Abstract
Objective
Glycine acts as a co-agonist for the activation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) by binding to glycine sites, thus potentiating glutamate-elicited responses and inhibiting NMDAR desensitization in a dose-dependent manner. The present study aimed to characterize the glycine-dependent inactivation of NMDARs and to explore its pathophysiological significance.
Methods
Primary hippocampal cell cultures from embryonic days 17–18 rats were treated with NMDA or NMDA plus glycine. Patch-clamp recording and intracellular Ca2+ imaging were performed to test the effects of glycine on NMDA-activated currents and increase of intracellular free Ca2+ respectively. Immunofluorescence staining was conducted to examine NR1 internalization. Cell damage was tested with MTT method and lactate dehydrogenase leakage.
Results
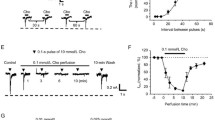
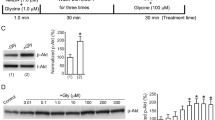
Glycine reduced the peak current and Ca2+ influx elicited by NMDA application at concentrations ≥300 μmol/L. This is a novel suppressive influence of glycine on NMDAR function, since it occurs via the NMDAR glycine-binding site, in contrast to the classic suppression, which occurs through the binding of glycine to glycine receptors. The level of membrane NMDARs was measured to evaluate whether internalization was involved. Immunohistochemical labeling showed that incubation with high concentrations of NMDA plus glycine did not change the expression of NMDARs on the cell surface when compared to the expression without glycine; hence the possibility of NMDAR internalization primed by glycine binding was excluded.
Conclusion
In summary, the novel suppressive effect of glycine on NMDARs was mediated via binding to the glycine site of the NMDAR and not by activation of the strychnine-sensitive glycine-receptor-gated chloride channel or by the internalization of NMDARs. The inhibitory influence of glycine on NMDARs adds a new insight to our knowledge of the complexity of synaptic transmission.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Petrovic M, Horak M, Sedlacek M, Vyklicky L Jr. Physiology and pathology of NMDA receptors. Prague Med Rep 2005, 106: 113–136.
Rao VR, Finkbeiner S. NMDA and AMPA receptors: old channels, new tricks. Trends Neurosci 2007, 30: 284–291.
Gardoni F, Di Luca M. New targets for pharmacological intervention in the glutamatergic synapse. Eur J Pharmacol 2006, 545: 2–10.
Johnson JW, Ascher P. Glycine potentiates the NMDA response in cultured mouse brain neurons. Nature 1987, 325: 529–531.
Kleckner NW, Dingledine R. Requirement for glycine in activation of NMDA-receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Science 1988, 241: 835–837.
Laube B, Hirai H, Sturgess M, Betz H, Kuhse J. Molecular determinants of agonist discrimination by NMDA receptor subunits: analysis of the glutamate binding site on the NR2B subunit. Neuron 1997, 18: 493–503.
Anson LC, Chen PE, Wyllie DJ, Colquhoun D, Schoepfer R. Identification of amino acid residues of the NR2A subunit that control glutamate potency in recombinant NR1/NR2A NMDA receptors. J Neurosci 1998, 18: 581–589.
Mayer ML, Vyklicky L Jr, Clements J. Regulation of NMDA receptor desensitization in mouse hippocampal neurons by glycine. Nature 1989, 338: 425–427.
Benveniste M, Clements J, Vyklicky L Jr, Mayer ML. A kinetic analysis of the modulation of N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptors by glycine in mouse cultured hippocampal neurones. J Physiol 1990, 428: 333–357.
Brewer GJ, Torricelli JR, Evege EK, Price PJ. Optimized survival of hippocampal neurons in B27-supplemented Neurobasal, a new serum-free medium combination. J Neurosci Res 1993, 35: 567–576.
Dingledine R, Borges K, Bowie D, Traynelis SF. The glutamate receptor ion channels. Pharmacol Rev 1999, 51: 7–61.
Liu Y, Zhang J. Recent development in NMDA receptors. Chin Med J (Engl) 2000, 113: 948–956.
Nong Y, Huang YQ, Ju W, Kalia LV, Ahmadian G, Wang YT, et al. Glycine binding primes NMDA receptor internalization. Nature 2003, 422: 302–307.
Roche KW, Standley S, McCallum J, Dune Ly C, Ehlers MD, Wenthold RJ. Molecular determinants of NMDA receptor internalization. Nat Neurosci 2001, 4: 794–802.
Snyder EM, Philpot BD, Huber KM, Dong X, Fallon JR, Bear MF. Internalization of ionotropic glutamate receptors in response to mGluR activation. Nat Neurosci 2001, 4: 1079–1085.
Vyklicky L Jr. Calcium-mediated modulation of N-methyl-Daspartate (NMDA) responses in cultured rat hippocampal neurones. J Physiol 1993, 470: 575–600.
Rosenmund C, Feltz A, Westbrook GL. Calcium-dependent inactivation of synaptic NMDA receptors in hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol 1995, 73: 427–430.
Obrenovitch TP, Hardy AM, Urenjak J. High extracellular glycine does not potentiate N-methyl-D-aspartate-evoked depolarization in vivo. Brain Res 1997, 746: 190–194.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, YF., Li, X., Peng, LL. et al. Novel glycine-dependent inactivation of NMDA receptors in cultured hippocampal neurons. Neurosci. Bull. 28, 550–560 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-012-1266-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-012-1266-y