Abstract
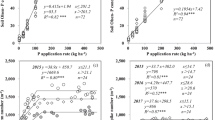
A greenhouse experiment was carried out to study the severity of phosphorus (P) deficiency symptoms on leaves, shoot dry matter production, and shoot concentration and content (the total amount per shoot) of P in 39 bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and 34 durum wheat (Triticum durum L.) genotypes grown in a severely P-deficient calcareous soil with low (20mgPkg−1 soil) and adequate (80mgPkg−1 soil) P supply for 39 days. As the seed P concentration or content can affect plant performance under P-deficient conditions, the seeds of the genotypes used in the present study were also analyzed for P concentration. Phosphorus efficiency (relative shoot growth) of genotypes, calculated by the ratio of shoot dry matter production under low P to that under adequate P supply, significantly differed among the genotypes, and varied between 46.7% and 78.6%. Phosphorus efficiency ranged from 51% to 71% with an average of 61% for bread and from 47% to 79% with an average of 66% for durum wheat genotypes. There was no correlation between P efficiency ratio and P concentration of plants (R 2=0.0001), but P efficiency of all bread and durum wheat genotypes showed a very significant correlation with the P content (the total amount of P per shoot) (R 2=0.333***). The relationship between the P efficiency and total amount of P per shoot was much more significant in bread (R 2=0.341***) than in durum wheat (R 2=0.135*). Like shoot P concentrations, also severity of visible leaf symptoms of P deficiency on older leaves, including leaf chlorosis and necrosis, did not correlate with P efficiency. In most cases, genotypes showing higher P efficiency had higher absolute shoot dry weight under P deficient conditions. Under P deficient conditions, the absolute shoot dry weight very significantly correlated with shoot P content (R 2=0.665***), but the correlation between the absolute shoot dry weight and shoot P concentration tended to be negative. There was also variation in native seed P reserve of the genotypes, but this variation had no influence on the P efficiency. The results indicate that the total amount of P per shoot and shoot dry matter production at low P supply are most reliable parameters in ranking genotypes for P efficiency at early growth stage. In wheat germplasm tested in the present study, several wheat genotypes are available showing both very high P efficiency and very high shoot content and concentration of P suggesting that P acquisition ability should be most important mechanism for high P efficiency in such genotypes. On the other hand, there are also genotypes in the germplasm having more or less same P concentration or P content in shoot but differing substantially in P efficiency, indicating importance of P utilization at cellular level in P efficiency. All these results suggest that P efficiency mechanisms can be different from one genotype to other within a given plant species.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
CJ. Barton (1948) ArticleTitlePhotometric analysis on phosphate rock Ind. Anal. Eng. Chem. 20 1068–1073 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaH1MXmtFSl
TR. Bates JP. Lynch (2001) ArticleTitleRoot hairs confer a competitive advantage under low phosphorus availability Plant Soil 236 243–250 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1012791706800 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXptlKhu7w%3D
NH. Batjes (1997) ArticleTitleA world data set of derived soil properties by FAO-UNESCO soil unit for global modelling Soil Use Manag. 13 9–16
GD. Batten (1986) ArticleTitleThe uptake and utilisation of phosphorus and nitrogen by diploid, tetraploid and hexaploid wheats (Triticum spp.). Annals Bot 58 49–59
I. Cakmak (2002) ArticleTitlePlant nutrition research: Priorities to meet human needs for food in sustainable ways Plant Soil 247 3–24 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1021194511492 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XovVCmu7o%3D
R Coltman R GC. Gerloff WH. Gabelman (1986) ArticleTitleEquivalent stress comparisons for evaluating physiological and morphological differences among tomato strains differentially tolerant to P deficiency J. Am. Soc. Hort. Sci., 111 IssueID3 422–426
