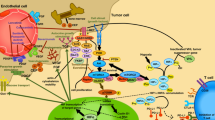
Abstract
Several targets have been identified for the therapy of metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC). The recognition of hypoxia-inducible factor-α signaling in the pathogenesis of clear-cell RCC has led to widespread study of angiogenesis inhibitors. Understanding this molecular pathogenesis of RCC led to a rapid evolvement of new systemic therapies, with seven targeted therapies approved and several more agents in late-stage clinical development. Due to the results of the currently used targeted therapies, the progression-free survival could be prolonged and the overall survival in sequential therapy can reach up to 40 months. The development of validated guidelines for sequential treatment or combination of targeted therapy remains a current challenge.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Escudier B, et al. Renal cell carcinoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2012;23(Suppl. 7):vii65–71.
Kaelin WG, Jr. Molecular basis of the VHL hereditary cancer syndrome. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2(9):673–82.
Kondo K, et al. Inhibition of HIF is necessary for tumor suppression by the von Hippel–Lindau protein. Cancer Cell. 2002;1(3):237–46.
Cho D, et al. Potential histologic and molecular predictors of response to temsirolimus in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2007;5(6):379–85.
Toi M, et al. Clinical significance of the determination of angiogenic factors. Eur J Cancer. 1996;32A(14):2513–9.
Yagoda A, Abi-Rached B, Petrylak D. Chemotherapy for advanced renal-cell carcinoma: 1983–1993. Semin Oncol. 1995;22(1):42–60.
Bellmunt J, et al. Optimal management of metastatic renal cell carcinoma: an algorithm for treatment. BJU Int. 2009;104(1):10–8.
Motzer RJ, et al. Sunitinib versus interferon alfa in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2007;356(2):115–24.
Motzer RJ, et al. Overall survival and updated results for sunitinib compared with interferon alfa in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(22):3584–90.
Escudier B, et al. Phase III trial of bevacizumab plus interferon alfa-2a in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (AVOREN): final analysis of overall survival. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(13):2144–50.
Motzer RJ, et al. Pazopanib versus sunitinib in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(8):722–31.
Escudier B, et al. Randomized, controlled, double-blind, cross-over trial assessing treatment preference for pazopanib versus sunitinib in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: PISCES Study. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(14):1412–8.
Hudes G, et al. Temsirolimus, interferon alfa, or both for advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2007;356(22):2271–81.
Poprach A, et al. Clinical and laboratory prognostic factors in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with sunitinib and sorafenib after progression on cytokines. Urol Oncol. 2014;32(4):488–95.
Herrmann E, et al. Prospective comparison of sorafenib and sunitinib for second-line treatment of cytokine-refractory kidney cancer patients. Oncology. 2008;74(3–4):216–22.
Gonzalez Larriba JL, et al. Sequential therapy in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: pre-clinical and clinical rationale for selecting a second- or subsequent-line therapy with a different mechanism of action. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2012;31(Suppl. 1):S11–7.
Escudier B, et al. Sorafenib in advanced clear-cell renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2007;356(2):125–34.
Motzer RJ, et al. Efficacy of everolimus in advanced renal cell carcinoma: a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase III trial. Lancet. 2008;372(9637):449–56.
Rini BI, et al. Comparative effectiveness of axitinib versus sorafenib in advanced renal cell carcinoma (AXIS): a randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2011;378(9807):1931–9.
Escudier B, et al. Randomized phase II trial of first-line treatment with sorafenib versus interferon Alfa-2a in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(8):1280–9.
Calvo E, Grunwald V, Bellmunt J. Controversies in renal cell carcinoma: treatment choice after progression on vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted therapy. Eur J Cancer. 2014;50(7):1321–1329.
Funakoshi T, Lee CH, Hsieh JJ. A systematic review of predictive and prognostic biomarkers for VEGF-targeted therapy in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Treat Rev. 2014;40(4):533–47.
Bierer S, et al. Lymphangiogenesis in kidney cancer: expression of VEGF-C, VEGF-D and VEGFR-3 in clear cell and papillary renal cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2008;20(4):721–5.
Ravaud A, Sire M. Arterial hypertension and clinical benefit of sunitinib, sorafenib and bevacizumab in first and second-line treatment of metastatic renal cell cancer. Ann Oncol. 2009;20(5):966–7. Author reply 967.
Schmidinger M, et al. Hypothyroidism in patients with renal cell carcinoma: blessing or curse? Cancer. 2011;117(3):534–44.
Asemissen AM, Brossart P. Vaccination strategies in patients with renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2009;58(7):1169–74.
Conflict of interest
The author declares that there are no actual or potential conflicts of interest in relation to this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leonhartsberger, N. Angiogenesis inhibition in renal cell cancer. memo 7, 211–213 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12254-014-0160-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12254-014-0160-x