Abstract
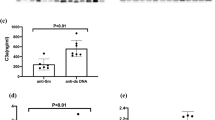
This study sought to determine whether the plasma levels of Von Willebrand factor (vWf) and the degree of red blood cell (RBC) fragmentation on peripheral smear correlate with disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Forty consecutive patients who fulfilled the criteria for SLE were studied prospectively for 1 year. Patients were categorized according to the SLE Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI) as either active (>2) or inactive disease and followed up monthly (active) or quarterly (inactive). At each visit, patients were examined fully and had complete blood count, tests on antibodies to double-stranded DNA, C3, and C4 levels, and urinalysis. Citrated plasma was analyzed for vWf antigen by standard enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. A Wright’s stained blood smear was obtained and schistocytes were quantitated on blood smear. The number of schistocytes per 500 RBCs was determined and a schistocyte index (SI) was calculated. At baseline, vWf correlated with SLEDAI (r = 0.64, p < 0.01), SI correlated with SLEDAI (r = 0.62, p < 0.01), and vWf and SI correlated with each other (r = 0.41, p = 0.01). There was an inverse correlation between baseline C3 levels and vWf (r = 0.49, p = 0.0013) and C3 levels and SI (r = 0.40, p = 0.01). Over time, there was also a correlation of SLEDAI with vWf (r = 0.53, p = 0.002) and SI (r = 0.57;p = 0.002). The relation of vWf with SI approached but did not reach statistical significance (r = 0.37, p = 0.06). We found that the plasma levels of vWf and the degree of RBC fragmentation correlate with lupus disease activity over time. Therefore, inflammation in SLE may be associated with endothelial injury.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cavazzana I, Pellegrini S, Salmaggi A (2003) Endothelium and the brain in CNS lupus. Lupus 12(12):919–928 doi:10.1191/0961203303lu503oa
Clancy R, Marder G, Martin V, Belmont HM, Abramson SB, Buyon J (2001) Circulating activated endothelial cells in systemic lupus erythematosus: further evidence for diffuse vasculopathy. Arthritis Rheum 44(5):1203–1208
Bridoux F, Vrtovsnik F, Noel C, Saunier P, Mougenot B, Lemaitre V, Dracon M, Lelievre G, Vanhille P (1998) Renal thrombotic microangiopathy in systemic lupus erythematosus: clinical correlations and long-term survival. Nephrol Dial Transplant 13(2):298–304 doi:10.1093/ndt/13.2.296
Mannucci PM, Vanoli M, Forza I, Canciani MT, Scorza R (2003) Von Willebrand factor cleaving protease (ADAMTS-13) in 123 patients with connective tissue diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus and systemic sclerosis). Haematologica 88(8):914–918
Manadan AM, Harris C, Schwartz MM, Block JA (2003) The frequency of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus undergoing kidney biopsy. J Rheumatol 30(6):1227–1230
Vasoo S, Thumboo J, Fong KY (2002) Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura in systemic lupus erythematosus: disease activity and the use of cytotoxic drugs. Lupus 11(7):443–450 doi:10.1191/0961203302lu224oa
Roman MJ, Shanker BA, Davis A, Lockshin MD, Sammaritano L, Simantov R, Crow MK, Schwartz JE, Paget SA, Devereux RB, Salmon JE (2003) Prevalence and correlates of accelerated atherosclerosis in systemic lupus erythematosus. New Engl J Med 349:2399–2406 doi:10.1056/NEJMoa035471
Al-Herz A, Ensworth S, Shojania K, Esdaile JM (2003) Cardiovascular risk factor screening in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol 30(3):493–496
Esdaile JM, Abrahamowicz M, Grodzicky T, Li Y, Panaritis C, du Berger R, Cote R, Grover SA, Fortin PR, Clarke AE, Senécal JL (2001) Traditional Framingham risk factors fail to fully account for accelerated atherosclerosis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 44(10):2331 doi:10.1002/1529-0131(200110)44:10<2331::AID-ART395>3.0.CO;2-I
Panza JA (1994) Endothelium-dependent vasodilatation and essential hypertension. N Engl J Med 331(14):951
Lima DS, Sato EI, Lima VC, Miranda F Jr, Hatta FH (2002) Brachial endothelial function is impaired in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol 29(2):292–297
Paleolog EM, Crossman DC, Mc Vey JH, Pearson JD (1990) Differential regulation by cytokines of constitutive and stimulated secretion of Von Willebrand factor from endothelial cells. Blood 75(3):688–695
Van Mourik JA, Boertjes R, Huisveld IA, Fijnvandraat K, Pajkrt D, Van Gendern PJ, Fijnheer R (1999) Von Willebrand factor propeptide in vascular disorders: a tool to distinguish between acute and chronic endothelial perturbation. Blood 94(1):179–185
Blann AD (2006) Plasma von Willebrand factor, thrombosis, and the endothelium: the first 30 years. Thromb Haemost 95(1):49–55
