) Manganese, monoamine metabolite levels at birth, and child psychomotor development. Neurotoxicology 24:667–674
Tsai SY, Chou H, The H, Meei CC, Jen CC (2003) The effects of chronic arsenic exposure from drinking water on the neurobehavioral development in adolescence. Neurotoxicology 24:747–753
Tsuji JS, Garry MR, Perez V, Chang ET (2015) Low-level arsenic exposure and developmental neurotoxicity in children: a systematic review and risk assessment. Toxicology 337(4):91–107
vanGeen A, Cheng ZY, Jia Q, Seddique AA, Rahman MW, Rahman MM (2007) Monitoring 51 deep community wells in Araihazar, Bangladesh, for up to 5 years: implications for arsenic mitigation. J Environ Sci Health 42:1729–1740
Varner JA, Jensen KF, Horvath W, Isaacson RL (1998) Chronic administration of aluminum-fluoride or sodium-fluoride to rats in drinking water: alterations in neuronal and cerebrovascular integrity. Brain Res 784(1–2):284–298
von Ehrenstein OS, Poddar S, Yuan Y, Mazumder DG, Eskenazi B, Basu A (2007) Children’s intellectual function in relation to arsenic exposure. Epidemiology 18:44–51
Wang SX, Wang ZH, Cheng XT, Li J, Sang ZP, Zhang XD (2007) Arsenic and fluoride exposure in drinking water: children’s IQ and growth in Shanyin county, Shanxi province, China. Environ Health Perspective 115:643–647
Wasserman GA, Liu X, Parvez F, Ahsan H, Factor-Litvak P, van Geen A (2004) Water arsenic exposure and children’s intellectual function Araihazar, Bangladesh. Environ Health Perspect 115:1–5
Wasserman GA, Liu X, Parvez F, Ahsan H, Factor-Litvak P, van Geen A (2006) Water arsenic exposure and intellectual function in 6-year-old children in Araihazar, Bangladesh. Environ Health Perspect 115:1–5
Wasserman GA, Liu X, Parvez F, Factor-Litvak P, Ahsan H, Levy D, Kline J, van Geen A, Mey J, Slavkovich V, Siddique AB, Islam T, Graziano JH (2011) Arsenic and manganese exposure and children’s intellectual function. Neurotoxicology 32:450–457
WHO (2008) Guidelines for drinking-water quality, third edition, incorporating first and second addenda, vol 1. World Health Organization, Geneva
Wright RO, Amarasiriwardena C, Woolf AD, Jim R, Bellinger DC (2006) Neuropsychological correlates of hair arsenic, manganese, and cadmium levels in school-age children residing near a hazardous waste site. Neurotoxicology 27:210–216
Xiang Q, Liang Y, Chen L, Wang C, Chen B, Zhou M (2003) Effects of fluoride in drinking water on children’s intelligence. Fluoride 36(2):84–94
Zhao LB, Liang GH, Zhang DN, Wu XR (1996) Effect of a high fluoride water supply on children’s intelligence. Fluoride 29(4):190–192
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to all villagers and school children for their unconditional help. They also express their sincere thanks to all the faculty of Environmental Science, The University of Burdwan, Burdwan, West Bengal, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghosh, S.B., Chakraborty, D. & Mondal, N.K. Effect of Arsenic and Manganese Exposure on Intellectual Function of Children in Arsenic Stress Area of Purbasthali, Burdwan, West Bengal. Expo Health 9, 1–11 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-016-0216-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-016-0216-8