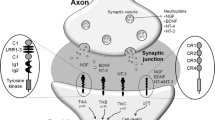
Abstract
The selective vulnerability of specific neuronal subpopulations to trimethyltin (TMT), an organotin compound with neurotoxicant effects selectively involving the limbic system and especially marked in the hippocampus, makes it useful to obtain in vivo models of neurodegeneration associated with behavioural alterations, such as hyperactivity and aggression, cognitive impairment as well as temporal lobe epilepsy. TMT has been widely used to study neuronal and glial factors involved in selective neuronal death, as well as the molecular mechanisms leading to hippocampal neurodegeneration (including neuroinflammation, excitotoxicity, intracellular calcium overload, mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress). It also offers a valuable instrument to study the cell–cell interactions and signalling pathways that modulate injury-induced neurogenesis, including the involvement of newly generated neurons in the possible repair processes. Since TMT appears to be a useful tool to damage the brain and study the various responses to damage, this review summarises current data from in vivo and in vitro studies on neuroprotective strategies to counteract TMT-induced neuronal death, that may be useful to elucidate the role of putative candidates for translational medical research on neurodegenerative diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vajda FJ (2002) Neuroprotection and neurodegenerative disease. J Clin Neurosci 9:4–8
Mattson MP (2008) Glutamate and neurotrophic factors in neuronal plasticity and disease. Ann NY Acad Sci 1144:97–112
Minghetti L (2005) Role of inflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Curr Opin Neurol 18:315–321
Craggs L, Kalaria RN (2011) Revisiting dietary antioxidants, neurodegeneration and dementia. NeuroReport 22:1–3
Hennigan A, O’Callaghan RM, Kelly AM (2007) Neurotrophins and their receptors: roles in plasticity, neurodegeneration and neuroprotection. Biochem Soc Trans 35:424–427
Parent JM (2003) Injury-induced neurogenesis in the adult mammalian brain. Neuroscientist 9:261–272
Geloso MC, Corvino V, Michetti F (2011) Trimethyltin-induced hippocampal degeneration as a tool to investigate neurodegenerative processes. Neurochem Int 58:729–738
Chang LW, Wenger GR, McMillan DE, Dyer RS (1983) Species and strain comparison of acute neurotoxic effects of trimethyltin in mice and rats. Neurobehav Toxicol Teratol 5:337–350
Balaban CD, O’Callaghan JP, Billingsley ML (1988) Trimethyltin-induced neuronal damage in the rat brain: comparative studies using silver degeneration stains, immunocytochemistry and immunoassay for neurotypic and gliotypic proteins. Neuroscience 26:337–361
Harry GJ, Lefebvre d’Hellencourt C (2003) Dentate Gyrus: alterations that occur with hippocampal injury. Neurotoxicology 24:343–356
Geloso MC, Vinesi P, Michetti F (1996) Parvalbumin-immunoreactive neurons are not affected by trimethyltin-induced neurodegeneration in the rat hippocampus. Exp Neurol 139:269–277
Geloso MC, Vinesi P, Michetti F (1997) Calretinin-containing neurons in trimethyltin-induced neurodegeneration in the rat hippocampus. An immunocytochemical study. Exp Neurol 146:67–73
Pugliese M, Carrasco JL, Geloso MC, Mascort J, Michetti F, Mahy N (2004) Gamma-aminobutyric acidergic interneuron vulnerability to aging in canine prefrontal cortex. J Neurosci Res 77:913–920
Geloso MC, Corvino V, Cavallo V, Toesca A, Guadagni E, Passalacqua R, Michetti F (2004) Expression of astrocytic nestin in the rat hippocampus during trimethyltin-induced neurodegeneration. Neurosci Lett 357:103–106