Ray KK, Morrow DA, Gibson CM, Murphy S, Antman EM, Braunwald E (2005) Predictors of the rise in vWF after ST elevation myocardial infarction: implications for treatment strategies and clinical outcome: an ENTIRE-TIMI 23 substudy. Eur Heart J 26(5):440–446 doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehi104
Nadar SK, Al Yemeni E, Blann AD, Lip GY (2004) Thrombomodulin, von Willebrand factor and E-selectin as plasma markers of endothelial damage/dysfunction and activation in pregnancy induced hypertension. Thromb Res 113(2):123–128 doi:10.1016/j.thromres.2004.02.010
Cherian P, Hankey GJ, Eikelboom JW, Thom J, Baker RI, McQuillan A, Staton J, Yi Q (2003) Endothelial and platelet activation in acute ischemic stroke and its etiological subtypes. Stroke 34(9):2132–2137 doi:10.1161/01.STR.0000086466.32421.F4
Scheja A, Akesson A, Geborek P, Wildt M, Wollheim CB, Wollheim FA, Vischer UM (2001) Von Willebrand factor propeptide as a marker of disease activity in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Res 3(3):178–182 doi:10.1186/ar295
Lopes AA, Maeda NY (1998) Circulating von Willebrand factor antigen as a predictor of short-term prognosis in pulmonary hypertension. Chest 114(5):1276–1282 doi:10.1378/chest.114.5.1276
Tan EM, Cohen AS, Fries JF et al (1982) The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 25:1271–1277 doi:10.1002/art.1780251101
Bombardier C, Gladman DD, Urowitz MB, Caron D, Chang CH (1992) Derivation of the SLEDAI. A disease activity index for lupus patients. The Committee on Prognosis Studies in SLE. Arthritis Rheum 35(6):630–640 doi:10.1002/art.1780350606
Rick ME, Moll S, Taylor MA, Krizek DM, White GC 2nd, Aronson DL (2002) Clinical use of a rapid collagen binding assay for von Willebrand factor cleaving protease in patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Thromb Haemost 88(4):598–604
Moake JL (2002) Thrombotic microangiopathies. N Engl J Med 347(8):589–600 doi:10.1056/NEJMra020528
Rick ME, Austin H, Leitman SF, Krizek DM, Aronson DL (2004) Clinical usefulness of a functional assay for the von Willebrand factor cleaving protease (ADAMTS-13) and its inhibitor in a patient with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Am J Hematol 75(2):96–100 doi:10.1002/ajh.10457
Ibañez D, Gladman D, Urowitz M (2007) Summarizing disease features over time: II. Variability measures of SLEDAI-2K. J Rheumatol 34(2):336–340
Bastian HM, Vila LM, Wu R, Shoenfeld Y, Roseman JM, Reveille JD, LUMINA Study Group (2004) Systemic lupus erythematosus in a multiethnic US cohort (LUMINA).XXIII. Baseline predictors of vascular events. Arthritis Rheum 50(12):3947–3957 doi:10.1002/art.20622
Constans J, Dupuy R, Blann AD, Resplandy F, Seigneur M, Renard M, Longy-Boursier M, Schaeverbeke T, Guerin V, Boisseau MR, Conri C (2003) Anti-endothelial cell autoantibodies and soluble markers of endothelial cell dysfunction in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol 30(9):1963–1966
Moscato S, Pratesi F, Bongiorni F, Scavuzzo MC, Chimenti D, Bombardieri S, Migliorini P (2002) Endothelial cell binding by systemic lupus antibodies: functional properties and relationship with anti-DNA activity. J Autoimmun 18(3):231–238 doi:10.1006/jaut.2002.0583
Yazici ZA, Raschi E, Patel A, Testoni C, Borghi MO, Graham AM, Meroni PL, Lindsey N (2001) Human monoclonal anti-endothelial cell IgG-derived from a systemic lupus erythematosus patient binds and activates human endothelium in vitro. Int Immunol 13(3):349–357 doi:10.1093/intimm/13.3.349
Bessant R, Hingorani A, Patel L, MacGregor A, Isenberg DA, Rahman A (2004) Risk of coronary heart disease and stroke in a large British cohort of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology (Oxford) 43(7):924–929 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keh213
Fischer LM, Schlienger RG, Matter C, Jick H, Meier CR (2004) Effect of rheumatoid arthritis or systemic lupus erythematosus on the risk of first-time acute myocardial infarction. Am J Cardiol 93(2):198–200
Karrar A, Sequeira W, Block JA (2001) Coronary artery disease in systemic lupus erythematosus: a review of the literature. Semin Arthritis Rheum 30(6):436–43 doi:10.1053/sarh.2001.23498
Urowitz M, Gladman D, Bruce I (2000) Atherosclerosis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr Rheumatol Rep 2(1):19–23 doi:10.1007/s11926-996-0064-9
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Level of Evidence: Level II: Development of diagnostic criteria on the basis of consecutive patients with reference to a gold standard.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Curiel, R.V., Bhagati, R., Basavaraju, L. et al. Von Willebrand Factor, Red Cell Fragmentation, and Disease Activity in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. HSS Jrnl 4, 170–174 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11420-008-9080-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11420-008-9080-9