Abstract
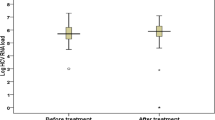
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is one of the most common blood-borne infections worldwide. Little is known with respect to changes in HCV status during chemotherapy for colorectal cancer (CRC), and the influence of HCV infection on chemotherapy remains unclear. Between 2001 and 2012, 3,260 patients were diagnosed with CRC in our institute. We studied 77 patients who were positive for anti-HCV antibodies. We retrospectively reviewed changes in HCV load and chemotherapy toxicities. Twenty-four of 77 HCV-infected patients with CRC received chemotherapy. Their median age was 66 years, and four patients had liver cirrhosis. The remaining 20 patients were diagnosed with chronic hepatitis, and their liver function tests and blood cell counts at baseline were normal. Serum HCV ribonucleic acid level before and after chemotherapy was evaluated in ten patients, with medians of 4.0 and 3.05 log IU/ml at baseline before and after chemotherapy, respectively. Two patients demonstrated elevated transaminase levels during chemotherapy. Among the 24 HCV patients received chemotherapy, no patients suffered from febrile neutropenia or treatment delay; two required chemotherapy dose reduction. Our results indicated that chemotherapy for CRC patients with HCV infection can be performed safely without changing the viral load.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tanaka J, Kumagai J, Katayama K, et al. Sex- and age-specific carriers of hepatitis B and C viruses in Japan estimated by the prevalence in the 3, 485, 648 first-time blood donors during 1995–2000. Intervirology. 2004;47:32–40.
Artz AS, Somerfield MR, Feld JJ, et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology provisional clinical opinion: chronic hepatitis B virus infection screening in patients receiving cytotoxic chemotherapy for treatment of malignant diseases. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:3199–202.
Lok AS, McMahon BJ. Chronic hepatitis B: update 2009. Hepatology. 2009;50:661–2.
Coppola N, Pisaturo M, Guastafierro S, et al. Increased hepatitis C viral load and reactivation of liver disease in HCV RNA-positive patients with onco-haematological disease undergoing chemotherapy. Dig Liver Dis. 2012;44:49–54.
Torres HA, Davila M. Reactivation of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus in patients with cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2012;9:156–66.
Melisko ME, Fox R, Venook A. Reactivation of hepatitis C virus after chemotherapy for colon cancer. In Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2004;16:204–5.
de Pree C, Giostra E, Galetto A, et al. Hepatitis C virus acute exacerbation during chemotherapy and radiotherapy for oesophageal carcinoma. Ann Oncol. 1994;5:861–2.
Shoji H, Hashimoto K, Kodaira M, et al. Hematologic safety of breast cancer chemotherapies in patients with hepatitis B or C virus infection. Oncology. 2012;82:228–33.
Hsieh CY, Huang HH, Lin CY, et al. Rituximab-induced hepatitis C virus reactivation after spontaneous remission in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:2584–6.
Morrow PK, Tarrand JJ, Taylor SH, et al. Effects of chronic hepatitis C infection on the treatment of breast cancer patients. Ann Oncol. 2010;21:1233–6.
Nooka A, Shenoy PJ, Sinha R, et al. Hepatitis C reactivation in patients who have diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with rituximab: a case report and review of literature. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2011;11:379–84.
Acknowledgments
The authors declare that no funding support was received for this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tomizawa, K., Suyama, K., Matoba, S. et al. The safety of chemotherapy for colorectal cancer patients with hepatitis C virus infection. Med Oncol 31, 212 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0212-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0212-4