Abstract
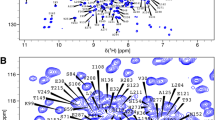
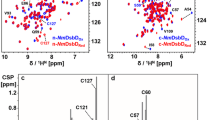
Approximately one-third of mankind has been exposed to Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the etiological agent responsible for tuberculosis (TB). As part of an effort to develop a new generation of anti-TB agents, the chemical shifts for the 261-residue, virulence-associated protein Rv0577 from M. tuberculosis has been extensively assigned.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreu N, Soto CY, Roca I, Martin C, Gibert I (2004) Mycobacterium smegmatis displays the Mycobacterium tuberculosis virulence-related neutral red character when expressing the Rv0577 gene. FEMS Microbiol 231:283–289
Buchko GW, Kim C-Y, Terwilliger TC, Kennedy MA (2006) Solution structure of the conserved hypothetical protein Rv2302 from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Bacteriol 188:5993–6001
Enarson DA (2003) Tuberculosis as a global public health problem. In: Kaufmann SHE, Hahn H (eds) Mycobacteria and TB. Kargel, Basel, pp 1–16
Myler PJ, Stacy R, Stewart LJ, Staker BL, Van Voorhis WC, Varani G, Buchko GW (2009) The Seattle Structural Genomics Center for Infectious Disease (SSGCID). Infect Diseases Drug Targets 9:493–506
Pethe K, Sequeira PC, Agarwalla S, Rhee K, Kuhen K, Phong WY, Patel V, Beer D, Walker JR, Duraiswamy J, Jiricek J, Keller TH, Chatterjee A, Tan MP, Ujjini M, Rao SPS, Camacho L, Bifani P, Mak PA, Ma I, Barnes SW, Chen Z, Plouffe D, Thayalan P, Ng SH, Au M, Lee BH, Tan BH, Ravindran S, Nanjundappa M, Lin X, Goh A, Lakshminarayana SB, Shoen C, Cynamon M, Kreiswirth B, Dartois V, Peters EC, Glynne R, Brenner S, Dick T (2010) A chemical genetic screen in Mycobacterium tuberculosis identifies carbon-source-dependent growth inhibitors devoid of in vivo efficiency. Nature Comm 1:57
Russell DG, Barry CE III, Flynn JL (2010) Tuberculosis: what we don’t know can, and does, hurt us. Science 328:852–856
Szyperski T, Yeh DC, Sukumaran DK, Moseley HNB, Montelione GT (2002) Reduced-dimensionality NMR spectroscopy for high-throughput protein resonance assignment. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:8009–8014
Wishart DS, Sykes BD (1994) The 13C chemical-shift index: a simple method for the identification of protein secondary structure using 13C chemical-shift data. J Biomol NMR 4:171–180
World Health Organization (2009) Globular tuberculosis control: a short update to the 2009 report. Geneva
Zuiderweg ERP (2002) Mapping protein–protein interactions in solution using NMR spectroscopy. Biochemistry 41:1–7
Acknowledgments
Funding for this research was provided by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, National Institute of Health, Department of Health and Human Services, under Federal Contract number HHSN272200700057C. The SSGCID internal ID for Rv0577 is MytuD.17269.a. Much of this research was performed at the W.R. Wiley Environmental Molecular Sciences Laboratory (EMSL), a national scientific user facility located at Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL) and sponsored by US Department of Energy’s Office of Biological and Environmental Research (BER) program. Battelle operates PNNL for the US Department of Energy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buchko, G.W., Kim, H., Myler, P.J. et al. Chemical shift assignments for Rv0577, a putative glyoxylase associated with virulence from Mycobacterium tuberculosis . Biomol NMR Assign 6, 43–46 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12104-011-9322-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12104-011-9322-5