Abstract
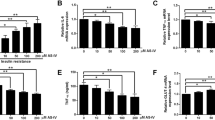
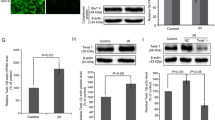
NYGGF4 (also called PID1) is a recently discovered gene that is involved in obesity-related insulin resistance (IR). We aimed in the present study to further elucidate the effects of NYGGF4 on IR and the underlying mechanisms through using metformin treatment in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Our data showed that the metformin pretreatment strikingly enhanced insulin-stimulated glucose uptake through increasing GLUT4 translocation to the PM in NYGGF4 overexpression adipocytes. NYGGF4 overexpression resulted in significant inhibition of tyrosine phosphorylation of IRS-1 and serine phosphorylation of Akt, whereas incubation with metformin strongly activated IRS-1 and Akt phosphorylation in NYGGF4 overexpression adipocytes. The reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels in NYGGF4 overexpression adipocytes were strikingly enhanced, which could be decreased by the metformin pretreatment. Our data also showed that metformin increased the expressions of PGC1-α, NRF-1, and TFAM, which were reduced in the NYGGF4 overexpression adipocytes. These results suggest that NYGGF4 plays a role in IR and its effects on IR could be reversed by metformin through activating IRS-1/PI3K/Akt and AMPK-PGC1-α pathways.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreyev AY et al (2005) Mitochondrial metabolism of reactive oxygen species. Biochemistry (Mosc) 70:200–214
Andreozzi F et al (2004) Angiotensin II impairs the insulin signaling pathway promoting production of nitric oxide by inducing phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate-1 on Ser312 and Ser616 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Circ Res 94:1211–1218
Bailey CJ, Turner RC (1996) Metformin. N Engl J Med 334:574–579
Bonnard C et al (2008) Mitochondrial dysfunction results from oxidative stress in the skeletal muscle of diet-induced insulin-resistant mice. J Clin Invest 118:789–800
Bryant NJ et al (2002) Regulated transport of the glucose transporter GLUT4. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3:267–277
Caratù G et al (2007) Identification of the ligands of protein interaction domains through a functional approach. Mol Cell Proteomics 6:333–345
Ceddia RB et al (2005) Globular adiponectin increases GLUT4 translocation and glucose uptake but reduces glycogen synthesis in rat skeletal muscle cells. Diabetoloqia 48:132–139
Ciaraldi TP et al (2002) Regulation of glucose transport and insulin signaling by troglitazone or metformin in adipose tissue of type 2 diabetic subjects. Diabetes 51:30–36
Cushman SW, Wardzala LJ (1980) Potential mechanism of insulin action on glucose transport in the isolated rat adipose cell. Apparent translocation of intracellular transport systems to the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem 255:4758–4762
Davidson MB, Peters AL (1997) An overview of metformin in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am J Med 102:99–110
de Jongh RT et al (2004) Free fatty acid levels modulate microvascular function: relevance for obesity-associated insulin resistance, hypertension, and microangiopathy. Diabetes 53:2873–2882
Ferrannini E et al (2007) Insulin resistance, insulin response, and obesity as indicators of metabolic risk. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92:2885–2892
Fridlyand LE, Philipson LH (2006) Reactive species and early manifestation of insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab 8:136–145
Guilherme A et al (2008) Adipocyte dysfunctions linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:367–377
Herz J, Strickland DK (2001) LRP: a multifunctional scavenger and signaling receptor. J Clin Invest 108:779–784
Hundal HS et al (1992) Cellular mechanism of metformin action involves glucose transporter translocation from an intracellular pool to the plasma membrane in L6 muscle cells. Endocrinology 131:1165–1173
Kahn CR (1978) Insulin resistance, insulin insensitivity, and insulin unresponsiveness: A necessary distinction. Metabolism 27:1893–1902
Kanzaki M (2006) Insulin receptor signals regulating GLUT4 translocation and actin dynamics. Endocr J 53:267–293
Kim JA et al (2008) Role of mitochondrial dysfunction in insulin resistance. Circ Res 102:401–414
Kim YB et al (2002) Troglitazone but not metformin restores insulinstimulated phosphoinositide 3-kinase activity and increases p110beta protein levels in skeletal muscle of type 2 diabetic subjects. Diabetes 51:443–448
