Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to correlate the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) value with the prognostic parameters of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC).
Materials and methods
This was a prospective study conducted on 30 consecutive patients (19 men, 11 women; mean age 61 years) with NPC. Patients underwent diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance (DW-MR) singleshot echoplanar imaging at 1.5 Tesla. NPC ADC value was correlated with pathological tumour type, pathological tumour grade, tumour volume and nodal status.
Results
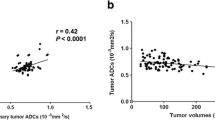
Mean NPC ADC value was 0.99±0.11×10−3mm2/s. ADC values of well-differentiated and moderately differentiated tumours differed significantly (p=0.005) from those of poorly differentiated and undifferentiated NPC. There was also a significant difference in ADC value among small, medium and large tumour volume (p=0.03). ADC value was also significantly lower (p=0.003) when metastatic cervical lymph nodes were present. ADC value correlated inversely with tumour volume (r=−0.799, p=0.03).
Conclusions
ADC value can be considered a noninvasive prognostic parameter that correlates well with prognostic parameters of NPC.
Riassunto
Obiettivo
Lo scopo di questo studio è stato quello di correlare il valore del coefficiente apparente di diffusione (ADC) con i parametri prognostici del carcinoma nasofaringeo (NPC).
Materiali e metodi
Questo è stato uno studio prospettico su 30 pazienti consecutivi (19 uomini e 11 donne, con un’età media di 61 anni) con NPC. I pazienti sono stati sottoposti a Risonanza Magnetica a 1,5 Tesla con studio di diffusione usando sequenze ecoplanari single-shot. Il valore di ADC del NPC è stato correlato con il tipo di tumore, il grado, il volume tumorale e lo stato linfonodale.
Risultati
Il valore medio dell’ADC dei NPC è stato 0,99±0,11x10−3mm2/s. I valori di ADC dei tumori ben differenziati e moderatamente differenziati sono stati significativamente diversi (p=0,005) rispetto ai valori degli NPC scarsamente differenziati o indifferenziati. C’è stata anche una differenza significativa nei valori di ADC tra tumori di piccole, medie o grandi dimensioni (p=0,03). I valori di ADC sono inoltre stati significativamente inferiori (p=0,003) in caso di presenza di metastasi linfonodali cervicali. Il valore di ADC dei carcinomi nasofaringei è risultato essere inversamente proporzionale al volume tumorale (r=-0,799, p=0,03).
Conclusioni
Il valore di ADC può essere considerato un parametro prognostico non invasivo che correla con i parametri prognostici per l’NPC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References/Bibliografia
King A, Bhatia KS (2010) Magnetic resonance imaging staging of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in the head and neck. World J Radiol 2:159–165
Chong V, Ong C (2008) Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Eur J Radiol 66:437–447
Lin J (2010) Prognostic factors in nasopharyngeal cancer. In Lu JJ, Cooper JS, Lee AW (eds) Nasopharyngeal Cancer Multidisciplinary Management. Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, pp. 95–136
Brandwein-Gensler M, Smith R (2010) Prognostic indicators in head and neck oncology including the new 7th edition of the AJCC staging system. Head and Neck Pathol 4:53–61
Abdel Razek A (2010) Diffusionweighted magnetic resonance imaging of head and neck. J Comput Assist Tomogr 34:808–815
Fong D, Bhatia KS, Yeung D et al (2010) Diagnostic accuracy of diffusion-weighted MR imaging for nasopharyngeal carcinoma, head and neck lymphoma and squamous cell carcinoma at the primary site. Oral Oncol 46:603–606
Sumi M, Ichikawa Y, Nakamura T (2007) Diagnostic ability of apparent diffusion coefficients for lymphomas and carcinomas in the pharynx. Eur Radiol 17:2631–2637
Ichikawa Y, Sumi M, Sasaki M et al (2012) Efficacy of diffusion-weighted imaging for the differentiation between lymphomas and carcinomas of the nasopharynx and oropharynx: correlations of apparent diffusion coefficients and histologic features. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 33:761–766
Abdel Razek A, Soliman N, Elkhammary S et al (2006) Role of diffusion-weighted MR imaging in cervical lymphadenopathy. Eur Radiol 16:1468–1477
King AD, Ahuja AT, Yeung DK et al (2007) Malignant cervical lymphadenopathy: diagnostic Accuracy of diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Radiology 245:806–813
Abdel Razek A, Kandeel A, Soliman N et al (2007) Role of diffusionweighted echo-planar MR imaging in differentiation of residual or recurrent head and neck tumors and posttreatment changes. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28:1146–1152
Abdel Razek A, Gaballa G, Denewer A (2010) Invasive ductal carcinoma: correlation of apparent diffusion coefficient value with pathological prognostic factors. NMR biomed 23:619–623
Kim S, Cha E, Kim H et al (2009) Diffusion-weighted imaging of breast cancer: correlation of the apparent diffusion coefficient value with prognostic factors. J Magn Reson Imaging 30:615–620
Abdel Razek A, Fathy A, Abdel Gawad T (2011) Correlation of apparent diffusion coefficient value with prognostic parameters of lung cancer. JCAT J Comput Assist Tomogr 35:248–252
Abdel Razek A, Elkhamary S, Al-Mesfer S et al (2012) Correlation of apparent diffusion coefficient at 3 tesla with prognostic parameters of retinoblastoma. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 33:944–948
Barnes L, Eveson JW, Reichart PW et al (2005) World Health Organization Classification of Tumours: Pathology & Genetics Head and Neck Tumours. chapter 2. Lyon, France: IARC Press. Tumours of the nasopharynx, pp. 83–97
Abdel Razek A, King A (2012) MRI and CT of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. AJR Am J Roentegenol 98:11–18
Lee CC, Huang TT, Lee MS et al (2010) Clinical application of tumor volume in advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma to predict outcome. Radiat Oncol 5:20
Sarisahin M, Cila A, Ozyar E et al (2011) Prognostic significance of tumor volume in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Auris Nasus Larynx 38:250–254
Liang SB, Sun Y, Liu LZ et al (2009) Extension of local disease in nasopharyngeal carcinoma detected by magnetic resonance imaging: improvement of clinical target volume delineation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 75:742–750
Chong V, Zhou J, Khoo J et al (2004) Nasopharyngeal carcinoma tumor volume measurement. Radiology 231:914–921
Ng W, Lee A, Kan W et al (2007) N-staging by magnetic resonance imaging for patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: pattern of nodal involvement by radiological levels. Radiother Oncol 82:70–75
Zhang G, Liu L, Wei W et al (2010) Retropharyngeal lymph node metastasis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma treated with radiation therapy. Radiology 255:605–612
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Presented as oral presentation at the Assembly and annual meeting of Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdel Razek, A.A.K., Kamal, E. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: correlation of apparent diffusion coefficient value with prognostic parameters. Radiol med 118, 534–539 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-012-0890-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-012-0890-x