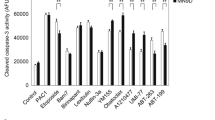
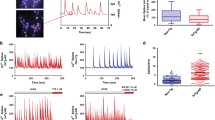
Abstract
X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis (XIAP) protects and preserves the function of neurons in both in vitro and in vivo models of excitotoxicity. Since calcium (Ca2+) overload is a pivotal event in excitotoxic neuronal cell death, we have determined whether XIAP over-expression influences Ca2+-signaling in primary cultures of mouse cortical neurons. Using cortical neuron cultures derived from wild-type (Wt) mice transiently transfected with XIAP or from transgenic mice that over-express XIAP, we show that XIAP opposes the rise in intracellular Ca2+ concentration by a variety of triggers. Relative to control neurons, XIAP over-expression produced a slight, but significant, elevation of resting Ca2+ concentrations. By contrast, the rise in intracellular Ca2+ concentrations produced by N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor stimulation and voltage gated Ca2+ channel activation were markedly attenuated by XIAP over-expression. The release of Ca2+ from intracellular stores induced by the sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase inhibitor thapsigargin was also inhibited in neurons transiently transfected with XIAP. The pan-caspase inhibitor zVAD did not, however, diminish the rise in intracellular Ca2+ concentrations elicited by l-glutamate suggesting that XIAP influences Ca2+ signaling in a caspase-independent manner. Taken together, these findings demonstrate that the ability of XIAP to block excessive rises in intracellular Ca2+ by a variety of triggers may contribute to the neuroprotective effects of this anti-apoptotic protein.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lotocki G, Keane RW (2002) Inhibitors of apoptosis proteins in injury and disease. IUBMB Life 54(5):231–240. doi:10.1080/15216540215675
Hu BR, Liu CL, Ouyang Y, Blomgren K, Siesjo BK (2000) Involvement of caspase-3 in cell death after hypoxia-ischemia declines during brain maturation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab: official j Int Soc Cereb Blood Flow Metab 20(9):1294–1300. doi:10.1097/00004647-200009000-00003
Yakovlev AG, Ota K, Wang G, Movsesyan V, Bao WL, Yoshihara K, Faden AI (2001) Differential expression of apoptotic protease-activating factor-1 and caspase-3 genes and susceptibility to apoptosis during brain development and after traumatic brain injury. J Neurosci 21(19):7439–7446
Kaur S, Wang F, Venkatraman M, Arsura M (2005) X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis (XIAP) inhibits c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 (JNK1) activation by transforming growth factor beta1 (TGF-beta1) through ubiquitin-mediated proteosomal degradation of the TGF-beta1-activated kinase 1 (TAK1). J Biol Chem 280(46):38599–38608. doi:10.1074/jbc.M505671200
Birkey Reffey S, Wurthner JU, Parks WT, Roberts AB, Duckett CS (2001) X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein functions as a cofactor in transforming growth factor-beta signaling. J Biol Chem 276(28):26542–26549
Kairisalo M, Korhonen L, Sepp M, Pruunsild P, Kukkonen JP, Kivinen J, Timmusk T, Blomgren K, Lindholm D (2009) NF-kappaB-dependent regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in hippocampal neurons by X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein. Eur J neurosci 30(6):958–966. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2009.06898.x
Wang J, Menchenton T, Yin S, Yu Z, Bance M, Morris DP, Moore CS, Korneluk RG, Robertson GS (2010) Over-expression of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein slows presbycusis in C57BL/6 J mice. Neurobiol Aging 31(7):1238–1249. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2008.07.016