El-Fawal HA, O’Callaghan JP (2008) Autoantibodies to neurotypic and gliotypic proteins as biomarkers of neurotoxicity: assessment of trimethyltin (TMT). Neurotoxicology 29:109–115
Little AR, Benkovic SA, Miller DB, O’Callaghan JP (2002) Chemically induced neuronal damage and gliosis: enhanced expression of the proinflammatory chemokine, monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP)-1, without a corresponding increase in proinflammatory cytokines(1). Neuroscience 115:307–320
Funk JA, Gohlke J, Kraft AD, McPherson CA, Collins JB, Jean Harry G (2011) Voluntary exercise protects hippocampal neurons from trimethyltin injury: possible role of interleukin-6 to modulate tumor necrosis factor receptor mediated neurotoxicity. Brain Behav Immun 25:1063–1077
Koczyk D (1996) How does trimethyltin affect the brain: facts and hypotheses. Acta Neurobiol Exp 56:587–596
Kreyberg S, Torvik A, Bjørneboe A, Wiik-Larsen W, Jacobsen D (1992) Trimethyltin poisoning: report of a case with postmortem examination. Clin Neuropathol 11:256–259
Aldrige WN, Street BW, Skilleter DN (1977) Oxidative phosphorylation. Halide-dependent and halide-independent effects of triorganotin and triorganolead compounds on mitochondrial functions. Biochem J 168:353–364
Misiti F, Orsini F, Clementi ME, Lattanzi W, Giardina B, Michetti F (2008) Mitochondrial oxygen consumption inhibition importance for TMT-dependent cell death in undifferentiated PC12 cells. Neurochem Int 52:1092–1099
Billingsley ML, Yun J, Reese BE, Davidson CE, Buck-Koehntop BA, Veglia G (2006) Functional and structural properties of stannin: roles in cellular growth, selective toxicity, and mitochondrial responses to injury. J Cell Biochem 98:243–250
Piacentini R, Gangitano C, Ceccariglia S, Del Fà A, Azzena GB, Michetti F, Grassi C (2008) Dysregulation of intracellular calcium homeostasis is responsible for neuronal death in an experimental model of selective hippocampal degeneration induced by trimethyltin. J Neurochem 105:2109–2121
Ceccariglia S, D’Altocolle A, Del Fa’ A, Pizzolante F, Caccia E, Michetti F, Gangitano C (2011) Cathepsin D plays a crucial role in the trimethyltin-induced hippocampal neurodegeneration process. Neuroscience 174:160–170
Kraft DA, McPherson CA, Harry GJ (2009) Heterogeneity of microglia and TNF signaling as determinants for neuronal death or survival. Neurotoxicology 30(5):785–793
Harry GJ, Bruccoleri A, Lefebvre d’Hellencourt C (2003) Differential modulation of hippocampal chemical-induced injury response by ebselen, pentoxifylline, and TNF-alpha- IL-1alpha-, and IL-6-neutralizing antibodies. J Neurosci Res 73:526–536
Harry GJ, Lefebvre d’Hellencourt C, McPherson CA, Funk JA, Aoyama M, Wine RN (2008) Tumor necrosis factor p55 and p75 receptors are involved in chemical-induced apoptosis of dentate granule neurons. J Neurochem 106:281–298
Harry GJ, Tyler K, Lefebvre d’Hellencourt C, Tilson HA, Maier WE (2002) Morphological alterations and elevations in tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin (IL)-1alpha, and IL-6 in mixed glia cultures following exposure to trimethyltin: modulation by proinflammatory cytokine recombinant proteins and neutralizing antibodies. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 180:205–218
Tran HY, Shin EJ, Saito K, Nguyen XK, Chung YH, Jeong JH, Bach JH, Park DH, Yamada K, Nabeshima T, Yoneda Y, Kim HC (2012) Protective potential of IL-6 against trimethyltin-induced neurotoxicity in vivo. Free Radic Biol Med 52:1159–1174
Reese BE, Davidson C, Billingsley ML, Yun J (2005) Protein kinase C epsilon regulates tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced stannin gene expression. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 314:61–69
