Abstract
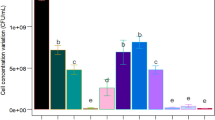
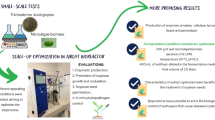
A novel cost-effective Bacillus atrophaeus Sterilization Bioindicator System (BIS) with a high quality and performance was developed from a soybean byproduct and compared with the commercial BIS. It was composed of recovery medium and dry-fermented spores with sand as the support. The BIS was developed and optimized using a sequential experimental design strategy. The recovery medium contained soluble starch (1.0 g/L), soybean molasses (30.0 g/L), tryptone (40.0 g/L), and bromothymol blue (0.02 g/L) at pH 8.5. The solid-state fermentation conditions of the bioreactor and environmental humidity had no significant effects on the spore yield and dry-heat resistance. The only substrate mineral that showed a positive effect was Mn2+, allowing Mg2+, K+, and Ca2+ to be eliminated from the formulation. Validation of optimized medium indicated D 160°C = 6.8±1.0 min (3.6 min more than the minimum) and spore yield = 2.3 ± 0.5 × 109 CFU/g dry sand (10,000 × initial values). BIS performance resulted in D 160°C = 6.6 ± 0.1 min. Sporulation and germination kinetics allowed the sporulation process to be reduced to three days, and the growth of heat-damaged spores was sufficient to achieve visual identification of a non-sterile BIS within 21 h. Process economics was a minimum of 23.9%, and process cycle time was reduced from 29 to 15 days. The new BIS parameters demonstrated compliance to all regulatory requirements. No studies have yet described a BIS production from soybean molasses.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Food and Drug Administration-FDA (2007) Guidance for industry and FDA Staff — Biological Indicator (BI) Intended to monitor sterilizers used in heath care facilities: Remarket notification [510(k)] submissions. http://www.fda.gov/MedicalDevices/DeviceRegulationandGuidance/GuidanceDocuments/ucm071261.htm.
International Standard ISO-11138-4 (2006) Sterilization of health care products-Biological indicators Part 4: Biological indicators for dry heat sterilization processes. ISO, Geneva.
Halfmann, H., B. Denis, N. Bibinov, J. Wunderlich, and P. Awakowicz (2007) Identification of the most efficient VUV/UV radiation for plasma based inactivation of Bacillus atrophaeus spores. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phy. 40: 5907–5911.
Oliveira, E. A., N. G. Nogueira, M. D. Innocentini, and R. Pisani (2010) Microwave inactivation of Bacillus atrophaeus spores in healthcare waste. Waste Manag. 30: 2327–2335.
Roth, S., J. Feichtinger, and C. Hertel (2010) Characterization of Bacillus subtilis spore inactivation in low-pressure, low-temperature gas plasma sterilization processes. J. Appl. Microbiol. 108: 521–531.
Szabo, J. G., E. W. Rice, and P. L. Bishop (2007) Persistence and decontamination of Bacillus atrophaeus subsp. globigii spores on corroded iron in a model drinking water system. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 73: 2451–2457.
Weber, D. J., E. Sickbert-Bennett, M. F. Gergen, and W. A. Rutala (2003) Efficacy of selected hand hygiene agents used to remove Bacillus atrophaeus (a surrogate of Bacillus anthracis) from contaminated hands. JAMA. 289: 1274–1277.
Hirakuri, M. H. and J. J. Lazzarotto (2011) Trends and prospects economic performance associated with soybean production in the brazilian and world contexts. Embrapa soja, Londrina.
Siqueira, P. F., S. G. Karp, W. Sturm, J. A. Rodríguez-León, J. Tholozan, R. R. Singhania, A. Pandey, and C. R. Soccol (2008) Production of bio-ethanol from soybean molasses by Saccharomyces cerevisiae at laboratory, pilot and industrial scales. Bioresour. Technol. 99: 8156–8163.
