Abstract
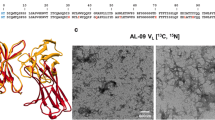
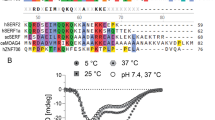
1H, 13C and 15N resonance assignments are presented for a recombinant 114 amino acid human immunoglobulin (Ig) κIV light-chain variable domain (VL) LEN, which displays a high degree of sequence identity with another human Ig κIV VL, SMA. While SMA is highly amyloidogenic in vivo and in vitro and has been linked to the pathogenesis of light-chain amyloidosis, LEN is non-amyloidogenic in vivo and can be converted to the amyloid state only in vitro under destabilizing conditions. Measurements of longitudinal and transverse amide 15N relaxation rates confirm that, as expected, LEN is a dimer at physiological pH and typical concentrations used for NMR studies, and the analysis of secondary chemical shifts indicates that the protein has a high β-sheet content. These findings are consistent with previously published biophysical data and the high-resolution X-ray structure of LEN.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baden EM, Owen BA, Peterson FC, Volkman BF, Ramirez-Alvarado M, Thompson JR (2008) Altered dimer interface decreases stability in an amyloidogenic protein. J Biol Chem 283:15853–15860
Bourne PC, Ramsland PA, Shan L, Fan ZC, DeWitt CR, Shultz BB, Terzyan SS, Moomaw CR, Slaughter CA, Guddat LW, Edmundson AB (2002) Three-dimensional structure of an immunoglobulin light-chain dimer with amyloidogenic properties. Acta Crystallogr D 58:815–823
Cai ML, Huang Y, Sakaguchi K, Clore GM, Gronenborn AM, Craigie R (1998) An efficient and cost-effective isotope labeling protocol for proteins expressed in Escherichia coli. J Biomol NMR 11:97–102
Cavanagh J, Fairbrother WJ, Palmer AG, Skelton NJ (1996) Protein NMR Spectroscopy: principles and practice. Academic Press, San Diego
Chiti F, Dobson CM (2006) Protein misfolding, functional amyloid, and human disease. Annu Rev Biochem 75:333–366
Delaglio F, Grzesiek S, Vuister GW, Zhu G, Pfeifer J, Bax A (1995) NMRPipe: a multidimensional spectral processing system based on UNIX pipes. J Biomol NMR 6:277–293
Epp O, Lattman EE, Schiffer M, Huber R, Palm R (1975) The molecular structure of a dimer composed of the variable portions of the Bence-Jones protein REI refined at 2.0 Å resolution. Biochemistry 14(494):3–4952
Falk RH, Comenzo RL, Skinner M (1997) The systemic amyloidoses. N Engl J Med 337:898–909
Farrow NA, Muhandiram R, Singer AU, Pascal SM, Kay CM, Gish G, Shoelson SE, Pawson T, Forman-Kay JD, Kay LE (1994) Backbone dynamics of a free and a phosphopeptide-complexed Src homology 2 domain studied by 15N NMR relaxation. Biochemistry 33:5984–6003
Goddard TD, Kneller DG (1993) SPARKY 3, University of California, San Francisco
Gutierrez-Gonzalez LH, Muresanu L, del Pozo-Yauner L, Sanchez R, Guereca L, Becerril B, Lucke C (2007) 1H, 13C and 15N resonance assignment of 6aJL2(R25G), a highly fibrillogenic λVI light chain variable domain. Biomol NMR Assign 1:159–161
Huang DB, Chang CH, Ainsworth C, Brunger AT, Eulitz M, Solomon A, Stevens FJ, Schiffer M (1994) Comparison of two homologous proteins: structural origin of altered domain interactions in immunoglobulin light-chain dimers. Biochemistry 33:14848–14857
Huang DB, Chang CH, Ainsworth C, Johnson G, Solomon A, Stevens FJ, Schiffer M (1997) Variable domain structure of κIV human light chain Len: high homology to the murine light chain McPC603. Mol Immunol 34:1291–1301
Hurle MR, Helms LR, Li L, Chan W, Wetzel R (1994) A role for destabilizing amino acid replacements in light-chain amyloidosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:5446–5450
