Abstract
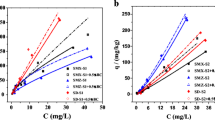
Sulfamethazine (SMZ) is an ionizable and highly mobile antibiotic which is frequently found in soil and water environments. We investigated the sorption of SMZ onto soils amended with biochars (BCs) at varying pH and contact time. Invasive plants were pyrolyzed at 700 °C and were further activated with 30 % sulfuric (SBBC) and oxalic (OBBC) acids. The sorption rate of SMZ onto SBBC and OBBC was pronouncedly pH dependent and was decreased significantly when the values of soil pH increased from 3 to 5. Modeled effective sorption coefficients (K D,eff) values indicated excellent sorption on SBBC-treated loamy sand and sandy loam soils for 229 and 183 L/kg, respectively. On the other hand, the low sorption values were determined for OBBC- and BBC700-treated loamy sand and sandy loam soils. Kinetic modeling demonstrated that the pseudo second order model was the best followed by intra-particle diffusion and the Elovich model, indicating that multiple processes govern SMZ sorption. These findings were also supported by sorption edge experiments based on BC characteristics. Chemisorption onto protonated and ligand containing functional groups of the BC surface, and diffusion in macro-, meso-, and micro-pores of the acid-activated BCs are the proposed mechanisms of SMZ retention in soils. Calculated and experimental q e (amount adsorbed per kg of the adsorbent at equilibrium) values were well fitted to the pseudo second order model, and the predicted maximum equilibrium concentration of SBBC for loamy sand soils was 182 mg/kg. Overall, SBBC represents a suitable soil amendment because of its high sorption rate of SMZ in soils.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad M, Lee SS, Dou X, Mohan D, Sung JK, Yang JE, Ok YS (2012a) Effects of pyrolysis temperature on soybean stover- and peanut shell-derived biochar properties and TCE adsorption in water. Bioresour Technol 118:536–544
Ahmad M, Lee SS, Yang JE, Ro H-M, Lee YH, Ok YS (2012b) Effects of soil dilution and amendments (mussel shell, cow bone, and biochar) on Pb availability and phytotoxicity in military shooting range soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 79:225–231
Ahmad M, Lee SS, Oh S-E, Mohan D, Moon DH, Lee Y, Ok YS (2013a) Modeling adsorption kinetics of trichloroethylene onto biochars derived from soybean stover and peanut shell wastes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:8364–8373
Ahmad M, Lee SS, Rajapaksha AU, Vithanage M, Zhang M, Cho JS, Lee S-E, Ok YS (2013b) Trichloroethylene adsorption by pine needle biochars produced at various pyrolysis temperatures. Bioresour Technol 143:615–622
Ahmad M, Moon DH, Vithanage M, Koutsospyros A, Lee SS, Yang JE, Lee SE, Jeon C, Ok YS (2013c) Production and use of biochar from buffalo-weed (Ambrosia trifida L.) for trichloroethylene removal from water. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 89:150–157
Ahmad M, Rajapaksha AU, Lim JE, Zhang M, Bolan N, Mohan D, Vithanage M, Lee SS, Ok YS (2013d) Biochar as a sorbent for contaminant management in soil and water: a review. Chemosphere 99:19–13
Almaroai YA, Usman ARA, Ahmad M, Kim KR, Vithanage M, Ok YS (2012) Role of chelating agents on release kinetics of metals and their uptake by maize from chromate copper arsenate contaminated soil. Environ Technol 34:747–755
Almaroai YA, Usman AA, Ahmad M, Moon DH, Cho J-S, Joo YK, Jeon C, Lee SS, Ok YS (2014) Effects of biochar, cow bone, and eggshell on Pb availability to maize in contaminated soil irrigated with saline water. Environ Earth Sci 71:1289–1296
Awad YM, Blagodatskaya E, Ok YS, Kuzyakov Y (2012) Effects of polyacrylamide, biopolymer, and biochar on decomposition of soil organic matter and plant residues as determined by 14C and enzyme activities. Eur J Soil Biol 48:1–10
Awad YM, Kim S-C, Abd El-Azeem SAM, Kim K-H, Kim K-R, Kim K, Jeon C, Lee SS, Ok YS (2013a) Veterinary antibiotics contamination in water, sediment, and soil near a swine manure composting facility. Environ Earth Sci 71:1433–1440
Awad YM, Blagodatskaya E, Ok YS, Kuzyakov Y (2013b) Effects of polyacrylamide, biopolymer and biochar on the decomposition of 14C-labeled maize residues and on their stabilization in soil aggregates. Eur J Soil Sci 64:488–499