Maier WE, Brown HW, Tilson HA, Luster MI, Harry GJ (1995) Trimethyltin increases interleukin (IL)-1 alpha, IL-6 and tumor necrosis factor alpha mRNA levels in rat hippocampus. J Neuroimmunol 59:65–75
Brabeck C, Michetti F, Geloso MC, Corvino V, Goezalan F, Meyermann R, Schluesener H (2002) Expression of EMAP-II activated monocytes/microglial cells in different regions of the rat hippocampus after timethyltin-induced brain damage. Exp Neurol 177:341–346
Little AR, Miller DB, Li S, Kashon ML, O’Callaghan JP (2012) Trimethyltin-induced neurotoxicity: gene expression pathway analysis, q-RT-PCR and immunoblotting reveal early effects associated with hippocampal damage and gliosis. Neurotoxicol Teratol 34:72–82
Morita M, Imai H, Liu Y, Xu X, Sadamatsu M, Nakagami R, Shirakawa T, Nakano K, Kita Y, Yoshida K, Tsunashima K, Kato N (2008) FK506-protective effects against trimethyltin neurotoxicity in rats: hippocampal expression analyses reveal the involvement of periarterial osteopontin. Neuroscience 153:1135–1145
Liu Y, Imai H, Sadamatsu M, Tsunashima K, Kato N (2005) Cytokines participate in neuronal death induced by trimethyltin in the rat hippocampus via type II glucocorticoid receptors. Neurosci Res 51:319–327
Corvino V, Marchese E, Zarkovic N, Zarkovic K, Cindric M, Waeg G, Michetti F, Geloso MC (2011) Distribution and time-course of 4-hydroxynonenal, heat shock protein 110/105 family members and cyclooxygenase-2 expression in the hippocampus of rat during trimethyltin-induced neurodegeneration. Neurochem Res 36:1490–1500
Pompili E, Nori SL, Geloso MC, Guadagni E, Corvino V, Michetti F, Fumagalli L (2004) Trimethyltin-induced differential expression of PAR subtypes in reactive astrocytes of the rat hippocampus. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 122:93–98
Allaman I, Belanger M, Magistretti PJ (2011) Astrocyte–neuron metabolic relationships: for better and for worse. Trends Neurosci 34:76–87
Abrahám IM, Harkany T, Horvath KM, Luiten PG (2001) Action of glucocorticoids on survival of nerve cells: promoting neurodegeneration or neuroprotection? J Neuroendocrinol 13:749–760
Nichols NR, Agolley D, Zieba M, Bye N (2005) Glucocorticoid regulation of glial responses during hippocampal neurodegeneration and regeneration. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 48:287–301
Dinkel K, MacPherson A, Sapolsky RM (2003) Novel glucocorticoid effects on acute inflammation in the CNS. J Neurochem 84:705–716
Gerbec EN, Messing RB, Sparber SB (1988) Parallel changes in operant behavioural adaptation and hippocampal corticosterone binding in rats treated with trimethyltin. Brain Res 460:346–351
Chang LW, Hough AJ, Bivins FG, Cockerill D (1989) Effects of adrenalectomy and corticosterone on hippocampal lesions induced by trimethyltin. Biomed Environ Sci 2:54–64
Stanton ME, Coussons ME, Kuhn CM (1992) Corticosterone hypersecretion in preweanling rats exposed neonatally to trimethyltin. Neurotoxicology 13:421–428
Imai H, Kabuto M, Takita M, Kato N (1998) Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist inhibits transient increase of plasma corticosterone in the initial phase of trimethyltin-induced hippocampal necrosis. Neurotoxicology 19:163–166
Imai H, Nishimura T, Sadamatsu M, Liu Y, Kabuto M, Kato N (2001) Type II glucocorticoid receptors are involved in neuronal death and astrocyte activation induced by trimethyltin in the rat hippocampus. Exp Neurol 171:22–28
Shuto M, Higuchi K, Sugiyama C, Yoneyama M, Kuramoto N, Nagashima R, Kawada K, Ogita K (2009) Endogenous and exogenous glucocorticoids prevent trimethyltin from causing neuronal degeneration of the mouse brain in vivo: involvement of oxidative stress pathways. J Pharmacol Sci 110:424–436
