Abstract
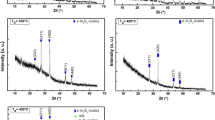
Isochronal annealing of amorphous Zn and Sn codoped In2O3 (a-ZITO) films was performed at the Synchrotron so that to extract, in situ, important kinetic nucleation and growth parameters from a single constant-rate heating experiment. First, amorphous Zn and Sn codoped In2O3 films were deposited via pulsed laser deposition and subjected to post-deposition annealing treatments to study their stability against crystallization. Crystallization on glass and ĉ-sapphire occurred near the same temperature, however higher codoping levels resulted in increased crystallization temperatures. Post-deposition anneal crystallization temperatures were found to be higher than the substrate temperatures required to grow crystalline films during deposition. Then, a-ZITO films were subjected to a constant temperature ramp during in situ grazing-incidence X-ray diffraction experiments. Crystallization of films on both glass and ĉ-sapphire showed similar gradual crystallization behavior between 300 and 345 °C and strong (111) texturing, which suggests the influence of surface energy minimization during crystallization. The activation energy was found to be 2.87 eV using Johnson-Mehl-Avrami analysis. This work presents the advantages of in situ experiments to study nucleation and growth during crystallization of transparent conducting oxides.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Fortunato, D. Ginley, H. Hosono, and D. C. Paine, “Transparent conducting oxides for photovoltaics,” MRS Bull., 32 [3] 242–247 (2007).
J.F. Wager, D.A. Keszler, R.E. Presley, Transparent electronics (Springer, New York, 2008)
D.S. Ginley, H. Hosono, D.C. Paine, Handbook of transparent conductors (Springer, New York, 2010)
T. Kamiya, H. Hosono, Material characteristics and applications of transparent amorphous oxide semiconductors. NPG Asia Mater. 2, 15–22 (2010)
J. Liu, D.B. Buchholz, R.P.H. Chang, A. Facchetti, T.J. Marks, High-performance flexible transparent thin-film transistors using a hybrid gate dielectric and amorphous zinc indium tin oxide channel. Adv. Mater. 22(21), 2333–2337 (2010)
M.P. Taylor, D.W. Readey, M.F.A.M. Van-Hest, C.W. Teplin, J.L. Alleman, M.S. Dabney, L.M. Gedvilas, B.M. Keyes, B. To, J.D. Perkins, D.S. Ginley, The remarkable thermal stability of amorphous In-Zn-O transparent conductors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 18(20), 3169–3178 (2008)
J.A. Jeong, H.K. Kim, S.I. Na, Low resistance and high transparent amorphous IZTO electrode cosputtered by linear facing target sputtering for organic photovoltaics. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 12(9), J80–J82 (2009)
G.S. Heo, Y. Matsumoto, I.G. Gim, J.W. Park, K.Y. Kim, T.W. Kim, Fabrication of cosputtered Zn-In-Sn-O films and their applications to organic light-emitting diodes. Solid State Comm 149(41–42), 1731–1734 (2009)
G.S. Heo, Y. Matsumoto, I.G. Gim, H.K. Lee, J.W. Park, T.W. Kim, Transparent conducting amorphous Zn-In-Sn-O anode for flexible organic light-emitting diodes. Solid State Comm 150(3–4), 223–225 (2010)
C.A. Hoel, T.O. Mason, J.F. Gaillard, K.R. Poeppelmeier, Transparent conducting oxides in the ZnO-In2O3-SnO2 System. Chem. Mater. 22(12), 3569–3679 (2010)
D.S. Ginley, C. Bright, Transparent conducting oxides. MRS Bull. 25(8), 15–18 (2000)
G.B. Palmer, K.R. Poeppelmeier, T.O. Mason, Conductivity and transparency of ZnO/SnO2-cosubstituted In2O3. Chem. Mater. 9(12), 3121–3126 (1997)
S.P. Harvey, T.O. Mason, D.B. Buchholz, R.P.H. Chang, C. Körber, A. Klein, Carrier generation and inherent Off-stoichiometry in Zn,Sn Co-doped indium oxide (ZITO) bulk and thin film specimens. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 91(2), 467–472 (2008)
D.B. Buchholz, J. Liu, T.J. Marks, M. Zhang, R.P.H. Chang, Control and characterization of the structural, electrical, and optical properties of amorphous zinc-indium-tin oxide thin films. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf 1(10), 2147–2153 (2009)