DE Elliott DJ Reuter GD. Reddy RJ. Abbott (1997) ArticleTitlePhosphorus nutrition of spring wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) 1. Effects of phosphorus supply on plant symptoms, yield, components of yield, and plant phosphorus uptake Aust. J. Agr. Res. 48 855–867 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXls1yltrc%3D
Eyupoglu F 1999 Türkiye topraklarinin verimlilik durumu. Soil and Fertilizer Res. Inst. General Publications No: 220, Ankara, Turkey. 221pp
NK. Fageria VC. Baligar (1997) ArticleTitleUpland rice genotypes evaluation for phosphorus use efficiency J. Plant Nutr. 20 499–509 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXjtFWlt7w%3D
NK. Fageria VC. Baligar (1999) ArticleTitlePhosphorus-use efficiency in wheat genotypes J. Plant Nutr. 22 331–340 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXhtlGhsL8%3D
NK Fageria RJ. Wright VC. Baligar (1988) ArticleTitleRice cultivar evaluation for phosphorus-use efficiency Plant Soil 111 105–109 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF02182043 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1MXls1GltA%3D%3D
AMC Furlani RB Clark JW. Maranville WM. Ross (1984) ArticleTitleRoot phosphatase activity of sorghum genotypes grown with organic and inorganic sources of phosphorus J. Plant Nutr. 7 1583–1595 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2MXnslylsA%3D%3D
TS Gahoonia NE. Nielsen OB. Lyshede (1999) ArticleTitlePhosphorus (P) acquisition of cereal cultivars in the field at three levels of P fertilization Plant Soil, 211 269–281 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1004742032367 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXntlKisb8%3D
MA Gill h. Rahmatulla M. Salim (1994) ArticleTitleGrowth responses of twelve wheat cultivars and their phosphorus utilization from rock phosphate J. Agron. Crop. Sci. 173 204–209 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXjvFSrur8%3D
CJP Gourley DL. Allan MP. Russelle (1994) ArticleTitlePlant nutrient efficiency: A comparison of definitions and suggested improvement Plant Soil 158 29–37 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00007914 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXhvFSnt7c%3D
CT Hash RE. Schaffert JM. Peacock (2002) ArticleTitleProspects for using conventional techniques and molecular biological tools to enhance performance of ‘orphan’ crop plants on soils low in available phosphorus Plant Soil 245 135–146 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1020627926131 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XnvVCitL4%3D
WJ Horst M. Abdou F. Wiesler (1993) ArticleTitleGenotypic differences in phosphorus efficiency of wheat Plant Soil 155 IssueID156 293–296
GPD Jones GJ. Blair RS. Jessop (1989) Phosphorus efficiency in wheat – A useful selection criterion? Field Crops Res. 21 257–264
GPD Jones RS. Jessop GJ. Blair (1992) ArticleTitleAlternative methods for the selection of phosphorus efficiency in wheat Field Crops Res. 30 29–40 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0378-4290(92)90054-D
K. Liao X. Yan (1999) ArticleTitleSeed size is closely related to phosphorus use efficiency and photosynthetic phosphorus use efficiency in common bean J. Plant Nutr. 22 877–888 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXjtFCjt7c%3D
Lynch J P., Ho MD 2004 Rhizoeconomics: Carbon costs of phosphorus acquisition. Plant Soil, (in press)
GGB Manske JI Ortiz-Monasterio M Van Ginkel RM Gonzalez S Rajaram E. Molina PLG. Vlek (2000) ArticleTitleTraits associated with improved P-uptake efficiency in CIMMYT’s semidwarf spring bread wheat grown on an acid andisol in Mexico Plant Soil 221 189–204 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1004727201568 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXlslynsb8%3D
GGB Manske JI Ortiz-Monasterio RM Ginkel Particlevan S. Rajaram PLG. Vlek (2002) ArticleTitlePhosphorus use efficiency in tall, semi-dwarf and dwarf near-isogenic lines of spring wheat Euphytica 125 113–119 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1015760600750 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XksFeiur0%3D
H. Marschner (1995) Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants, 2nd edn., Academic Press London