Ogita K, Sugiyama C, Acosta GB, Kuramoto N, Shuto M, Yoneyama M, Nakamura Y, Shiba T, Yamaguchi T (2012) Opposing roles of glucocorticoid receptor and mineralocorticoid receptor in trimethyltin-induced cytotoxicity in the mouse hippocampus. Neurosci Lett 511:116–119
Tsutsumi S, Akaike M, Arimitsu H, Imai H, Kato N (2002) Circulating corticosterone alters the rate of neuropathological and behavioural changes induced by trimethyltin in rats. Exp Neurol 173:86–94
Little AR, Sriram K, O’Callaghan JP (2006) Corticosterone regulates expression of CCL2 in the intact and chemically injured hippocampus. Neurosci Lett 399:162–166
Bruccoleri A, Pennypacker KR, Harry JG (1999) Effect of dexamethasone on elevated cytokine mrna levels in chemical-induced hippocampal injury. Neurosci Res 57:916–926
Kraft AD, Harry GJ (2011) Features of microglia and neuroinflammation relevant to environmental exposure and neurotoxicity. Int J Environ Res Public Health 8:2980–3018
Woods AG, Poulsen FR, Gall CM (1999) Dexamethasone selectively suppresses microglial trophic responses to hippocampal deafferentation. Neuroscience 91:1277–1289
Viscomi MT, Florenzano F, Latini L, Amantea D, Bernardi G, Molinari M (2008) Methylprednisolone treatment delays remote cell death after focal brain lesion. Neuroscience 154:1267–1282
Kiefer R, Kreutzberg GW (1991) Effects of dexamethasone on microglial activation in vivo: selective downregulation of major histocompatibility complex class II expression in regenerating facial nucleus. J Neuroimmunol 34:99–108
Benkovic SA, O’Callaghan JP, Miller DB (2009) Protracted exposure to supraphysiological levels of corticosterone does not cause neuronal loss or damage and protects against kainic acid-induced neurotoxicity in the hippocampus of C57BL/6 J mice. Neurotoxicology 30:965–976
Minghetti L (2004) Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in inflammatory and degenerative brain diseases. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 63:901–910
Geloso MC, Vercelli A, Corvino V, Repici ME, Boca M, Haglid K, Zelano G, Michetti F (2002) Cyclooxygenase-2 and caspase-3 expression in trimethyltin-induced apoptosis in the mouse hippocampus. Exp Neurol 175:152–160
Shirakawa T, Nakano K, Hachiya NS, Kato N, Kaneko K (2007) Temporospatial patterns of COX-2 expression and pyramidal cell degeneration in the rat hippocampus after trimethyltin administration. Neurosci Res 59:117–123
Huong NQ, Nakamura Y, Kuramoto N, Yoneyama M, Nagashima R, Shiba T, Yamaguchi T, Hasebe S, Ogita K (2011) Indomethacin ameliorates trimethyltin-induced neuronal damage in vivo by attenuating oxidative stress in the dentate gyrus of mice. Biol Pharm Bull 34:1856–1863
Shohami E, Ginis I, Hallenbeck JM (1999) Dual role of tumor necrosis factor alpha in brain injury. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 10:119–130
Latini L, Geloso MC, Corvino V, Giannetti S, Florenzano F, Viscomi MT, Michetti F, Molinari M (2010) TMT intoxication induces expression of nitric oxide synthase in neurons and purinergic ionotropic receptor 2 in astrocytes in the hippocampus. J Neurosci Res 88:500–509
Shirakawa T, Nakano K, Hachiya N, Kato N, Kaneko K (2011) The involvement of P2X1 degeneration in the rat hippocampus after trimethyltin administration. Neurosci Res 71:396–404
Brambilla R, Ceruti S, Malorni W, Cattabeni F, Abbracchio MP (2000) A novel gliotic P2 receptor mediating cyclooxygenase-2 induction in rat and human astrocytes. J Auton Nerv Syst 81:3–9
Nito C, Ueda M, Inaba T, Katsura K, Katayama Y (2011) FK506 ameliorates oxidative damage and protects rat brain following transient focal cerebral ischemia. Neurol Res 33:881–889