Kirpichnikov D et al (2002) Metformin: An update. Ann Intern Med 137:25–33
Klip A, Ishiki M (2005) Recent developments in the regulation of glucose transporter-4 traffic: New signals, locations, and partners. Endocrinology 146:5071–5078
Kohn AD et al (1996) Expression of a constitutively active Akt Ser/Thr kinase in 3T3/L1 adipocytes stimulates glucose uptake and glucose transporter 4 translocation. J Biol Chem 271:31372–31378
Kremen J et al (2006) Increased subcutaneous and epicardial adipose tissue production of proinflammatory cytokines in cardiac surgery patients: Possible role in postoperative insulin resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91:4620–4627
Kukidome D et al (2006) Activation of AMP-Activated protein kinase reduces hyperglycemiainduced mitochondrial reactive oxygen species production and promotes mitochondrial biogenesis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Diabetes 55:120–127
Kumar N, Dey CS (2002) Metformin enhances insulin signalling in insulindependent and -independent pathways in insulin resistant muscle cells. Br J Pharmacol 137:329–336
Poyton RO, McEwen JE (1996) Crosstalk between nuclear and mitochondrial genomes. Annu Rev Biochem 65:563–607
Pryor PR et al (2000) Chronic insulin effects on insulin signaling and GLUT4 endocytosis are reversed by metformin. Biochem J 348:83–91
Qatanani M, Lazar MA (2007) Mechanisms of obesity-associated insulin resistance: Many choices on the menu. GenesDev 21:1443–1455
Reaven GM (1988) Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes 37:1595–1607
Sonntag B et al (2005) Metformin alters insulin signaling and viability of human granulosa cells. Fertil Steril 84:1173–1179
St-Pierre J et al (2003) Bioenergetic analysis of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivators 1alpha and 1beta (PGC-1alpha and PGC-1beta) in muscle cells. J Biol Chem 278:26597–26603
Sundaresan M et al (1995) Requirement for generation of H2O2 for platelet-derived growth factor signal transduction. Science 270:296–299
Suzuki K, Kono T (1980) Evidence that insulin causes translocation of glucose transport activity to the plasma membrane from an intracellular storage site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 77:2542–2545
Taniguchi CM et al (2006) Critical nodes in signalling pathways: Insights into insulin action. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7:85–96
Tilg H, Moschen AR (2006) Adipocytokines: mediators linking adipose tissue, inflammation and immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 6:772–783
Vallea I et al (2005) PGC-1alpha regulates the mitochondrial antioxidant defense system in vascular endothelial cells. Cardiovasc Res 66:562–573
Wang B et al (2006) Identification and characterization of NYGGF4, a novel gene containing a phosphotyrosine-binding (PTB) domain that stimulates 3T3-L1 preadipocytes proliferation. Gene 379:132–140
Wu WL et al (2011) Over-expression of NYGGF4 (PID1) inhibits glucose transport in skeletal myotubes by blocking the IRS1/PI3K/AKT insulin pathway. Mol Genet Metab 102:374–377
Wu Z et al (1999) Mechanisms controlling mitochondrial biogenesis and respiration through the thermogenic coactivator PGC-1. Cell 98:115–124
Yuan L et al (2003) Metformin modulates insulin post-receptor signaling transduction in chronically insulin-treated Hep G2 cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin 24:55–60
Zhang CM et al (2009) Over-expression of NYGGF4 inhibits glucose transport in 3T3-L1 adipocytes via attenuated phosphorylation of IRS-1 and Akt. Acta Pharmacol Sin 30:120–124
Zhang CM et al (2010) Effects of NYGGF4 knockdown on insulin sensitivity and mitochondrial function in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Bioenerg Biomembr 42:433–439
Zhao Y et al (2010) Overexpression of NYGGF4 (PID1) induces mitochondrial impairment in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Mol Cell Biochem 340:41–48
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Jie Qiu and Yu-mei Wang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qiu, J., Wang, Ym., Shi, Cm. et al. NYGGF4 (PID1) effects on insulin resistance are reversed by metformin in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Bioenerg Biomembr 44, 665–671 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-012-9472-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-012-9472-x