Abstract
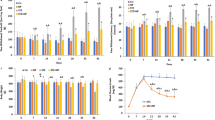
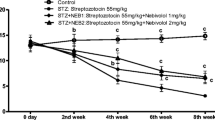
Several studies have indicated the involvement of oxidative stress and high glucose-induced cell death in the development of diabetic neuropathy. Satureja khuzestanica has been recommended in the literature as a remedy for the treatment of diabetes, and also contains antioxidant agents. Here, we investigated the possible neuroprotective effects of Satureja khuzestanica extract (SKE) on in vitro and in vivo models of diabetic neuropathy pain. High-glucose-induced damage to pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells and in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats was studied. Tail-flick and rotarod treadmill tests were used to access nociceptive threshold and motor coordination, respectively. Cell viability was determined by MTT assay. Activated caspase 3 and Bax/Bcl-2 ratio—biochemical markers of apoptosis—were evaluated using immunoblotting. We found that elevating the glucose in the medium (to 4× normal) increased cell toxicity and caspase-3 activation in PC12 cells. Incubation with SKE (200 and 250 μg/ml) decreased cell damage. Furthermore, the diabetic rats developed neuropathy, which was evident from thermal hyperalgesia and motor deficit. Administering SKE at a daily dose of between 50 and 200 mg/kg to the diabetic animals for 3 weeks ameliorated hyperglycemia, weight loss, hyperalgesia, and motor deficit, inhibited caspase 3 activation, and decreased the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio. The results suggest that SKE exerts neuroprotective effects against hyperglycemia-induced cellular damage. The mechanisms of these effects may be related to (at least in part) the prevention of neural apoptosis, and the results suggest that Satureja has the therapeutic potential to attenuate side effects of diabetes, such as neuropathy.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dyck PJ, Albers JW, Andersen H, Arezzo JC, Biessels GJ, Bril V, Feldman EL, Litchy WJ, O’Brien PC, Russell JW (on behalf of the Toronto Expert Panel on Diabetic Neuropathy) (2011) Diabetic polyneuropathies: update on research definition, diagnostic criteria and estimation of severity. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. doi:10.1002/dmrr.1226
Tomlinson DR, Gardiner NJ (2008) Glucose neurotoxicity. Nat Rev Neurosci 9:36–45
Edwards JL, Vincent AM, Cheng HT, Feldman EL (2008) Diabetic neuropathy: mechanisms to management. Pharmacol Ther 120:1–34
Kamboj SS, Vasishta RK, Sandhir R (2010) N-acetylcysteine inhibits hyperglycemia-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis markers in diabetic neuropathy. J Neurochem 112:77–91
Lelkes E, Unsworth BR, Lelkes PI (2001) Reactive oxygen species, apoptosis and altered NGF-induced signaling in PC12 pheochromocytoma cells cultured in elevated glucose: an in vitro cellular model for diabetic neuropathy. Neurotox Res 3:189–203
Russell JW, Golovoy D, Vincent AM, Mahendru P, Olzmann JA, Mentzer A, Feldman EL (2002) High glucose-induced oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in neurons. FASEB J 16:1738–1748
Ji HF, Zhang HY (2008) Multipotent natural agents to combat Alzheimer’s disease. Functional spectrum and structural features. Acta Pharmacol Sin 29:143–151
Bei W, Zang L, Guo J, Peng W, Xu A, Good DA, Hu Y, Wu W, Hu D, Zhu X, Wei M, Li G (2009) Neuroprotective effects of a standardized flavonoid extract from Diospyros kaki leaves. J Ethnopharmacol 126:134–142
Kaeidi A, Esmaeili-Mahani S, Sheibani V, Abbasnejad M, Rasoulian B, Hajializadeh Z, Afrazi S (2011) Olive (Olea europaea L.) leaf extract attenuates early diabetic neuropathic pain through prevention of high glucose-induced apoptosis: in vitro and in vivo studies. J Ethnopharmacol 136:188–196
Zargari A (1990) Medicinal plants. Tehran University Publications, Tehran, pp 42–45
Momtaz S, Abdollahi M (2010) An update on pharmacology of satureja species; from antioxidant, antimicrobial, antidiabetes and anti-hyperlipidemic to reproductive stimulation. Int J Pharmacol 6:346–353
Vosough-Ghanbari S, Rahimi R, Kharabaf S, Zeinali S, Mohammadirad A, Amini S, Yasa N, Salehnia A, Toliat T, Nikfar S, Larijani B, Abdollahi M (2010) Effects of Satureja khuzestanica on serum glucose, lipids and markers of oxidative stress in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a double-blind randomized controlled trial. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 7:465–470
Denizot F, Lang R (1986) Rapid colorimetric assay for cell growth and survival. Modifications to the tetrazolium dye procedure giving improved sensitivity and reliability. J Immunol Methods 89:271–277
Zimmermann M (1983) Ethical guidelines for investigations of experimental pain in conscious animals. Pain 16:109–110
Hajializadeh Z, Esmaeili-Mahani S, Sheibani V, Kaeidi A, Atapour M, Abbasnejad M (2010) Changes in the gene expression of specific G-protein subunits correlate with morphine insensitivity in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Neuropeptides 44:299–304