Nishimura T, Imai H, Minabe Y, Sawa A, Kato N (2006) Beneficial effects of FK506 for experimental temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurosci Res 56:386–390
Zawadzka M, Kaminska B (2005) A novel mechanism of FK506-mediated neuroprotection: downregulation of cytokine expression in glial cells. Glia 49:36–51
Barrientos RM (2011) Voluntary exercise as an anti-neuroinflammatory therapeutic. Brain Behav Immun 25:1061–1062
Ding YH, Mrizek M, Lai Q, Wu Y, Reyes R Jr, Li J, Davis WW, Ding Y (2006) Exercise preconditioning reduces brain damage and inhibits TNF-alpha receptor expression after hypoxia/reoxygenation: an in vivo and in vitro study. Curr Neurovasc Res 3:263–271
Parachikova A, Nichol KE, Cotman CW (2008) Short-term exercise in aged Tg2576 mice alters neuroinflammation and improves cognition. Neurobiol Dis 30:121–129
Nybo L, Nielsen B, Pedersen BK, Secher NH (2002) Interleukin-6 release from the human brain during prolonged exercise. J Physiol 542:991–995
Zarković N, Zarković K, Schaur RJ, Stolc S, Schlag G, Redl H, Waeg G, Borović S, Loncarić I, Jurić G, Hlavka V (1999) 4-Hydroxynonenal as a second messenger of free radicals and growth modifying factor. Life Sci 65:1901–1904
Coyle JT, Puttfarken P (1993) Oxidative stress, glutamate and neurodegenerative disorders. Science 262:689–695
Schulz JB, Lindenau J, Seyfried J, Dichgans J (2000) Glutathione, oxidative stress and neurodegeneration. Eur J Biochem 267:4904–4911
Ali SF, LeBel CP, Bondy SC (1992) Reactive oxygen species formation as a biomarker of methylmercury and trimethyltin neurotoxicity. Neurotoxicology 13:637–648
Zhang L, Li L, Prabhakaran K, Borowitz JL, Isom GE (2006) Trimethyltin-induced apoptosis is associated with upregulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase and Bax in a hippocampal cell line. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 216:34–43
Viviani B, Corsini E, Pesenti M, Galli CL, Marinovich M (2001) Trimethyltin-activated cyclooxygenase stimulates tumor necrosis factor-alpha release from glial cells through reactive oxygen species. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 172:93–97
Shin EJ, Suh SK, Lim YK, Jhoo WK, Hjelle OP, Ottersen OP, Shin CY, Ko KH, Kim WK, Kim DS, Chun W, Ali S, Kim HC (2005) Ascorbate attenuates trimethyltin-induced oxidative burden and neuronal degeneration in the rat hippocampus by maintaining glutathione homeostasis. Neuroscience 133:715–727
Yoneyama M, Nishiyama N, Shuto M, Sugiyama C, Kawada K, Seko K, Nagashima R, Ogita K (2008) In vivo depletion of endogenous glutathione facilitates trimethyltin-induced neuronal damage in the dentate gyrus of mice by enhancing oxidative stress. Neurochem Int 52:761–769
Shuto M, Seko K, Kuramoto N, Sugiyama C, Kawada K, Yoneyama M, Nagashima R, Ogita K (2009) Activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase cascades is involved in part of the neuronal degeneration induced by trimethyltin in cortical neurons of mice. J Pharmacol Sci 109:60–70
Wood PL, Khan MA, Kulow SR, Mahmood SA, Moskal JR (2006) Neurotoxicity of reactive aldehydes: the concept of “aldehyde load” as demonstrated by neuroprotection with hydroxylamines. Brain Res 1095:190–199
Haddad El-B, McCluskie K, Birrell MA, Dabrowski D, Pecoraro M, Underwood S, Chen B, DeSanctis GT, Webber SE, Foster ML, Belvisi MG (2002) Differential effects of ebselen on neutrophil recruitment, chemokine, and inflammatory mediator expression in a rat model of lipopolysaccharide-induced pulmonary inflammation. J Immunol 169:974–982
Koizumi H, Fujisawa H, Suehiro E, Shirao S, Suzuki M (2011) Neuroprotective effects of ebselen following forebrain ischemia: involvement of glutamate and nitric oxide. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 51:337–343
