Abstract
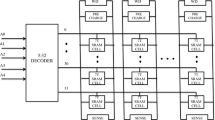
A multi-bit antifuse-type one-time programmable (OTP) memory is designed, which has a smaller area and a shorter programming time compared with the conventional single-bit antifuse-type OTP memory. While the conventional antifuse-type OTP memory can store a bit per cell, a proposed OTP memory can store two consecutive bits per cell through a data compression technique. The 1 kbit OTP memory designed with Magnachip 0.18 μm CMOS (complementary metal-oxide semiconductor) process is 34% smaller than the conventional single-bit antifuse-type OTP memory since the sizes of cell array and row decoder are reduced. And the programming time of the proposed OTP memory is nearly 50% smaller than that of the conventional counterpart since two consecutive bytes can be compressed and programmed into eight OTP cells at once. The layout area is 214 μm × 327 μm, and the read current is simulated to be 30.4 μA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ALAVI M, BOHR M, HICKS J, DENHAM M, CASSENS A, DOUGLAS D, TSAI M C. A PROM element based on salicide agglomeration of poly fuses in a CMOS logic process [C]// Proceedings of IEEE Electron Devices Meeting. Washington, 1997: 855–858.
LIM K N, KANG S S, CHOI J H, JOO J H, LEE Y S, LEE J S, CHO S I, RYU B G. Bit line coupling scheme and electrical fuse circuit for reliable operation of high density DRAM [C]// Proceedings of Symposium on VLSI Circuits. Kyoto, 2001: 33–34.
KPTHANDARAMAN C, IYER S K, IYER S S. Electrically programmable fuse (efuse) using electromigration in silicides [J]. IEEE Electron Device Letters, 2002, 23(9): 523–525.
FELLNER J, BOESMUELLER P, REITER H. Lifetime study for a poly fuse in a 0.35 μm polycide CMOS process [C]// Proceedings of IEEE the 43rd Annual International Reliability Physics Symposium. San Jose, 2005: 446–449.
FELLNER J, PREMSTAETTEN S. A one time programming cell using more than two resistance levels of a polyfuse [C]// Proceedings of IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference. San Jose, 2005: 263–266.
MIN B J, LEE K W, LEE H J, KIM S R, OH S G, JEON B G, YANG H H, KIM M K, CHO S H, CHEONG H S, CHUNG C H, KIM K N. An embedded non-volatile FRAM with electrical fuse repair scheme and one-time programming scheme for high performance smart cards [C]// Proceedings of IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference. San Jose, 2005: 255–258.
UEDA T, TAKAOKA H, HAMADA M, KOBAYASHI Y, ONO A. A novel Cu electrical fuse structure and blowing scheme utilizing crack-assisted mode for 90-45 nm-node and beyond [C]// Proceedings of Symposium on VLSI Technology. Hawaii, 2006: 138–139.
SAFRAN J, LESLIE A, FREDEMAN G, KOTHANDARAMAN C, CESTERO A, CHEN X, RAJEEVAKUMAR R, KIM D K, LI Y Z, MOY D, ROBSON N, KIRIHATA T, IYER S. A compact efuse programmable array memory for SOI CMOS [C]// Proceedings of Symposium on VLSI Circuits. Kyoto, 2007: 72–73.
ROBSON N, SAFRAN J, KOTHANDARAMAN C, CESTERO A, CHEN X, RAJEEVAKUMAR R, LESLIE A, MOY D, KIRIHATA T, IYER S. Electrically programmable fuse (efuse): From memory redundancy autonomic chips [C]// Proceedings of IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference. San Jose, 2007: 799–804.
CHOI J S, WEE J K, CHO H Y, KIM P J, OH J K, LEE C H, CHUNG J Y, KIM S J, YANG W. Antifuse EPROM circuit for field programmable DRAM [C]// Proceedings of IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference. San Francisco, 2000: 406–407.
CHA H K, YUN I H, KIM J B, SO B C, CHUN K H, NAM I K, LEE K R. A 32-KB standard CMOS antifuse one-time programmable ROM embedded in a 16-bit microcontroller [J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2006, 41(9): 2115–2124.
BARSATAN R, MAN T Y, CHAN M S. A zero mask one-time programmable memory array for RFID applications [C]// Proceedings of IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems. Island of Kos, 2006: 975–978.
MATSUFUJI K, NAMEKAWA T, NAKANO H, ITO H, WADA O, OTSUKA N. A 65 nm pure CMOS one-time programmable memory using a two-port antifuse cell implemented in a matrix structure [C]// Proceedings of IEEE Asian Solid-State Circuit Conference. Jeju, 2007: 212–215.
LI L Z, KIM T H, SHIM O Y, PARK M H, HA P B, KIM Y H. Design of synchronous 256-bit OTP memory [J]. KIMICS of Semiconductors and Communications, 2008, 12(7): 1227–1234.
LEE J H, KIM J H, LIM G H, KIM T H, LEE J H, PARK K H, PARK M H, HA P B, KIM Y H. Low-power 512-bit EEPROM designed for UHF RFID tag chip [J]. ETRI Journal, 2008, 30(3): 347–354.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Project supported by the 2nd Stage of Brain Korea; Project supported by the Korea Research Foundation
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Lz., Lee, J.H., Kim, T.H. et al. Design of small-area multi-bit antifuse-type 1 kbit OTP memory. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 16, 467–473 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-009-0078-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-009-0078-3