Sella, S. R. B. R., B. P. Guizelini, L. P. S. Vandenberghe, A. B. P. Medeiros, and C. R. Soccol (2009) Bioindicator production with Bacillus atrophaeus’ thermal-resistant spores cultivated by solidstate fermentation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 82: 1019–1026.
Sella, S. R. B. R., B. P. Guizelini, P. H. Zanello, L. P. S. Vandenberghe, C. A. O. Ribeiro, J. C. Minozzo, and C. R. Soccol (2012) Development of a low-cost sterilization biological indicator using bacillus atrophaeus by solid state fermentation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 93: 151–158.
Pflug, I. J., G. M. Smith, and R. Christensen (1981) Effect of soybean casein digest agar on number of Bacillus stearothermophilus spores recovered. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 42: 226–230.
Shintani, H. and J. E. Akers (2000) On the cause of performance variation of biological indicator used for sterility assurance. PDA J. Pharm. Sci. Tech. 54: 332–342.
López, M., I. González, M. Mazas, J. González, R. Martin, and A. Bernardo (1997) Influence of recovery conditions on apparent heat resistance of Bacillus stearothermophilus spores. Int. J. Food Sci. Tech. 32: 305–311.
Sasaki, K., H. Shintani, J. Itoh, T. Kamogawa, and Y. Kajihara (2000) Effect of calcium in assay medium on D value of Bacillus stearothermophilus ATCC7953 spores. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 66: 5509–5513.
Sella, S. R. B. R., R. E. F. Dlugokenski, B. P. Guizelini, L. P. S. Vandenberghe, A. B. P. Medeiros, A. Pandey, and C. R. Soccol (2008) Selection and optimization of Bacillus atrophaeus inoculum medium and its effect on spore yield and thermal resistance. Appl. Biochem. Biotech. 15: 380–392.
United States Pharmacopeia XXXI (2008) Biological indicators resistance and performance tests. In: The United States Pharmacopeia, 31th rev. United States Pharmacopoeia Convection, Rockville.
Nelson, N. A. (1944) Photometric adaptation of the Somogyi method for the determination of glucose. J. Biol. Chem. 153: 375–380.
International Standard ISO 14644-1(1999) Cleanrooms and associated controlled environments, Part 1: Classification of air cleanliness. ISO, Geneva.
Gillis, J. R., G. A. Mosley, J. B. Kowaslski, G. Krushefski, P. T. Nigenau, and K. McCauley (2010) Understanding biological indicator grow-out times. Pharm. Tech. 34: 1–9.
De Vries, Y. P. (2004) The role of calcium in bacterial spore germination. Microb. Environ. 19: 199–202.
Puri, S., Q. K. Beg, and R. Gupta (2002) Optimization of alkaline protease production from Bacillus sp. by response surface methodology. Curr. Microbiol. 44: 286–290.
Xiao, Z. J., P. H. Liu, J. Y. Qin, and P. Xu (2007) Statistical optimization of medium components for enhanced acetoin production from molasses and soybean meal hydrolysate. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 74: 61–68.
Mallidis, C. G. and J. Scholefield (1986) Evaluation of recovery media for heated spores of Bacillus stearothermophilus. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 61: 517–523.
Penna, T. C. V., I. A. Machoshvili, M. E. S. Taqueda, and M. Ishii (2000) The effect of media composition on the thermal resistance of Bacillus stearothermophilus.PDA J. Pharm. Sci. Tech. 54: 398–412.
Penna, T. C. V., I. A. Machoshvili, and M. Ishii (2003) Effect of media on spore yield and thermal resistance of Bacillus stearothermophilus. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 105–108: 287–294.
Rose, R., B. Setlow, A. Monroe, M. Mallozzi, A. Driks, and P. Setlow (2007) Comparison of the properties of Bacillus subtilis spores made in liquid or on agar plates. J. Appl. Microbiol. 103: 691–699.