Bloch ML, Hong LS (2005) Microglia and inflammation-mediated neurodegeneration: multiple triggers with a common mechanism. Prog Neurobiol 76:77–98
Bjorklund A, Lindvall O (2000) Cell replacement therapies for central nervous systems disorders. Nat Neurosci 3:537–544
Kim SU, de Vellis J (2009) Stem cell-based cell therapy in neurological diseases: a review. J Neurosci Res 87:2183–2200
Freeman JN III, Baisden RH, Woodruff ML (1995) Fetal Ammon’s horn transplants improve acquisition of a radial arm maze and a low-rate operant schedule in trimethyltin-treated rats. Cell Transplant 4:113–122
Woodruff ML, Baisden RH, Nonneman AJ (1991) Anatomical and behavioral sequelae of fetal brain transplants in rats with TMT-induced neurodegeneration. Neurotoxicology 12:427–444
Roy A, Agrawal AK, Husain R, Dubey MP, Seth PK (1999) Cholinergic and serotonergic alterations in the rat hippocampus following trimethyltin exposure and fetal neural transplantation. Neurosci Lett 259:173–176
Geloso MC, Giannetti S, Cenciarelli C, Budoni M, Casalbore P, Maira G, Michetti F (2007) Transplantation of foetal neural stem cells into the rat hippocampus during trimethyltin-induced neurodegeneration. Neurochem Res 1032:2054–2061
Yoneyama M, Seko K, Kawada K, Sugiyama C, Ogita K (2009) High susceptibility of cortical neural progenitor cells to trimethyltin toxicity: involvement of both caspases and calpain in cell death. Neurochem Int 55:257–264
Casalbore P, Barone I, Felsani A, D’Agnano I, Michetti F, Maira G, Cenciarelli C (2010) Neural stem cells modified to express BDNF antagonize trimethyltin-induced neurotoxicity through PI3 K/Akt and MAP kinase pathways. J Cell Physiol 224:710–721
Martino G, Pluchino S, Bonfanti L, Schwartz M (2011) Brain regeneration in physiology and pathology: the immune signature driving therapeutic plasticity of neural stem cells. Physiol Rev 91:1281–1304
McPherson CA, Aoyama M, Harry GJ (2011) Interleukin (IL)-1 and IL-6 regulation of neural progenitor cell proliferation with hippocampal injury: differential regulatory pathways in the subgranular zone (SGZ) of the adolescent and mature mouse brain. Brain Behav Immun 25:850–862
McPherson CA, Kraft AD, Harry GJ (2011) Injury-induced neurogenesis: consideration of resident microglia as supportive of neural progenitor cells. Neurotox Res 19:341–352
Ogita K, Nishiyama N, Sugiyama C, Higuchi K, Yoneyama M, Yoneda Y (2005) Regeneration of granule neurons after lesioning of hippocampal dentate gyrus: evaluation using adult mice treated with trimethyltin chloride as a model. J Neurosci Res 82:609–621
Yoneyama M, Kaxada K, Ogita K (2010) Enhanced neurogenesis in the olfactory bulb in adult mice after injury induced by acute treatment with trimethyltin. J Neurosci Res 88:1242–1251
Corvino V, Geloso MC, Cavallo V, Guadagni E, Passalacqua R, Florenzano F, Giannetti S, Molinari M, Michetti F (2005) Enhanced neurogenesis during trimethyltin-induced neurodegeneration in the hippocampus of the adult rat. Brain Res Bull 65:471–477
Gray WP (2008) Neuropeptide Y signalling on hippocampal stem cells in heath and disease. Mol Cell Endocrinol 288:52–62
Corvino V, Marchese E, Giannetti S, Lattanzi W, Bonvissuto D, Biamonte F, Mongiovì AM, Michetti F, Geloso MC (2012) The neuroprotective and neurogenic effects of neuropeptide Y administration in an animal model of hippocampal neurodegeneration and temporal lobe epilepsy induced by trimethyltin. J Neurochem 122:415–426
Coyle JT, Price DL, DeLong MR (1983) Alzheimer’s disease: a disorder of cortical cholinergic innervation. Science 219:1184–1190
