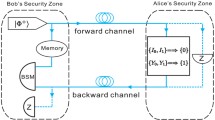
Abstract
Quantum secure direct communication protocols offer confidential transmission of classic information over quantum channel without prior key agreement. The ping-pong based protocols provide asymptotic security and detailed analysis of security level provided by each variant of the protocol is required. The paper presents a general method of calculation of the eavesdropped information as a function of the attack detection probability. The method is applied to the ping-pong protocol based on completely entangled pairs of qudits. The upper and lower bounds on the amount of the leaked information and eavesdropping detection probability are provided.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bechmann-Pasquinucci H., Peres A.: Quantum cryptography with 3-state systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85(15), 3313–3316 (2000). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.85.3313
Beige A., Englert B.G., Kurtsiefer Ch., Weinfurter H.: Secure communication with a publicly known key. Act. Phys. Pol. 101(3), 357–368 (2002)
Bengtsson, I.: Three ways to look at mutually unbiased bases. quant-ph/0610216v1 (2006)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G.: Quantum cryptography: public key distribution and coin tossing. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Computers, Systems and Signal Processing, pp. 175–179. New York (1984)
Boström K., Felbinger T.: Deterministic secure direct communication using entanglement. Phys. Rev. Lett. 89(18), 187–902 (2002). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.89.187902
Boström K., Felbinger T.: On the security of the ping-pong protocol. Phys. Lett. A 372(22), 3953–3956 (2008)
Cai Q.Y., Li B.W.: Improving the capacity of the Boström-Felbinger protocol. Phys. Rev. A 69(5), 054–301 (2004). doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.69.054301
Chamoli A., Bhandari C.: Secure direct communication based on ping-pong protocol. Quantum Inf. Process. 8, 347–356 (2009). doi:10.1007/s11128-009-0112-2
Deng F.G., Long G.L.: Quantum privacy amplification for a sequence of single qubits. Commun. Theor. Phys. 46(3), 443 (2006)
Deng, F.G., Long, G.L., Wang, Y., Xiao, L.: Increasing the efficiencies of random-choice-based quantum communication protocols with delayed measurement. Chin. Phys. Lett. 21(11), 2097–2100 (2004). URL:http://cpl.iphy.ac.cn/qikan/manage/wenzhang/0212097.pdf
Durt T., Kaszlikowski D., Chen J.L., Kwek L.C.: Security of quantum key distributions with entangled qudits. Phys. Rev. A 69(3), 032–313 (2004). doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.69.032313
Ekert A.K.: Quantum cryptography based on Bell’s theorem. Phys. Rev. Lett. 67(6), 661–663 (1991). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.67.661
Gao T., Yan F.L., Wang Z.X.: Deterministic secure direct communication using GHZ states and swapping quantum entanglement. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 38(25), 5761 (2005). doi:10.1088/0305-4470/38/25/011
Keyl M.: Fundamentals of quantum information theory. Phys. Rep. 369(5), 431–548 (2002). doi:10.1016/S0370-1573(02)00266-1
Korchenko, O., Vasiliu, Y., Gnatyuk, S.: Modern quantum technologies of information security against cyberterrorist attacks. Aviation 14(2), 58–69 (2010). doi:10.3846/aviation.2010.10 URL:http://arxiv.org/abs/1005.5553
Liu X.S., Long G.L., Tong D.M., Li F.: General scheme for superdense coding between multiparties. Phys. Rev. A 65(2), 022–304 (2002). doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.65.022304
Long G.l., Deng F.g., Wang C., Li X.h., Wen K., Wang W.y.: Quantum secure direct communication and deterministic secure quantum communication. Front. Phys. China 2(3), 251–272 (2007). doi:10.1007/s11467-007-0050-3
Long G.L., Liu X.S.: Theoretically efficient high-capacity quantum-key-distribution scheme. Phys. Rev. A 65(3), 032302 (2002). doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.65.032302
Ostermeyer, M., Walenta, N.: On the implementation of a deterministic secure coding protocol using polarization entangled photons. Opt. Commun. 281(17), 4540–4544 (2008). doi:10.1016/j.optcom.2008.04.068. URL: http://quant-ph/0703242v2.
Rivest, R., Shamir, A., Adleman, L.: A method for obtaining digital signatures and public-key cryptosystems. Commun. ACM 21(2), 120–126 (1978). doi:10.1145/359340.359342. URL:http://theory.lcs.mit.edu/rivest/rsapaper.pdf
Shor, P.W.: Polynomial-time algorithms for prime factorization and discrete logarithms on a quantum computer. SIAM J. Sci. Stat. Comput. 26, 1484–1509 (1997). URL:http://www.citebase.org/abstract?id=oai:arXiv.org:quant-ph/9508027
Vasiliu, E.V.: Asymptotic security of the ping-pong quantum direct communication protocol with three-qubit Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger states. Georgian Elec. Sci. J. Comput. Sci. Telecomm. 3(20), 3–15 (2009). URL:http://gesj.internet-academy.org.ge/gesj_articles/1427.pdf
Vasiliu E.V.: Non-coherent attack on the ping-pong protocol with completely entangled pairs of qutrits. Quantum Inf. Process. 10, 189–202 (2011). doi:10.1007/s11128-010-0188-8
Wang C., Deng F.G., Li Y.S., Liu X.S., Long G.L.: Quantum secure direct communication with high-dimension quantum superdense coding. Phys. Rev. A 71(4), 044305 (2005). doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.71.044305
Wójcik A.: Eavesdropping on the ping-pong quantum communication protocol. Phys. Rev. Lett. 90(15), 157–901 (2003)
Yang Y.G., Teng Y.W., Chai H.P., Wen Q.Y.: Revisiting the security of secure direct communication based on ping-pong protocol. Quantum Inf. Process. (2010). doi:10.1007/s11128-010-0199-5
Zawadzki P.: A fine estimate of quantum factorization success probability. Int. J. Quantum Inf. 8(8), 1233–1238 (2010). doi:10.1142/S0219749910006940
Zawadzki P.: Numerical estimation of the quantum factorization effectiveness. Theor. Appl. Inf. 22(1), 63–72 (2010)
Zhang Z., Man Z., Li Y.: Improving Wójciks eavesdropping attack on the ping-pong protocol. Phys. Lett. A 333, 46–50 (2004). doi:10.1016/j.physleta.2004.10.025
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zawadzki, P. Security of ping-pong protocol based on pairs of completely entangled qudits. Quantum Inf Process 11, 1419–1430 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-011-0307-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-011-0307-1