Boxall ABA (2012) New and emerging water pollutants arising from agriculture. Organization for Economic Corporation and Development (OECD), Environment Department, University of York, United Kingdom
Boxall ABA, Fogg LA, Blackwell PA, Blackwell P, Kay P, Pemberton EJ, Croxford A (2004) Veterinary medicines in the environment. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 180:1–91
Choppala GK, Bolan NS, Megharaj M, Chen Z, Naidu R (2012) The influence of biochar and black carbon on reduction and bioavailability of chromate in soils. J Environ Qual 41:1175–1184
Chun Y, Sheng G, Chiou CT, Xing B (2004) Compositions and sorptive properties of crop residue-derived chars. Environ Sci Technol 38:4649–4655
Gao J, Pedersen JA (2005) Adsorption of sulfonamide antimicrobial agents to clay minerals. Environ Sci Technol 39:9509–9516
Gao L, Shi Y, Li W, Niu H, Liu J, Cai Y (2012) Occurrence of antibiotics in eight sewage treatment plants in Beijing, China. Chemosphere 86:665–671
García-Galán MJ, Garrido T, Fraile J, Ginebreda A, Díaz-Cruz MS, Barceló D (2010) Simultaneous occurrence of nitrates and sulfonamide antibiotics in two ground water bodies of Catalonia (Spain). J Hydol 383:93–101
Haham H, Oren A, Chefetz B (2012) Insight into the role of dissolved organic matter in sorption of sulfapyridine by semiarid soils. Environ Sci Technol 46:11870–11877
Heuer H, Smalla K (2007) Manure and sulfadiazine synergistically increased bacterial antibiotic resistance in soil over at least two months. Environ Microbiol 9:657–666
Ho YS, McKay G (1999) Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem 34:451–465
Ho YS, Ofomaja AE (2005) Kinetics and thermodynamics of lead ion sorption on palm kernel fibre from aqueous solution. Process Biochem 40:3455–3461
Kahle M, Stamm C (2007) Time and pH-dependent sorption of the veterinary antimicrobial sulfathiazole to clay minerals and ferrihydrite. Chemosphere 68:1224–1231
Kil JH, Kong HY, Koh KS, Kim JM (2006) Management of Sicyos angulata spread in Korea. In: Neobiota. From ecology to conservation. 4th European Conference on Biological Invasions, Vienna, BfN-Skripten,
Kim SC, Davis JG, Truman CC, Ascough Ii JC, Carlson K (2010a) Simulated rainfall study for transport of veterinary antibiotics—mass balance analysis. J Hazard Mater 175:836–843
Kim SC, Yang JE, Ok YS, Carlson K (2010b) Dissolved and colloidal fraction transport of antibiotics in soil under biotic and abiotic conditions. Water Qual Res J Can 45:275–285
Kim KR, Owens G, Kwon SI, So KH, Lee DB, Ok YS (2011) Occurrence and environmental fate of veterinary antibiotics in the terrestrial environment. Water Air Soil Pollut 214:163–174
Kim KR, Owens G, Ok YS, Park WK, Lee DB, Kwon SI (2012) Decline in extractable antibiotics in manure-based composts during composting. Waste Manag 32:110–116
Knicker H, González-Vila FJ, Polvillo O, González JA, Almendros G (2005) Fire-induced transformation of C- and N-forms in different organic soil fractions from a Dystric Cambisol under a Mediterranean pine forest (Pinus pinaster). Soil Biol Biochem 37:701–718
Kurwadkar ST, Adams CD, Meyer MT, Kolpin DW (2007) Effects of sorbate speciation on sorption of selected sulfonamides in three loamy soils. J Agric Food Chem 55:1370–1376
Kwon SI, Owens G, Ok YS, Lee DB, Jeon WT, Kim JG, Kim KR (2011) Applicability of the Charm II system for monitoring antibiotic residues in manure-based composts. Waste Manag 31:39–44
Lagergren S (1898) Zur theorie der sogenannten adsorption geloster stoffe. Kungliga Svenska Vetenskapsakademiens. Handlingar 24:1–39
Li W, Shi Y, Gao L, Liu J, Cai Y (2012) Occurrence of antibiotics in water, sediments, aquatic plants, and animals from Baiyangdian Lake in North China. Chemosphere 89(11):1307–1315
Liu MY, Tsang DCW, Hu J, Ng KTW, Liu T, Lo IMC (2008) Adsorption of methylene blue and phenol by wood waste derived activated carbon. J Environ Eng 134:338–345
Naiya TK, Bhattacharya AK, Das SK (2009) Adsorption of Cd(II) and Pb(II) from aqueous solutions on activated alumina. J Colloid Interface Sci 333:14–26
OECD (2000) Adsorption-desorption using a batch equilibrium method. Technical Guideline 106. Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, Paris, France
Ok YS, Kim SC, Kim KR, Lee SS, Moon DH, Lim KJ, Sung JK, Hur SO, Yang JE (2011) Monitoring of selected veterinary antibiotics in environmental compartments near a composting facility in Gangwon Province, Korea. Environ Monit Assess 174:693–701