Kabat EA, Wu TT, Perry HM, Gottesman KS, Foeller C (1991) Sequences of proteins of immunological interest, 5th edn. NIH publication No. 91-3242, U.S., Department of Health and Human Services, Washington, DC
Khurana R, Gillespie JR, Talapatra A, Minert LJ, Ionescu-Zanetti C, Millett I, Fink AL (2001) Partially folded intermediates as critical precursors of light chain amyloid fibrils and amorphous aggregates. Biochemistry 40:3525–3535
Kim YS, Wall JS, Meyer J, Murphy C, Randolph TW, Manning MC, Solomon A, Carpenter JF (2000) Thermodynamic modulation of light chain amyloid fibril formation. J Biol Chem 275:1570–1574
Kyle RA, Gertz MA (1995) Primary systemic amyloidosis: clinical and laboratory features in 474 cases. Semin Hematol 32:45–59
Palmer AG, Rance M, Wright PE (1991) Intramolecular motions of a zinc finger DNA-binding domain from Xfin characterized by proton-detected natural abundance 13C heteronuclear NMR spectroscopy. J Am Chem Soc 113:4371–4380
Raffen R, Dieckman LJ, Szpunar M, Wunschl C, Pokkuluri PR, Dave P, Wilkins Stevens P, Cai X, Schiffer M, Stevens FJ (1999) Physicochemical consequences of amino acid variations that contribute to fibril formation by immunoglobulin light chains. Protein Sci 8:509–517
Schormann N, Murrell JR, Liepnieks JJ, Benson MD (1995) Tertiary structure of an amyloid immunoglobulin light chain protein: a proposed model for amyloid fibril formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:9490–9494
Solomon A, Weiss DT (1995) Protein and host factors implicated in the pathogenesis of light chain amyloidosis (AL amyloidosis). Amyloid 2:269–279
Souillac PO, Uversky VN, Millett IS, Khurana R, Doniach S, Fink AL (2002) Effect of association state and conformational stability on the kinetics of immunoglobulin light chain amyloid fibril formation at physiological pH. J Biol Chem 277:12657–12665
Souillac PO, Uversky VN, Fink AL (2003) Structural transformations of oligomeric intermediates in the fibrillation of the immunoglobulin light chain LEN. Biochemistry 42:8094–8104
Wall JS, Gupta V, Wilkerson M, Schell M, Loris R, Adams P, Solomon A, Stevens F, Dealwis C (2004) Structural basis of light chain amyloidogenicity: comparison of the thermodynamic properties, fibrillogenic potential and tertiary structural features of four Vλ6 proteins. J Mol Recognit 17:323–331
Wilkins Stevens P, Raffen R, Hanson DK, Deng YL, Berrios-Hammond M, Westholm FA, Murphy C, Eulitz M, Wetzel R, Solomon A, Schiffer M, Stevens FJ (1995) Recombinant immunoglobulin variable domains generated from synthetic genes provide a system for in vitro characterization of light-chain amyloid proteins. Protein Sci 4:421–432
Yamazaki T, Lee W, Arrowsmith CH, Muhandiram DR, Kay LE (1994) A suite of triple resonance NMR experiments for the backbone assignment of 15N, 13C, 2H labeled proteins with high sensitivity. J Am Chem Soc 116:11655–11666
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a grant from the American Heart Association (0865410D) and a Young Investigator Award from Eli Lilly and Company to C.P.J. S.M. thanks the American Heart Association for a Postdoctoral Fellowship (09POST2220178). N.H. acknowledges support from grants provided by the Science Foundation Ireland (07/IN.1/B1836) and the National Institutes of Health (GM75915) to Dr. Martin Caffrey (University of Limerick). We thank Dr. Fred J. Stevens for the gift of the LEN plasmid.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mukherjee, S., Pondaven, S.P., Höfer, N. et al. Backbone and side-chain 1H, 13C and 15N resonance assignments of LEN, a human immunoglobulin κIV light-chain variable domain. Biomol NMR Assign 3, 255–259 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12104-009-9188-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12104-009-9188-y