Xu D, Bureau Y, McIntyre DC, Nicholson DW, Liston P, Zhu Y, Fong WG, Crocker SJ, Korneluk RG, Robertson GS (1999) Attenuation of ischemia-induced cellular and behavioral deficits by X chromosome-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein overexpression in the rat hippocampus. J Neurosci 19(12):5026–5033
Trapp T, Korhonen L, Besselmann M, Martinez R, Mercer EA, Lindholm D (2003) Transgenic mice overexpressing XIAP in neurons show better outcome after transient cerebral ischemia. Mol Cell Neurosci 23(2):302–313
Choi DW (2005) Neurodegeneration: cellular defences destroyed. Nature 433(7027):696–698. doi:10.1038/433696a
Arundine M, Tymianski M (2003) Molecular mechanisms of calcium-dependent neurodegeneration in excitotoxicity. Cell Calcium 34(4–5):325–337
Leissring MA, Yamasaki TR, Wasco W, Buxbaum JD, Parker I, LaFerla FM (2000) Calsenilin reverses presenilin-mediated enhancement of calcium signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(15):8590–8593
Paschen W, Mengesdorf T (2005) Endoplasmic reticulum stress response and neurodegeneration. Cell Calcium 38(3–4):409–415. doi:10.1016/j.ceca.2005.06.019
Pringle AK (2004) In, out, shake it all about: elevation of [Ca2 +]i during acute cerebral ischaemia. Cell Calcium 36(3–4):235–245. doi:10.1016/j.ceca.2004.02.014
Szydlowska K, Tymianski M (2010) Calcium, ischemia and excitotoxicity. Cell Calcium 47(2):122–129. doi:10.1016/j.ceca.2010.01.003
Kass GE, Orrenius S (1999) Calcium signaling and cytotoxicity. Environ Health Perspect 107(Suppl 1):25–35
Nagley P, Higgins GC, Atkin JD, Beart PM (2010) Multifaceted deaths orchestrated by mitochondria in neurones. Biochim Biophys Acta 1802 1:167–185. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2009.09.004
Hu P, Han Z, Couvillon AD, Exton JH (2004) Critical role of endogenous Akt/IAPs and MEK1/ERK pathways in counteracting endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced cell death. J Biol Chem 279(47):49420–49429. doi:10.1074/jbc.M407700200
Mercer EA, Korhonen L, Skoglosa Y, Olsson PA, Kukkonen JP, Lindholm D (2000) NAIP interacts with hippocalcin and protects neurons against calcium-induced cell death through caspase-3-dependent and -independent pathways. EMBO J 19(14):3597–3607
Hirata H, Lopes GS, Jurkiewicz A, Garcez-do-Carmo L, Smaili SS (2012) Bcl-2 modulates endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondrial calcium stores in PC12 cells. Neurochem Res 37(2):238–243. doi:10.1007/s11064-011-0600-5
Saille C, Marin P, Martinou JC, Nicole A, London J, Ceballos-Picot I (1999) Transgenic murine cortical neurons expressing human Bcl-2 exhibit increased resistance to amyloid beta-peptide neurotoxicity. Neuroscience 92(4):1455–1463
Cheung NS, Beart PM, Pascoe CJ, John CA, Bernard O (2000) Human Bcl-2 protects against AMPA receptor-mediated apoptosis. J Neurochem 74(4):1613–1620
Offen D, Beart PM, Cheung NS, Pascoe CJ, Hochman A, Gorodin S, Melamed E, Bernard R, Bernard O (1998) Transgenic mice expressing human Bcl-2 in their neurons are resistant to 6-hydroxydopamine and 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6- tetrahydropyridine neurotoxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95(10):5789–5794
Moore CS, Hebb AL, Blanchard MM, Crocker CE, Liston P, Korneluk RG, Robertson GS (2008) Increased X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP) expression exacerbates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). J Neuroimmunol 203(1):79–93. doi:10.1016/j.jneuroim.2008.06.030
Mattson MP (2007) Calcium and neurodegeneration. Aging Cell 6(3):337–350
Schmidt EV, Christoph G, Zeller R, Leder P (1990) The cytomegalovirus enhancer: a pan-active control element in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol 10(8):4406–4411