Nguyen Thi Minh, H., A. Durand, P. Loison, J. Perrier-Cornet, and P. Gervais (2011) Effect of sporulation conditions on the resistance of Bacillus subtilis spores to heat and high pressure. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 90: 1409–1417.
Pandey, A., C. R. Soccol, J. A. Rodriguez-Leon, and P. Nigam (2001) Solidstate fermentation in biotechnology: Fundamentals and applications. Asiatech, New Delhi, India.
Gervais, P. and P. Molin (2003) The role of water in solid-state fermentation. Biochem. Eng. J. 13: 85–101.
Nguyen Thi Minh, H., J. Perrier-Cornet, and P. Gervais (2008) Effect of the osmotic conditions during sporulation on the subsequent resistance of bacterial spores. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 80: 107–114.
Grossman, A. D. and R. Losick (1988) Extracellular control of spore formation in Bacillussubtilis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 85: 4369–4373.
Sella, S. R. B. R., B. P. Guizelini, L. P. S. Vandenberghe, A. B. P. Medeirosand, and C. R. Soccol (2009) Lab-Scale production of Bacillus atrophaeus’ spores by solid state fermentation in different types of bioreactors. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 52: 159–170.
Cazemier, A. E., S. F. M. Wagenaars, and P. F. Ter Steeg (2001) Effect of sporulation and recovery medium on the heat resistance and amount of injury of spores from Bacilli. J. Appl. Microbiol. 90: 761–770.
Oomes, S. J., A. C. van Zuijlen, J. O. Hehenkamp, H. Witsenboer, J. M. van der Vossen, and S. Brul (2007) The characterization of Bacillus spores occurring in the manufacturing of (low acid) canned products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 120: 85–94.
Beaman, T. C. and P. Gerhardt (1986) Heat resistance of bacterial spores correlated with protoplast dehydration, mineralization, and thermal adaptation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 52: 1242–1246.
Nicholson, W. L., N. Munakata, G. Horneck, H. J. Meloshand, and P. Setlow (2000) Resistance of Bacillus endospores to extreme terrestrial and extraterrestrial environments. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 64: 548–572.
Molin, G. and M. Svensson (1976) Formation of dry-heat resistant Bacillus subtilis var. niger spores as influenced by the composition of the sporulation medium. A. Van. Leeuw. J. Microb. 42: 387–395.
Granger, A. C., E. K. Gaidamakova, V. Y. Matrosova, M. J. Daly, and P. Setlow (2011) Effects of Mn and Fe levels on Bacillus subtilis spore resistance and effects of Mn2+, other divalent cations, orthophosphate, and dipicolinic acid on protein resistance to ionizing radiation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 77: 32–40.
Sanada, C. T. N., S. G. Karp, M. R. Spier, A. C. Portella, P. M. Gouvea, C. T. Yamaguishi, L. P. S. Vandenberghe, A. Pandey, and C. R. Soccol (2009) Utilization of soybean vinasse for α-galactosidase production. Food Res. Int. 42: 476–483.
Yazdany, S. and K. B. Lashkari (1975) Effect of pH on sporulation of Bacillus stearothermophilus. Appl. Microbiol. 30: 1–3.
Stülk, J. and W. Hillen (2000) Regulation of carbon catabolism in Bacillus species. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 54: 849–80.
Chen, Z. M., Q. Li, H. M. Liu, N. Yu, T. J. Xie, M. Y. Yang, P. Shen, and X. D. Chen (2010) Greater enhancement of Bacillus subtilis spore yields in submerged cultures by optimization of medium composition through statistical experimental designs. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 85: 1353–1360.
Warriner, K. and W. M. Waites (1999) Enhanced sporulation in Bacillus subtilis grown on medium containing glucose: Ribose. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 29: 97–102.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sella, S.R.B.R., Masetti, C., Figueiredo, L.F.M. et al. Soybean molasses-based bioindicator system for monitoring sterilization process: Designing and performance evaluation. Biotechnol Bioproc E 18, 75–87 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-012-0356-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-012-0356-z