Olsen S R, Cole CV, Watanabe FS., Dean LA 1954 Estimation of Available Phosphorus in Soil by Extraction with Sodium Bicarbonate. USDA Circ., 939. U. S. Gov. Print Office, Washington, DC
LD. Osborne Z. Rengel (2002a) ArticleTitleScreening cereals for genotypic variation in efficiency of phosphorus uptake and utilization Aust. J. Agr. Res. 53 295–303
LD. Osborne Z. Rengel (2002b) ArticleTitleGenotypic differences in wheat for uptake and utilisation of P from iron phosphate Aust. J. Agr. Res. 53 837–844 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38Xmt1GmtLg%3D
LD. Osborne Z. Rengel (2002c) ArticleTitleGrowth and P uptake by wheat genotypes supplied with phytate as the only P source Aust. J. Agr. Res. 53 845–850 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38Xmt1GmtLk%3D
DJ. Reuter JB. Robinson (1997) Plant Analysis: An Interpretation Manual, 2nd edn., CSIRO Publishing Australia
KG. Raghothama (1999) ArticleTitlePhosphate acquisition Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 50 665–693 Occurrence Handle10.1146/annurev.arplant.50.1.665 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXkt1yktrs%3D Occurrence Handle15012223
Rengel Z 1999 Physiological mechanisms underlying differential nutrient efficiency of crop genotypes. In Mineral Nutrition of Crops: Fundamental Mechanisms and Implications. Ed. Z. Rengel. pp.227–265. Haworth Press, New York
PD Schachtman RJ. Reid SM. Ayling (1998) ArticleTitlePhosphorus uptake by plants: from soil to cell Plant Physiol. 116 447–453 Occurrence Handle10.1104/pp.116.2.447 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXht1ajtbc%3D Occurrence Handle9490752
MG Teixeira J Guilherme M Guerra DL De Almeida AP. Araujo AA. Franco (1999) ArticleTitleEffect of seed phosphorus concentration on nodulation and growth of three common bean cultivars J. Plant Nutr. 22 1599–1611 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXmtFClsbk%3D
CP Vance C. Uhde-Stone DL. Allan (2003) ArticleTitlePhosphorus acquisition and use: critical adaptations by plants for securing a nonrenewable resource New Phytol. 157 423–447 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1469-8137.2003.00695.x Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXisF2gu70%3D
M. Wissuwa (2003) ArticleTitleHow do plants achieve tolerance to phosphorus deficiency? Small causes with big effects. Plant Physiol. 133 1947–1958 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXhvFKn
M Wissuwa J Wegner N. Ae M. Yano (2002) ArticleTitleSubstitution mapping of Pup1: a major QTL increasing phosphorus uptake of rice from a phosphorus-deficient soil Theor. App. Gen. 105 890–897 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XosVCntLs%3D
Yan X, Liao H, Beebe SE, Blair MW., Lynch JP 2004 QTL mapping of root hair and acid exudation traits and their relationship to phosphorus uptake in common bean. Plant Soil (in press)
X Yan J. Lynch SE. Beebe (1995) ArticleTitleGenetic variation for phosphorus efficiency of common bean in contrasting soil types: I. vegetative response Crop Sci. 35 1086–1093
Q Yao L. Li X P. Christie (2001) ArticleTitleFactors affecting arbuscular mycorrhizal dependency of wheat genotypes with different phosphorus efficiencies J. Plant Nutr. 24 1409–1419 Occurrence Handle10.1081/PLN-100106991 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXnt12hu7s%3D
LJ. Youngdahl (1990) ArticleTitleDifferences in phosphorus efficiency in bean genotypes J. Plant Nutr. 13 1381–1392 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXhtVSnt7s%3D
YG. Zhu SE. Smith (2001) ArticleTitleSeed phosphorus (P) content affects growth, and P uptake of wheat plants and their association with arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungi Plant Soil 231 105–112 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1010320903592 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXjvVSjtLc%3D
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ozturk, L., Eker, S., Torun, B. et al. Variation in phosphorus efficiency among 73 bread and durum wheat genotypes grown in a phosphorus-deficient calcareous soil. Plant Soil 269, 69–80 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-004-0469-z
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-004-0469-z