Abstract
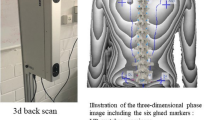
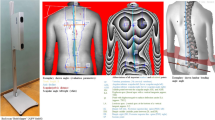
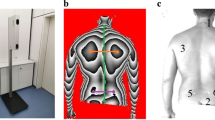
In this work, a new technique for symmetry line detection for non-erected postures, which can not be investigated with the other methods presented in the literature, is proposed. It evaluates the symmetry line by means an adaptive process in which a first attempt is modified step by step until the solution converges to the best estimation. The method here proposed is validated by analysing four different non-erected postures in which the spine does not lie onto sagittal plane, by the comparison with the traditional approach to symmetry line detection, having as reference the cutaneous marking. Results are analysed and critically discussed.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Keller, T.S., Colloca, C.J., Harrison, D.E., Harrison, D.D., Tadeusz, T.J.: Influence of spine morphology on intervertebral disc loads and stresses in asymptomatic adults: implications for the ideal spine. Spine J. 5, 297–309 (2005)
Kothiyal, K., Kayis, B.: Workplace layout for seated manual handling tasks: an electromyography study. Int. J. Indus. Ergonomics 27, 19–32 (2001)
Huysmans, T., Haex, B., De Wilde, T., Van Audekercke, R., Van der Perre, G.: A 3D active shape model for the evaluation of the alignment of the spine during sleeping. Gait Posture 24, 54–61 (2006)
Drerup, B., Hierholzer, E.: Back shape measurement using video rasterstereography and three-dimensional reconstruction of spinal shape. Clin. Biomech. 9(1), 28–36 (1994)
Turner-Smith, A.R.: A method for analysis of back shape in scoliosis. In J. Biomech. 21(6), 497–509 (1988)
Pazos, V., Cheriet, F., Song, L., Labelle, H., Dansereau, J.: Accuracy assessment of human trunk surface 3D reconstructions from an optical digitising system. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 43(1), 11–15 (2005)
Bergeron, C., Cheriet, F., Ronsky, J., Zernicke, R., Labelle, H.: Prediction of anterior scoliotic spinal curve from trunk surface using support vector regression. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 18, 973–983 (2005)
Santiesteban, Y., Sanchez, J.M., Sotoca, J.M.: A method for detection and modelling of the human spine based on principal curvature. CIARP 2006, 168–177 (2006)
Di Angelo, L., Di Stefano, P., Vinciguerra, M.G.: Experimental validation of a new method for symmetry line detection. Comput. Aided Des. Appl. 8(1), 71–86 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Di Angelo, L., Di Stefano, P. & Spezzaneve, A. Symmetry line detection for non-erected postures. Int J Interact Des Manuf 7, 271–276 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12008-012-0168-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12008-012-0168-6