Abstract
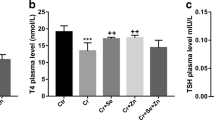
Chlorpyrifos is a widely used organophosphate insecticide for domestic, agricultural and industrial purposes. Lead is a toxic heavy metal and it is used for domestic and industrial purposes. Taurine is a semi essential amino acid with bioprotective properties. The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of taurine on thyroid function in Wistar rats co-administered with chlorpyrifos and lead. The rats were divided into 5 groups of 10 rats each. The first two groups were administered with distilled water and soya oil (1 ml/kg) respectively. The other groups received taurine (50 mg/kg), chlorpyrifos + lead [chlorpyrifos (4.25 mg/kg, 1/20 median lethal dose] and lead (233.25 mg/kg, 1/20 median lethal dose) and taurine + chlorpyrifos + lead respectively. The treatments were administered once daily by oral gavage for 16 weeks. The rats were euthanized after the completion of the study and the thyroid function and thyroid histoarchitecture were evaluated. The results revealed that co-administration of chlorpyrifos and lead to the rats induced perturbations in thyroid function and this was manifested by reductions in the concentrations of triiodothyronine and thyroxine, increased thyroid stimulating hormone concentration and degeneration of the follicular epithelia of the thyroid gland. Taurine alleviated the perturbations in thyroid function and improved thyroid gland histoarchitecture. The beneficial effects of taurine may be attributed to its ability to protect the body from toxicity and oxidative stress. Taurine may be useful for prophylaxis against disruptions in thyroid function in animals that are exposed to environmental chlorpyrifos and lead.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad MK, Khan AA, Ali SN, Mahmood R (2015) Chemoprotective effect of taurine on potassium bromate-induced DNA damage, DNA-protein cross-linking and oxidative stress in rat intestine. PLoS One 10(3):e0119137. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0119137
Akande MG, Aliu YO, Ambali SF, Ayo JO (2014a) Co-treatment of chlorpyrifos and lead induce serum lipid disorders in rats: alleviation by taurine. Toxicol Ind Health 32(7):1328–1334
Akande MG, Aliu YO, Ambali SF, Ayo JO (2014b) Taurine alleviated biochemical alterations in male Wistar rats co-exposed to chlorpyrifos and lead. J Toxicol Environ Health Sci 6:13–25. doi:10.5897/jtehs2013.0291
Akande MG, Aliu YO, Ambali SF, Ayo JO (2014c) Taurine mitigates cognitive impairment induced by chronic co-exposure of male Wistar rats to chlorpyrifos and lead acetate. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 37:315–325. doi:10.1016/j.etap.2013.11.023
Alvarez AA, Ramírez-San Juan E, Canizales-Román A (2008) Chlorpyrifos induces oxidative stress in rats. Toxicol Environ Chem 90:1019–1025. doi:10.1080/02772240701806576
Ambali SF, Orieji C, Woziri OA, Shittu M, Kawu MU (2011) Ameliorative effect of vitamin C on alterations in thyroid hormones concentrations induced by subchronic coadministration of chlorpyrifos and lead in Wistar rats. J Thyroid Res 1:1–6. doi:10.4061/2011/214924
Badiei K, Nikghadam P, Mostaghni K, Zarifi M (2009) Effect of lead on thyroid function in sheep. Iranian J Vet Res 10:223–227
Bauer M, Goetz T, Glenn T, Whybrow PC (2008) The thyroid-brain interaction in thyroid disorders and mood disorders. J Neuroendocrinol 20:1101–1114. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2826.2008.01774.x
Becker K, Seiwert M, Angerer J, Kolossa-Gehring M, Hoppe HW, Ball M, Schulz C, Thumulla J, Seifert B (2006) GerES IV pilot study: assessment of the exposure of German children to organophosphorus and pyrethroids pesticides. Int J Hyg Environ Health 209:221–233
Burns CJ, Mcintosh LJ, Mink PJ, Jurek AM, Li AA (2013) Pesticide exposure and neurodevelopmental outcomes: review of the epidemiologic and animal studies. J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev Part B 16:127–283. doi:10.1080/10937404.2013.783383
Carpenter DO, Arcaro K, Spink DC (2002) Understanding the human health effects of chemical mixtures. Environ Health Perspect 110:25–42 PMCID: PMC1241145
Chen S, Liu C, Peng C, Liu H, Hu M, Zhong G (2012) Biodegradation of chlorpyrifos and its hydrolysis product 3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridinol by a new fungal strain Cladosporium cladosporioides Hu-01. PLoS One 7:e47205. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0047205