Nakanishi S, Nakajima Y, Masu M, Ueda Y, Nakahara K, Watanabe D, Yamaguchi S, Kawabata S, Okada M (1998) Glutamate receptors: brain function and signal transduction. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 26(2–3):230–235
Krause T, Gerbershagen MU, Fiege M, Weisshorn R, Wappler F (2004) Dantrolene–a review of its pharmacology, therapeutic use and new developments. Anaesthesia 59(4):364–373. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2044.2004.03658.x
Eckelman BP, Salvesen GS, Scott FL (2006) Human inhibitor of apoptosis proteins: why XIAP is the black sheep of the family. EMBO Rep 7(10):988–994. doi:10.1038/sj.embor.7400795
Shiozaki EN, Chai J, Rigotti DJ, Riedl SJ, Li P, Srinivasula SM, Alnemri ES, Fairman R, Shi Y (2003) Mechanism of XIAP-mediated inhibition of caspase-9. Mol Cell 11(2):519–527
Shi Y (2002) Mechanisms of caspase activation and inhibition during apoptosis. Mol Cell 9(3):459–470
Motagally MA, Lukewich MK, Chisholm SP, Neshat S, Lomax AE (2009) Tumour necrosis factor alpha activates nuclear factor kappaB signalling to reduce N-type voltage-gated Ca2+ current in postganglionic sympathetic neurons. J Physiol 587(Pt 11):2623–2634. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2009.172312
Li SY, Sun WG, Jia YH, Wu GS, An GS, Ni JH, Jia HT (2010) Calcium signal-initiated early activation of NF-kappaB in neurons is a neuroprotective event in response to kainic acid-induced excitotoxicity. Biochem Biokhimiia 75(1):101–109
Wootz H, Hansson I, Korhonen L, Lindholm D (2006) XIAP decreases caspase-12 cleavage and calpain activity in spinal cord of ALS transgenic mice. Exp Cell Res 312(10):1890–1898. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2006.02.021
Pinton P, Rizzuto R (2006) Bcl-2 and Ca2+ homeostasis in the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell Death Differ 13(8):1409–1418. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4401960
Pinton P, Ferrari D, Magalhaes P, Schulze-Osthoff K, Di Virgilio F, Pozzan T, Rizzuto R (2000) Reduced loading of intracellular Ca(2+) stores and downregulation of capacitative Ca(2+) influx in Bcl-2-overexpressing cells. J Cell Biol 148(5):857–862
Eckenrode EF, Yang J, Velmurugan GV, Foskett JK, White C (2010) Apoptosis protection by Mcl-1 and Bcl-2 modulation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor-dependent Ca2+ signaling. J Biol Chem 285(18):13678–13684. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.096040
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Council of Canada and the Alzheimer’s Society of Canada. Graduate student funding for J Grant was provided by the Alzheimer’s Society of Canada Doctoral Studentship Award and the National Research Council of Canada GSSSP. This work was supported in part by a biomedical research grant from the MS Society of Canada (GSR). The authors would like to thank Dr. Peter Liston for providing the XIAP-dsRed plasmid.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11064_2013_989_MOESM1_ESM.docx
Supplemental Figure 1. XIAP over-expression protects neurons from L-glutamate-induced toxicity. An MTT assay was used to assess cell viability of cortical neuronal cultures derived from ubXIAP mice (n = 13) and Wt littermates (n = 12), 24 hours after a 15 minute exposure to 1 mM glutamate (glut). Bars represent mean percent cell viability, expressed as a ratio of viable glutamate treated samples relative to vehicle treated controls. Error bars represent mean +/-standard error of the mean. *p<0.05, unpaired Student’s t-test. (DOCX 31 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grant, J., Parker, K., Moore, C.S. et al. Over-expression of X-Linked Inhibitor of Apoptosis Protein Modulates Multiple Aspects of Neuronal Ca2+ Signaling. Neurochem Res 38, 847–856 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-013-0989-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-013-0989-0