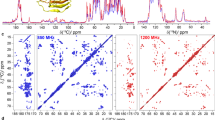
Abstract
Crenarchaeal viruses are commonly found in hyperthermal acidic environments such as those of Yellowstone National Park. These remarkable viruses not only exhibit unusual morphologies, but also display extreme genetic diversity. However, little is known about crenarchaeal viral life cycles, virus–host interactions, and their adaptation to hyperthermophilic environments. In an effort to better understand the functions of crenarchaeal viruses and the proteins encoded by their genomes, we have undertaken detailed structural and functional studies of gene products encoded in the open reading frames of Sulfolobus spindle-shaped virus ragged hills. Herein, we report (15N, 13C, 1H) resonance assignments of backbone and side chain atoms of a 19.1 kDa homodimeric E73 protein of SSVRH.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- NH4Cl:
-
Ammonium chloride
- CSI:
-
Chemical shift index
- IPTG:
-
Isopropylthiogalactoside
- EDTA:
-
Ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid
- HSQC:
-
Heteronuclear single quantum correlation
- MDG:
-
Non inducing media
- NMR:
-
Nuclear magnetic resonance
- PMSF:
-
Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride
- ORF:
-
Open reading frame
References
Clore AJ, Stedman KM (2007) The SSV1 viral integrase is not essential. Virol 361:103–111
Frols S, Gordon PM, Panlilio MA, Schleper C, Sensen CW (2007) Elucidating the transcription cycle of the UV-inducible hyperthermophilic archaeal virus SSV1 by DNA microarrays. Virol 365:48–59
Koonin EV (1992) Archaebacterial virus SSV1 encodes a putative DnaA-like protein. Nucl Acid Res 20:1143
Lawrence CM, Menon S, Eilers BJ, Bothner B, Khayat R, Douglas T, Young MJ (2009) Structural and functional studies of archaeal viruses. J Biol Chem 284(19):12599–12603
Menon SK, Maaty WS, Corn GJ, Kwok SC, Eilers BJ, Kraft P, Gillitzer E, Young MJ, Bothner B, Lawrence CM (2008) Cysteine usage in Sulfolobus spindle-shaped virus 1 and extension to hyperthermophilic viruses in general. Virol 376:270–278
Prangishvili D, Vestergaard G, Haring M, Aramayo R, Basta T, Rachel R, Garrett RA (2006) Structural and genomic properties of the hyperthermophilic archaeal virus ATV with an extracellular stage of the reproductive cycle. J Mol Biol 359:270–278
Reiter WD, Palm P, Henschen A, Lottspeich F, Zillig W, Grampp B (1987) Identification and characterization of the genes encoding three structural proteins of the Sulfolobus virus-like particle SSV1. Mol Genet Genom 206:144–153
Studier WF (2005) Protein production by auto-induction in high density shaking cultures. Prot Exp Purif 41:207–234
Taubner L, McGuirl MA, Dooley DM, Copié V (2006) Structural studies of Apo NosL, an accessory protein of the nitrous oxide reductase system: insights from structural homology with MerB, a mercury resistance protein. Biochemistry 45:12240–12252
Wiedenheft B, Stedman K, Roberto F, Willits D, Gleske AK, Zoeller L, Snyder J, Douglas T, Young M (2004) Comparative genomic analysis of hyperthermophilic archaeal Fuselloviridae viruses. J Virol 78:1954–1961
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation (grant number MCB 0444056 to V.C. and MCB 0628732 to C.M.L). The NMR experiments were recorded at Montana State University on a DRX600 Bruker solution NMR spectrometer, purchased in part with funds from the NIH shared instrumentation grant program (SIG grant # 1-S10RR13878-01), and the NSF-EPSCOR program for the State of Montana.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schlenker, C., Menon, S., Lawrence, C.M. et al. 1H, 13C, 15N backbone and side chain NMR resonance assignments for E73 from Sulfolobus spindle-shaped virus ragged hills, a hyperthermophilic crenarchaeal virus from Yellowstone National Park. Biomol NMR Assign 3, 219–222 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12104-009-9179-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12104-009-9179-z