Chesselet MF, Richter F (2011) Modelling of Parkinson’s disease in mice. Lancet Neurol 10:1108–1118
Ishikawa K, Kubo T, Shibanoki S, Matsumoto A, Hata H, Asai S (1997) Hippocampal degeneration inducing impairment of learning in rats: model of dementia? Behav Brain Res 83:39–44
Gunasekar P, Li L, Prabhakaran K, Eybl V, Borowitz JL, Isom GE (2001) Mechanisms of the apoptotic and necrotic actions of trimethyltin in cerebellar granule cells. Toxicol Sci 64:83–89
Naalsund LU, Allen CN, Fonnum F (1985) Changes in neurobiological parameters in the hippocampus after exposure to trimethyltin. Neurotoxicology 6:145–158
Patel M, Ardelt BK, Yim GK, Isom GE (1990) Interaction of trimethyltin with hippocampal glutamate. Neurotoxicology 11:601–608
Aschner M, Gannon M, Kimelberg HK (1992) Interactions of trimethyltin (TMT) with rat primary astrocyte cultures: altered uptake and efflux of rubidium, L-glutamate and D-aspartate. Brain Res 582:181–185
Patterson TA, Eppler B, Dawson R Jr (1996) Attenuation of trimethyltin-evoked glutamate (GLU) efflux from rat cortical and hippocampal slices. Neurotoxicol Teratol 18:697–702
Lipe GW, Ali SF, Newport GD, Scallet AC, Slikker W Jr (1991) Effect of trimethyltin on amino acid concentrations in different regions of the mouse brain. Pharmacol Toxicol 68:450–455
Bahr BA, Tiriveedhi S, Park GY, Lynch G (1995) Induction of calpain-mediated spectrin fragments by pathogenic treatments in long-term hippocampal slices. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 273:902–908
Munirathinam S, Rogers G, Bahr BA (2002) Positive modulation of alpha-amino-3 hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid-type glutamate receptors elicits neuroprotection after trimethyltin exposure in hippocampus. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 185:111–118
Arai AC, Kessler M (2007) Pharmacology of ampakine modulators: from AMPA receptors to synapses and behavior. Curr Drug Targets 8:583–602
Earley B, Burke M, Leonard BE, Gouret CJ, Junien JL (1990) A comparison of the psychopharmacological profiles of phencyclidine, ketamine and (+) SKF 10,047 in the trimethyltin rat model. Neuropharmacology 29:695–703
Earley B, Burke M, Leonard BE (1992) Behavioural, biochemical and histological effects of trimethyltin (TMT) induced brain damage in the rat. Neurochem Int 21:351–366
Nishimura T, Schwarzer C, Furtinger S, Imai H, Kato N, Sperk G (2001) Changes in the GABA-ergic system induced by trimethyltin application in the rat. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 97:1–6
Doctor SV, Costa LG, Kendall DA, Murphy SD (1982) Trimethyltin inhibits uptake of neurotransmitters into mouse forebrain synaptosomes. Toxicology 25:213–221
O’Connell A, Earley B, Leonard BE (1994) Effects of the GABA agonist THIP (gaboxadol) on trimethyltin induced behavioural neurotoxicity in the rat. Med Sci Res 22:201–202
Ishikura N, Tsunashima K, Watanabe KI, Nishimura T, Shirayama Y, Kato N (2001) Temporal change of hippocampal enkephalin and dynorphin mRNA following trimethyltin intoxication in rats: effect of anticonvulsant. Neurosci Lett 306:157–160
Zimmer L, Woolley D, Chang L (1985) Does phenobarbital protect against trimethyltin-induced neuropathology of limbic structures? Life Sci 36:851–858
Earley B, Biegon A, Leonard BE (1989) Quantitative autoradiographic analysis of muscarinic receptors and quantitative histochemistry of acetylcholinesterase in the rat brain after trimethyltin intoxication. Neurochem Int 15:475–483
O’Connell A, Earley B, Leonard BE (1994) Changes in muscarinic (M1 and M2 subtypes) and phencyclidine receptor density in the rat brain following trimethyltin intoxication. Neurochem Int 25:243–522
