Abstract
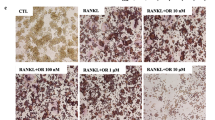
Ginkgo biloba extract (GBE) has a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM)-like biphasic effect on estrogen, and could be a potential alternative to hormone replacement therapy (HRT). Here, we investigated whether GBE can ameliorate estrogen-depleted osteoporosis in in vitro osteoblast cells and in estrogen-deprived ovariectomized (OVX) rats, a classical animal model for postmenopausal osteoporosis. GBE (50–150 μg/mL) significantly increased ALP (Alkaline phosphatase) activity of osteoblast cells, indicating that GBE promotes osteoblast mineralization. OVX rats exposed to GBE (100 and 200 mg/kg/day, oral treatment), raloxifene (3 mg/kg/day, oral treatment) or estradiol (E2, 10 μg/kg/day, subcutaneous injection) decreased osteoclast resorptive activity compared with OVX rats. GBE and raloxifene did not increase uterine weight compared with OVX rats, while E2 and Sham control did, suggesting that GBE has no uterotrophic activity, which is a disadvantage of estrogen therapy. In OVX rats, GBE did not restore severe bone density loss induced by OVX, indicating that GBE may be insufficient as therapeutic material for severe osteoporosis. However, despite its no effects on bone density loss in OVX rats, GBE did stimulate osteoblast differentiation and antiosteoclastic activity in vitro. Therefore, GBE may have preventive potential on osteoporosis as do other phytoestrogens.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adlercreutz, H. and Mazur, W., Phytoestrogens and western diseases. Ann. Med., 29, 95–120 (1997).
Arjmandi, B. H., Birnbaum, R. S., Juma, S., Barengolts, E., and Kukreja, S. C., The synthetic phytoestrogen, ipriflavone, and estrogen prevent none loss by different mechanisms. Calcif. Tissue Int., 66, 61–65 (2000).
Beck, V., Rohr, U., and Jungbauer, A., Phytoestrogens derived from red clover: an alternative to estrogen replacement therapy? J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol., 94, 499–518 (2005).
Bellows, C. G., Aubin, J. E., and Heersche, J. N. M., Initiation and progression of mineralization of bone nodules formed in vitro-the role of alkaline-phosphatase and organic phosphate. Bone Miner., 14, 27–40 (1991).
Bellows, C. G., Heersche, J. N., and Aubin, J. E., Inorganic phosphate added exogenously or released from β-glycerophosphate initiates mineralization of osteoid nodules in vitro. Bone Miner., 17, 15–29 (1992).
Boyle, W. J., Simonet, W. S., and Lacey, D. L., Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature, 423, 337–342 (2003).
Brayboy, J. R., Chen, X. W., Lee, Y. S., and Anderson, J. J. B., The protective effects of ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) against free radical damage to osteoblast-like bone cells (MC3T3-E1) and the proliferative effects of EGb 761 on these cells. Nutr. Res., 21, 1275–1285 (2001).
Brzexinski, A. and Debi, A., Phytoestrogens: the “Natural” selective estrogen receptor modulators? Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol., 85, 47–51 (1999).
Dempster, D. W. and Lindsay, R., Pathogenesis of osteoporosis. Lancet, 341, 797–805 (1993).
Dew, J., Eden, J., Beller, E., Magarcy, C., Schwartz, P., Crca, P., and Wren, B., A cohort study of hormone replacement therapy given to women previously treated for breast cancer. Climacteric, 1, 137–142 (1998).
Faber, A., Bouvy, M. L., Loskamp, L., van de Berg, P. B., Egberts, T. C., and de Jong-van den Berg, L. T., Dramatic change in prescribing of hormone replacement therapy in The Netherlands after publication of the Million Women Study: a follow-up study. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol., 60, 641–647 (2005).
Fanti, P., Monier-Faugere, M. C., Geng, Z., Schmidt, J., Morris, P. E., Cohen, D., and Malluche, H. H., The phytoestrogens genistein reduces bone loss in short-term ovariectomized rats. Osteoporos. Int., 8, 274–281 (1998).