Cooper J, Dobson H (2007) The benefits of pesticides to mankind and the environment. Crop Prot 26:1337–1348. doi:10.1016/j.cropro.2007.03.022
Davies DT (1993) Assessment of rodent thyroid endocrinology: advantages and pit-falls. Comp Haematol Int 3:142–152. doi:10.1007/BF00186098
De Angelis S, Tassinari R, Maranghi F, et al. (2009) Developmental exposure to chlorpyrifos induces alterations in thyroid and thyroid hormone levels without other toxicity signs in CD-1 mice. Toxicol Sci 108(2):311–319. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfp017
Dirican M, Taş S, Sarandöl E (2007) High-dose taurine supplementation increases serum paraoxonase and arylesterase activities in experimental hypothyroidism. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 34:833–837
Drury RA, Wallington EA, Cancerson R (1976) Carlton’s histopathological techniques, 4th edn. Oxford University Press, London
Elgawish RAR, Abdelrazek HMA (2014) Effects of lead acetate on testicular function and caspase-3 expression with respect to the protective effect of cinnamon in albino rats. Toxicol Rep 1:795–0801. doi:10.1016/j.toxrep.2014.10.010
El-Mehi AE, Amin SA (2012) Effect of lead acetate on the thyroid gland of adult male albino rats and the possible protective role of zinc supplementation: a biochemical, histological and morphometric study. J Am Sci 8:61–71
Ercal N, Gurer-Orhan H, Aykin-Burns N (2001) Toxic metals and oxidative stress part I: mechanisms involved in metal-induced oxidative damage. Curr Top Med Chem 1:529–539
Fortenberry GZ, Hu H, Turyk M, Barr DB, Meeker JD (2012) Association between urinary 3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridinol, a metabolite of chlorpyrifos and chlorpyrifos-methyl, and serum T4 and TSH in NHANES 1999–2002. Sci Total Environ 424:351–355. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.02.039
Garber JC, Barbee RW, Bielitzki JT, Clayton LA, Donovan JC, Kohn DF, Lipman NS, Locke P, Melcher J, Quimby FW, Turner PV, Wood GA, Wurbel H (2011) Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals, eighth edn. National Academies Press, Washington DC
Gilbert ME, Rovet J, Chen Z, Koibuchi N (2012) Developmental thyroid hormone disruption: prevalence, environmental contaminants and neurodevelopmental consequences. Neurotoxicology 33:842–852. doi:10.1016/j.neuro.2011.11.005
Goldner WS, Sandler DP, Yu F, Hoppin JA, Kamel F, Levan TD (2010) Pesticide use and thyroid disease among women in the agricultural health study. Am J Epidemiol 171:455–464. doi:10.1093/aje/kwp404
Haviland JA, Butz DE, Porter WP (2010) Long-term sex selective hormonal and behavioural alterations in mice exposed to low doses of chlorpyrifos in utero. Reprod Toxicol 29:74–79. doi:10.1016/j.reprotox.2009.10.008
Hu J, Xu X, Yang J, Wu G, Sun C, Lv Q (2009) Antihypertensive effect of taurine in rat. Adv Exp Med Biol 643:75–84. doi:10.1007/978-0-387-75681-3_8
Ibrahim NM, Eweis EA, El-Beltagi HS, Abdel-Mobdy YE (2012) Effect of lead acetate toxicity on experimental male albino rats. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 2:41–46. doi:10.1016/S2221-1691(11):60187-1
Jeong S, Kim B, Kang H, Ku H, Cho J (2006) Effect of chlorpyrifos-methyl on steroid and thyroid hormones in rat F0- and F1-generations. Toxicology 220:189–202
Jett DA (2011) Neurotoxic pesticides and neurologic effects. Neurol Clin 29:667–677. doi:10.1016/j.ncl.2011.06.002
Kim B (2008) Thyroid hormone as a determinant of energy expenditure and the basal metabolic rate. Thyroid 18:141–144. doi:10.1089/thy.2007.0266
Kim C, Cha YN (2009) Production of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species in phagocytes is regulated by taurine chloramine. Adv Exp Med Biol 643:463–472. doi:10.1007/978-0-387-75681-3_48
Li M, Reynolds CM, Sloboda DM, Gray C, Vickers MH (2013) Effects of taurine supplementation on hepatic markers of inflammation and lipid metabolism in mothers and offspring in the setting of maternal obesity. PLoS One 8:e76961. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0076961
Meeker JD, Barr DB, Hauser R (2006) Thyroid hormones in relation to urinary metabolites of non-persistent insecticides in men of reproductive age. Reprod Toxicol 22:437–442