O’Connell A, Earley B, Leonard BE (1994) The neuroprotective effect of tacrine on trimethyltin induced memory and muscarinic receptor dysfunction in the rat. Neurochem Int 25:555–566
Earley B, Glennon M, Leonard BE, Junien JL (1995) Effects of JO 1784, a selective sigma ligand, on the autoradiographic localization of M1 and M2 muscarinic receptor subtypes in trimethyltin treated rats. Neurochem Int 26:559–570
O’Connell AW, Earley B, Leonard BE (1996) The sigma ligand JO 1784 prevents trimethyltin-induced behavioural and sigma-receptor dysfunction in the rat. Pharmacol Toxicol 78:296–302
van Waarde A, Ramakrishnan NK, Rybczynska AA, Elsinga PH, Ishiwata K, Nijholt IM, Luiten PG, Dierckx RA (2011) The cholinergic system, sigma-1 receptors and cognition. Behav Brain Res 221:543–554
Maurice T, Phan VL, Noda Y, Yamada K, Privat A, Nabeshima T (1999) The attenuation of learning impairments induced after exposure to CO or trimethyltin in mice by sigma (s) receptor ligands involves both s1 and s2 sites. Br J Pharmacol 127:335–342
Kim HC, Nabeshima T, Jhoo WK, Ko KH, Kim WK, Shin EJ, Cho M, Lee PH (2001) Anticonvulsant effects of new morphinan derivatives. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 11:1651–1654
Shin EJ, Nah SY, Kim WK, Ko KH, Jhoo WK, Lim YK, Cha JY, Chen CF, Kim HC (2005) The dextromethorphan analogue dimemorfan attenuates kainate-induced seizures via s1 receptor activation: comparison with the effects of dextromethorphan. Br J Pharmacol 144:908–918
Shin EJ, Nah SY, Chae JS, Bing G, Shin SW, Yen TP, Baek IH, Kim WK, Maurice T, Nabeshima T, Kim HC (2007) Dextromethorphan attenuates trimethyltin-induced neurotoxicity via sigma1 receptor activation in rats. Neurochem Int 50:791–799
DeHaven DL, Krigman MR, Mailman RB (1986) Temporal changes in dopaminergic and serotonergic function caused by administration of trimethyltin to adult rats. Neurobehav Toxicol Teratol 8:475–479
Andersson H, Luthman J, Lindqvist E, Olson L (1995) Time-course of trimethyltin effects on the monoaminergic systems of the rat brain. Neurotoxicology 16:201–210
Swartzwelder HS, Holahan W, Myers RD (1983) Antagonism by d-amphetamine of trimethyltin-induced hyperactivity evidence toward an animal model of hyperkinetic behavior. Neuropharmacology 22:1049–1054
Tamburella A, Micale V, Mazzola C, Salomone S, Drago F (2012) The selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor atomoxetine counteracts behavioral impairments in trimethyltin-intoxicated rats. Eur J Pharmacol 683:148–154
Zheng XY, Zhang HL, Luo Q, Zhu J (2011) Kainic acid-induced neurodegenerative model: potentials and limitations. J Biomed Biotechnol 2011:457079
Curia G, Longo D, Biagini G, Jones RS, Avoli M (2008) The pilocarpine model of temporal lobe epilepsy. J Neurosci Methods 172:143–157
Nilsberth C, Kostyszyn B, Luthman J (2002) Changes in APP, PS1 and other factors related to Alzheimer’s disease pathophysiology after trimethyltin-induced brain lesion in the rat. Neurotox Res 4:625–636
O’Connell AW, Strada O, Earley B, Leonard BE (1997) Altered expression of amyloid protein precursor mRNA in the rat hippocampus following trimethyltin intoxication: an in situ hybridization study. Neurochem Int 30:313–320
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank Mr E. Guadagni for excellent technical support.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Corvino, V., Marchese, E., Michetti, F. et al. Neuroprotective Strategies in Hippocampal Neurodegeneration Induced by the Neurotoxicant Trimethyltin. Neurochem Res 38, 240–253 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-012-0932-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-012-0932-9