Felsen, D. T., Zhang, Y., Hannan, M. T., Kiel, D. P., Wilson, P. W., and Anderson, J. J., The effect of postmenopausal estrogen therapy on bone density in elderly woman. N. Engl. J. Med., 329, 1141–1146 (1993).
Genge, B. R., Sauer, G. R., Wu, L. N. Y., McLean, F. M., and Wuthier, R. E., Correlation between loss of alkaline-phosphatase activity and accumulation of calcium during matrix vesicle-mediated mineralization. J. Biol. Chem., 263, 18513–18519 (1988).
Greendale, G. A., Reboussin, B. A., Hogan, P., Barnabei, V. M., Shumaker, S., Johnson, S., and Barrett-Connor, E., Symptom relief and side effects of postmenopausal hormone: results from the postmenopausal estrogen/progestin interventions trial. Obstet. Gynecol., 92, 982–988 (1998).
Hallworth, R. B., Prevention and treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Pharm. World Sci., 20, 198–205 (1998).
Hedblad, B., Merio, J., Manjer, J., Engstrom, G., Berglund, G., and Janzon, L., Incidence of cardiovascular disease, cancer and death in postmenopausal women affirming use of hormone replacement therapy. Scand. J. Public Health, 30, 12–19 (2002).
Hiroi, H., Inoue, S., Watanabe, T., Goto, W., Orimo, A., Momoeda, M., Tsutsumi, O., Taketani, Y., and Muramatsu, M., Differential immunolocalization of estrogen receptor a and b in rat ovary and uterus. J. Mol. Endocrinol., 22, 37–44 (1999).
Hsu, H., Lacey, D. L., Dunstan, C. R., Solovyev, I., Colombero, A., Timms, E., Tan, H. L., Elliott, G., Kelley, M. J., Sarosi, I., Wang, L., Xia, X. Z., Elliott, R., Chiu, L., Black, T., Scully, S., Capparelli, C., Morony, S., Shimamoto, G., Bass, M. B., and Boyle, W. J., Tumor necrosis factor receptor family member RANK mediates osteoclast differentiation and activation induced by osteoprotegerin ligand. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 96, 3540–3545 (1999).
Ibrahim, N. K. and Hortobagyi, G. N., The evolving role of specific estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs). Surg. Oncol., 8, 103–123 (1999).
Ikeda, S., Tsurukami, H., Ito, M., Sakai, A., Sakata, T., Nishida, S., Takeda, S., Shiraishi, A., and Nakamura, T., Effect of trabecular bone contour on ultimate strength of lumbar vertebra after bilateral ovariectomy in rats. Bone, 28, 625–633 (2001).
Ishida, H., Uesugi, T., Hirai, K., Toda, T., Nukaya, H., Yokotsuka, K., and Tsuji, K., Preventive effects of the plant isoflavones, daidzin and genistin, on bone loss in ovariectomized rats fed a calcium-deficient diet. Biol. Pharm. Bull., 21, 62–66 (1998).
Kalu, D. N., The ovariectomized rat model of postmenopausal bone loss. Bone Miner., 15, 175–191 (1991).
Kanno, S., Anuradha, C. D., and Hirano, S., Localization of zinc after in vitro mineralization in osteoblastic cells. Biol. Trace Elem. Res., 83, 39–47 (2001).
Kanno, S., Hirano, S., and Kayama, F., Effects of phytoestrogens and environmental estrogens on osteoblastic differentiation in MC3T3-E1 cells. Toxicology, 196, 137–145 (2004).
Kim, H. J., Bae, Y. C., Park, R. W., Choi, S. W., Cho, S. H., Choi, Y. S., and Lee, W. J., Bone-protecting effect of safflower seeds in ovariectomized rats. Calcif. Tissue Int., 71, 88–94 (2002).