D’Amour FE, Smith DL (1941) A method of determining loss of pain sensation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 27:74–79
Esmaeili-Mahani S, Shimokawa N, Javan M, Maghsoudi N, Motamedi F, Koibuchi N, Ahmadiani A (2008) Low-dose morphine induces hyperalgesia through activation of Gαs, protein kinase C, and L-type Ca2+ channels in rats. J Neurosci Res 86:471–479
Cartmell SM, Gelgor L, Mitchell D (1991) A revised rota-rod procedure for measuring the effect of antinociceptive drugs on motor function in the rat. J Pharmacol Methods 26:149–159
Vincent AM, Mclean LL, Backus C, Feldman LL (2005) Short-term hyperglycemia produces oxidative damage and apoptosis in neurons. FASEB J 19:638–640
Vincent AM, Callaghan BC, Smith AL, Feldman EL (2011) Diabetic neuropathy: cellular mechanisms as therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Neurol 13:573–583
Pazdro R, Burgess JR (2010) The role of vitamin E and oxidative stress in diabetes complications. Mech Ageing Dev 131:276–286
Guimarães AG, Oliveira GF, Melo MS, Cavalcanti SC, Antoniolli AR, Bonjardim LR, Silva FA, Santos JP, Rocha RF, Moreira JC, Araújo AA, Gelain DP, Quintans-Júnior LJ (2010) Bioassay-guided evaluation of antioxidant and antinociceptive activities of carvacrol. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 107:949–957
Abdollahi M, Salehnia A, Mortazavi SH, Ebrahimi M, Shafiee A, Fouladian F, Keshavarz K, Sorouri S, Khorasani R, Kazemi A (2003) Antioxidant, antidiabetic, antihyperlipidemic, reproduction stimulatory properties and safety of essential oil of Satureja khuzestanica in rat in vivo: a oxicopharmacological study. Med Sci Monit 9:BR331–5
Orrenius S, Gogvadze V, Zhivotovsky B (2007) Mitochondrial oxidative stress: implications for cell death. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 47:143–183
Circu ML, Aw TY (2010) Reactive oxygen species, cellular redox systems, and apoptosis. Free Radic Biol Med 48:749–762
Sharifi AM, Eslami H, Larijani B, Davoodi J (2009) Involvement of caspase-8, -9, and -3 in high glucose-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells. Neurosci Lett 459:47–51
Joseph EK, Levine JD (2004) Caspase signalling in neuropathic and inflammatory pain in the rat. Eur J Neurosci 20:2896–2902
Sekiguchi M, Sekiguchi Y, Konno S, Kobayashi H, Homma Y, Kikuchi S (2009) Comparison of neuropathic pain and neuronal apoptosis following nerve root or spinal nerve compression. Eur Spine J 18:1978–1985
Amanlou M, Dadkhah F, Salehnia A, Farsam H, Dehpour AR (2005) An anti-inflammatory and anti-nociceptive effects of hydroalcoholic extract of Satureja khuzestanica Jamzad extract. J Pharm Pharm Sci 8:102–106
Kumar A, Negi G, Sharma SS (2011) JSH-23 targets nuclear factor-kappa B and reverses various deficits in experimental diabetic neuropathy: effect on neuroinflammation and antioxidant defence. Diabetes Obes Metab 13:750–758
Negi G, Kumar A, Sharma SS (2011) Melatonin modulates neuroinflammation and oxidative stress in experimental diabetic neuropathy: effects on NF-κB and Nrf2 cascades. J Pineal Res 50:124–131
Chopra K, Tiwari V, Arora V, Kuhad A (2010) Sesamol suppresses neuro-inflammatory cascade in experimental model of diabetic neuropathy. J Pain 11:950–957
Guimarães AG, Xavier MA, de Santana MT, Camargo EA, Santos CA, Brito FA, Barreto EO, Cavalcanti SC, Antoniolli AR, Oliveira RC, Quintans-Júnior LJ (2012) Carvacrol attenuates mechanical hypernociception and inflammatory response. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol PMID:22139435
Hotta M, Nakata R, Katsukawa M, Hori K, Takahashi S, Inoue H (2010) Carvacrol, a component of thyme oil, activates PPAR alpha and gamma, and suppresses COX-2 expression. J Lipid Res 51:132–139
Adriaensen H, Plaghki L, Mathieu C, Joffroy A, Vissers K (2005) Critical review of oral drug treatments for diabetic neuropathic pain-clinical outcomes based on efficacy and safety data from placebo-controlled and direct comparative studies. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 21:231–240
Tesfaye S, Tandan R, Bastyr EJ 3rd, Kles KA, Skljarevski V, Price KL (2007) Factors that impact symptomatic diabetic peripheral neuropathy in placebo-administered patients from two 1-year clinical trials. Diabetes Care 30:2626–2632
Shahsavari R, Ehsani-Zonouz A, Houshmand M, Salehnia A, Ahangari G, Firoozrai M (2009) Plasma glucose lowering effect of the wild Satureja khuzestanica Jamzad essential oil in diabetic rats: role of decreased gluconeogenesis. Pak J Biol Sci 12:140–145
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by funds from the Razi Herbal Medicines Research Center, Khoraman Pharmaceutical Co., and Kerman Neuroscience Research Center.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaeidi, A., Esmaeili-Mahani, S., Abbasnejad, M. et al. Satureja khuzestanica attenuates apoptosis in hyperglycemic PC12 cells and spinal cord of diabetic rats. J Nat Med 67, 61–69 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-012-0646-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-012-0646-y