Plazinski W, Rudzinski W, Plazinska A (2009) Theoretical models of sorption kinetics including a surface reaction mechanism: a review. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 152:2–13
Qiang Z, Adams C (2004) Potentiometric determination of acid dissociation constants (pKa) for human and veterinary antibiotics. Water Res 38:2874–2890
Qiu H, Lv L, B-c P, Q-j Z, W-m Z, Q-x Z (2009) Critical review in adsorption kinetic models. J Zhejiang Univ Sci A 10:716–724
Rajapaksha AU, Vithanage M, Oze C, Bandara WMAT, Weerasooriya R (2012) Nickel and manganese release in serpentine soil from the Ussangoda Ultramafic Complex, Sri Lanka. Geoderma 189–190:1–9
Rajapaksha AU, Vithanage M, Lim JE, Ahmed MBM, Zhang M, Lee SS, Ok YS (2014) Invasive plant-derived biochar inhibits sulfamethazine uptake by lettuce in soil. Chemosphere 111:500–504
Richter MK, Sander M, Krauss M, Christl I, Dahinden MG, Schneider MK, Schwarzenbach RP (2009) Cation binding of antimicrobial sulfathiazole to leonardite humic acid. Environ Sci Technol 43:6632–6638
Sewwandi BGN, Vithanage M, Wijesekara SSRMDHR, Rajapaksha AU, Jayarathna DGLM, Mowjood MIM (2012) Characterization of aqueous Pb(II) and Cd(II) biosorption on native and chemically modified Alstonia macrophylla saw dust. Biorem J 16:113–124
ShamsiJazeyi H, Kaghazchi T (2010) Investigation of nitric acid treatment of activated carbon for enhanced aqueous mercury removal. J Ind Eng Chem 16:852–858
Shinogi Y, Kanri Y (2003) Pyrolysis of plant, animal and human waste: physical and chemical characterization of the pyrolytic products. Bioresour Technol 90:241–247
Soleimani M, Kaghazchi T (2007) Agricultural waste conversion to activated carbon by chemical activation with phosphoric acid. Chem Eng Tech 30:649–654
Sparks DL (1996) Methods of soil analysis. Part 3. Chemical methods. Soil Science Society of America, Madison, WI
Srivastava VC, Swamy MM, Mall ID, Prasad B, Mishra IM (2006) Adsorptive removal of phenol by bagasse fly ash and activated carbon: equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamics. Colloids Surf Physicochem Eng Aspects 272:89–104
Teixidó M, Pignatello JJ, Beltrán JL, Granados M, Peccia J (2011) Speciation of the ionizable antibiotic sulfamethazine on black carbon (Biochar). Environ Sci Technol 45:10020–10027
Thiele-Bruhn S, Seibicke T, Schulten H-R, Leinweber P (2004) Sorption of sulfonamide pharmaceutical antibiotics on whole soils and particle-size fractions. J Environ Qual 33:1331–1342
Toles CA, Marshall WE, Johns MM (1999) Surface functional groups on acid-activated nutshell carbons. Carbon 37:1207–1214
Tsang DCW, Hu J, Liu MY, Zhang W, Lai KCK, Lo IMC (2007) Activated carbon produced from waste wood pallets: adsorption of three classes of dyes. Water Air Soil Pollut 184:141–155
Tsang DCW, Olds WE, Weber PA, Yip ACK (2013) Soil stabilisation using AMD sludge, compost and lignite: TCLP leachability and continuous acid leaching. Chemosphere 93:2839–2847
Uchimiya M, Bannon DI, Wartelle LH (2012) Retention of heavy metals by carboxyl functional groups in small arms range soil. J Agric Food Chem 60:1798–1809
Uchimiya M, Lima IM, Klasson KT, Wartelle LH (2010) Contaminant immobilization and nutrient release by biochar soil amendment: roles of natural organic matter. Chemosphere 80:935–940
Yao Y, Gao B, Chen H, Jiang L, Inyang M, Zimmerman AR, Cao X, Yang L, Xue Y, Li H (2012) Adsorption of sulfamethoxazole on biochar and its impact on reclaimed water irrigation. J Hazard Mater 209–210:408–413
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Korea Ministry of Environment as a Geo-Advanced Innovative Action Project (G112-00056-0004-0). Instrumental analyses were supported by the Korea Basic Science Institute, the Environmental Research Institute and the Central Laboratory of Kangwon National University, Korea. The Ministry of Technology, Research and Atomic Energy in Sri Lanka partially supported the first author.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Zhihong Xu
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vithanage, M., Rajapaksha, A.U., Zhang, M. et al. Acid-activated biochar increased sulfamethazine retention in soils. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 2175–2186 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3434-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3434-2