Kwan, T. S., Padrines, M., Theoleyre, S., Heymann, D., and Fortun, Y., IL-6, RANKL, TNF-alpha/IL-1: interrelations in bone resorption pathophysiology. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev., 15, 49–60 (2004).
Lieberman, S., A review of the effectiveness of Cimicifuga racemosa (black cohosh) for the symptoms of menopause. J. Women’s Health, 7, 525–529 (1998).
Mackie, E. J., Osteoblasts: Novel roles in orchestration of skeletal architecture. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol., 35, 1301–1305 (2003).
MacLennan, A. H., Lawton, B., and Baber, R. J., Hormone replacement therapy and the breast. Studies must determine the evidence. BMJ, 324, 915 (2002).
Manolagas, S. C., Birth and death of bone cells: Basic regulatory mechanisms and implications for the pathogenesis and treatment of osteoporosis. Endocr. Rev., 21, 115–137 (2000).
Manolagas, S. C. and Jilka, R. L., Bone marrow, cytokines, and bone remodeling. Emerging insights into the pathophysiology of osteoporosis. N. Engl. J. Med., 332, 305–311 (1995).
Messina, M. and Hughes, C., Efficacy of soyfoods and soybean isoflavones supplements for alleviating menopausal symptoms is positively related to initial hot flush frequency. J. Med. Food, 6, 1–11 (2003).
Miyake, M., Arai, N., Ushio, S., Iwaki, K., Ikeda, M., and Kurimoto, M., Promoting effect of kaempferol on the differentiation and mineralization of murine pre-osteoblastic cell line MC3T3-E1. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem., 67, 1199–1205 (2003).
MWS, Million Women Study Collaborators, Breast cancer and hormonereplacement therapy in the Million Women Study. Lancet 362, 419–427 (2003).
Novack D. V., Estrogen and bone: Osteoclasts take center stage. Cell Metabolism, 6, 254–256 (2007).
O’Connell, D., Robertson, J., Henry, D., and Gillespie, W., A systemic review of the skeletal effects of estrogen therapy in postmenopausal women II. An assessment of treatment effects. Climacteric, 1, 112–123 (1998).
Oh, S. M. and Chung, K. H., Estrogenic activities of Ginkgo biloba extracts. Life Sciences, 74, 1325–1335 (2004).
Oh, S. M. and Chung, K. H., Antiestrogenic activities of Ginkgo biloba extracts. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol., 100, 167–176 (2006).
Pang, J. L., Ricupero, D. A., Huang, S., Fatma, N., Singh, D. P., Romero, J. R., and Chattopadhyay, N., Differential activity of kaempferol and quercetin in attenuating tumor necrosis factor receptor family signaling in bone cells. Biochem. Pharmacol., 71, 818–826 (2006).
Pepping, J., Black cohosh: Cimicifuga racemosa. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm., 56, 1400–1402 (1999).
Picherit, C., Coxam, V., Bennetau-Pelissero, C., Kati-Coulibaly, S., Davicco, M. J., Lebecque, P., and Barlet, J. P., Daidzein is more efficient than genistein in preventing ovariectomy induced bone loss in rats. J. Nutr., 130, 1675–1681 (2000).
Prouillet, C., Mazière, J. C., Mazière, C., Wattel, A., Brazier, M., and Kamel, S., Stimulatory effect of naturally occurring flavonols quercetin and kaempferol on alkaline phosphatase activity in MG-63 human osteoblasts through ERK and estrogen receptor pathway. Biochem. Pharmacol., 67, 1307–1313 (2004).
Riggs, B. L. and Melton, L. J., Involutional osteoporosis. N. Engl. J. Med., 26, 1676–1684 (1986).
Sagraves, R., Estrogen therapy for postmenopausal symptoms and prevention of osteoporosis. J. Clin. Pharmacol., 35, 2S–10S (1995).
Setchell, K. D. and Lydeking-Olsen, E., Dietary phytoestrogens and their effect on bone: evidence from in vitro and in vivo, human observational, and dietary intervention studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr., 78(suppl), 593S–609S (2003).