Morgan MK, Sheldon LS, Croghan CW, Jones PA, Robertson GL, Chuang JC, Wilson NK, Lyu CW (2005) Exposures of preschool children to chlorpyrifos and its degradation product 3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridinol in their everyday environments. J Expo Anal Environ Epidemiol 15:297–309
Oerke EC, Dehne HW (2004) Safeguarding production losses in major crops and the role of crop protection. Crop Prot 23:275–285. doi:10.1016/j.cropro.2003.10.001
Parildar-Karpuzoğlu H, Mehmetçik G, Özdemirler-Erata G, Doğru-Abbasoğlu S, Koçak-Toker N, Uysal M (2008) Effect of taurine treatment on pro-oxidant-antioxidant balance in livers and brains of old rats. Pharmacol Rep 60:673–678
Patra RC, Rautray AK, Swarup D (2011) Oxidative stress in lead and cadmium toxicity and its amelioration. Vet Med Int 2011:457327 PMCID: PMC3087445
Roegge CS, Timofeeva OA, Seidler FJ, Slotkin TA, Levin ED (2008) Developmental diazinon neurotoxicity in rats: later effects on emotional response. Brain Res Bull 75:166–172
Sarandöl E, Taş S, Dirican M, Serdar Z (2005) Oxidative stress and serum paraoxonase activity in experimental hypothyroidism: effect of vitamin E supplementation. Cell Biochem Funct 23:1–8
Saulsbury MD, Heyliger SO, Wang K, Johnson DJ (2009) Chlorpyrifos induces oxidative stress in oligodendrocyte progenitor cells. Toxicology 259:1–9. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2008.12.026
Saunders M, Magnanti BL, Carreira SC, Yang A, Alamo-Hernández U, Riojas-Rodriguez H, Calamandrei G, Koppe JG, von Krauss MK, Keune H, Bartonova A (2012) Chlorpyrifos and neurodevelopmental effects: a literature review and expert elicitation on research and policy. Environ Health 11:1–11. doi:10.1186/1476-069X-11-S1-S5
Schuller-Levis G, Gordon RE, Wang C, Park SY, Park E (2009) Protection of bleomycin-induced fibrosis and inflammation by taurine. Int Immunopharmacol 9:971–977. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2009.04.003
Sharbidre AA, Metkari V, Patode P (2011) Effect of methyl parathion and chlorpyrifos on certain biomarkers in various tissues of guppy fish. Poecilia reticulate. Pestic Biochem Physiol 101:132–141. doi:10.1016/j.pestbp.2011.09.002
Sivaprasad R, Nagaraj M, Varalakshmi P (2004) Combined efficacies of lipoic acid and 2,3-dimercaptosuccinic acid against lead-induced lipid peroxidation in rat liver. J Nutr Biochem 15:18–23
Tan DH, Peng SQ, Wu YL, Wang YM, Lu CF, Ding W, Wang QX, Yan CH (2009) Chlorpyrifos induces delayed cytotoxicity after withdrawal in primary hippocampal neurons through extracellular signal-regulated kinase inhibition. Biol Pharm Bull 32:1649–1655
Taranukhin AG, Taranukhina EY, Saransaari P, Podkletnova IM, Pelto-Huikko M, Oja SS (2010) Neuroprotection by taurine in ethanol-induced apoptosis in the developing cerebellum. J Biomed Sci 17(Supplement 1: 12). doi:10.1186/1423-0127-17-S1-S12
Taş S, Dirican M, Sarandöl E, Serdar Z (2006) The effect of taurine supplementation on oxidative stress in experimental hypothyroidism. Cell Biochem Funct 24:153–158
Verma RS, Mehta A, Srivastava N (2007) In vivo chlorpyrifos induced oxidative stress: attenuation by antioxidant vitamins. Pestic Biochem Physiol 88:191–196. doi:10.1016/j.pestbp.2006.11.002
Wu CY, Liu B, Wang HL, Ruan DY (2011) Levothyroxine rescues the lead-induced hypothyroidism and impairment of long-term potentiation in hippocampal CA1 region of the developmental rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 256:191–197. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2011.08.010
Yousif AS, Ahmed AA (2009) Effects of cadmium and lead on the structure and function of the thyroid gland. Afr J Environ Sci Technol 3:78–85
Zadjali SA, Nemmar A, Fahim MA, Azimullah S, Subramanian D, Yasin J, Amir N, Hasan MY, Adem A (2015) Lead exposure causes thyroid abnormalities in diabetic rats. Int J Clin Exp Med 8:7160–7167
Zheng W, Aschner M, Ghersi-Egea JF (2003) Brain barrier systems: a new frontier in metal neurotoxicological research. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 192:1–11
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international and institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akande, M.G., Shittu, M., Uchendu, C. et al. Taurine ameliorated thyroid function in rats co-administered with chlorpyrifos and lead. Vet Res Commun 40, 123–129 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-016-9662-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-016-9662-9