Shumaker, S. A., Legault, C., Rapp, S. R., Thal, L., Wallace, R. B., Ockene, J. K., Hendrix, S. L., Jones, B. N., Assaf, A. R., Jackson, R. D., Kotchen, J. M., Wassertheil-Smoller, S., and Wactawski-Wende, J., WHIMS Investigators, Estrogen plus progestin and the incidence of dementia and mild cognitive impairment in postmenopausal women. The Women’s Health Initiative Memory study: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA, 289, 2654–2662 (2003).
Stanford, C. M., Jacobson, P. A., Eanes, E. D., Lembke, L. A., and Midura, R. J., Rapidly forming apatite mineral in an osteoblastic cell-line (UMR 106-01 BSP). J. Biol. Chem., 270, 9420–9428 (1995).
Suda, T., Takahashi, N., Udagawa, N., Jimi, E., Gillespie, M. T., and Martin, T. J., Modulation of osteoclast differentiation and function by the new members of the tumor necrosis factor receptor and ligand families. Endocrinol. Rev., 20, 345–347 (1999).
Ukeda, H., Shimamura, T., Tsubouchi, M., Harada, Y., Nakai, Y., and Sawamura, M., Spectrophotometric assay of superoxide anion formed in maillard reaction based on highly water-soluble tetrazolium salt. Anal. Sci., 18, 1151–1154 (2002).
Wattel, A., Kamel, S., Mentaverri, R., Lorget, F., Prouillet, C., Petit, J. P., Fardelonne, P., and Brazier M., Potent inhibitory effect of naturally occurring flavonids quercetin and kaempferol on in vitro osteoclastic bone resorption. Biochem. Pharmcol., 65, 35–42 (2003).
Weistein, R. S. and Manolagas, S. C., Apoptosis and osteoporosis. Am. J. Med., 108, 153–164 (2000).
Weitzmann, M. N. and Pacifici, R., Estrogen deficiency and bone loss: an inflammatory tale. J. Clin. Invest., 116, 1186–1194 (2006).
WHI, Writing Group for the Women’s Health Initiative Investigators, Risks and benefits of estrogen plus progestin in healthy postmenopausal women. Principal results from the Women’s Health Initiative randomized controlled trial. JAMA 288, 321–333 (2002).
WHI, Writing Group for the Women’s Health Initiative Investigators, Effects of conjugated equine estrogen in postmenopausal women with hysterectomy. JAMA 291, 1701–1712 (2004).
Wuttke, W., Jarry, H., Westphalen, S., Christoffel, V., and Seidlová-Wuttke, D., Phytoestrogens for hormone replacement therapy? J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol., 83, 133–147 (2003).
Xie, F., Wu, C. F., Lai, W. P., Yang, X. J., Cheung, P. Y., Yao, X. S., Leung, P. C., and Wong, M. S., The osteoprotective effect of Herba epimedii (HEP) extract in vivo and in vitro. Evid. Based Complement Alternat. Med., 2, 353–361 (2005).
Yamazaki, I. and Yamaguchi, H., Characteristics of an ovariectomized osteopenic rat model. J. Bone Miner. Res., 4, 13–22 (1989).
Yasuda, H., Shima, N., and Nakagawa, N., Osteoclast differentiation factor is a ligand for osteoprotegerin/osteoclastogenesis inhibitory factor and is identical to TRANCE/RANKL. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 95, 3597–3602 (1998).
Yudoh, K., Matsuno, H., Nakazawa F., Katayama, R., and Kimura, T., Reconstituting telomerase activity using the telomerase catalytic subunit prevents the telomere shorting and replicative senescence in human osteoblasts. J. Bone Miner. Res., 16, 1453–1464 (2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oh, S.M., Kim, H.R. & Chung, K.H. Effects of ginkgo biloba on in vitro osteoblast cells and ovariectomized rat osteoclast cells. Arch. Pharm. Res. 31, 216–224 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-001-1144-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-001-1144-z