D.S. Liu, C.S. Sheu, C.T. Lee, C.H. Lin, Thermal stability of indium tin oxide thin films co-sputtered with zinc oxide. Thin Solid Films 516(10), 3196–3203 (2008)
K.J. Chen, F.Y. Hung, S.J. Chang, S.P. Chang, Y.C. Mai, Z.S. Hu, A study on crystallization, optical and electrical properties of the advanced ZITO thin films using co-sputtering system. J. Alloys Compd. 509(8), 3667–3671 (2011)
A. Rogozin, M. Vinnichenko, N. Shevchenko, U. Kreissig, A. Kolitsch, W. Moller, Real-time evolution of electrical properties and structure of indium oxide and indium tin oxide during crystallization. Scr. Mater. 60(4), 199–202 (2009)
A. Rogozin, N. Shevchenko, M. Vinnichenko, F. Prokert, V. Cantelli, A. Kolitsch, W. Moller, Real-time evolution of the indium tin oxide film properties and structure during annealing in vacuum. Appl. Phys. Lett. 85(2), 212–214 (2004)
F.O. Adurodija, L. Semple, R. Brüning, Real-time in situ crystallization and electrical properties of pulsed laser deposited indium oxide thin films. Thin Solid Films 492, 153–157 (2005)
F.O. Adurodija, L. Semple, R. Brüning, Crystallization process and electro-optical properties of In2O3 and ITO thin films. J. Mater. Sci. 41(21), 7096–7102 (2006)
M. Avrami, Kinetics of phase change. II transformation-time relations for random distribution of nuclei. J. Chem. Phys. 8, 212–224 (1940)
D.C. Paine, T. Whitson, D. Janiac, R. Berseford, C.O. Wang, B. Lewis, A study of Low temperature crystallization of amorphous thin film indium Tin oxide. J. Appl. Phys. 85, 8445–8450 (1999)
H. Wulff, M. Quaas, H. Steffen, R. Hippler, In situ studies of diffusion and crystal growth in plasma deposited thin ITO films. Thin Solid Films 377, 418–424 (2000)
M. Quaas, H. Steffen, R. Hippler, H. Wulff, Investigation of diffusion and crystallization processes in thin ITO films by temperature and time resolved grazing incidence X-ray diffractometry. Surf. Sci. 540(2–3), 337–342 (2003)
C.W. Ow-Yang, D. Spinner, Y. Shigesato, D.C. Paine, A time-resolved reflectivity study of the amorphous-to-crystalline transformation kinetics in dc-magnetron sputtered indium tin oxide. J. Appl. Phys. 83(1), 145–154 (1998)
G.S. Heo, I.G. Gim, J.W. Park, K.Y. Kim, T.W. Kim, Effects of substrate temperature on properties of ITO-ZnO composition spread films fabricated by combinatorial RF magnetron sputtering. J. Solid State Chem. 182(10), 2937–2940 (2009)
D.B. Buchholz, D.E. Proffit, M.D. Wisser, T.O. Mason, R.P.H. Chang, Electrical and band-gap properties of amorphous zinc–indium–tin oxide thin films. Prog. Nat. Sci: Mater Int 22(1), 1–6 (2012)
E. Cetinorgu, S. Goldsmith, Z. Barkay, R.L. Boxman, The dependence of filtered vacuum arc deposited ZnO-SnO2 thin films characteristics on substrate temperature. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 39(24), 5245–5251 (2006)
E. Cetinorgu, S. Goldsmith, R.L. Boxman, The effect of post-deposition annealing on the optical properties of filtered vacuum arc deposited ZnO-SnO2. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 19(25), 256206 (2007)
D.E. Proffit, D.B. Buchholz, R.P.H. Chang, M.J. Bedzyk, T.O. Mason, Q. Ma, X-ray absorption spectroscopy study of the local structures of crystalline Zn-In-Sn oxide thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 106(11), 113524–113526 (2009)
D.E. Proffit, Q. Ma, D.B. Buchholz, R.P.H. Chang, M.J. Bedzyk, T.O. Mason, Structural and physical property studies of amorphous Zn-in-Sn-O thin films. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 95(11), 3657–3664 (2012)
D. Bruce Buchholz, Z. Li, M.J. Bedzyk, R.P.H. Chang, Differences between amorphous indium oxide thin films. Prog in Nat Sci: Mater Int (2013). doi:10.1016/jpnsc.2013.08.004
M. Zhang, D.B. Buchholz, S.J. Xie, R.P.H. Chang, Twinned domains in epitaxial ZnO/SnO2-cosubstituted In2O3 thin films. J. Cryst. Growth 308, 376–381 (2007)
J. Ilavsky, Nika – software for 2D data reduction. J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 324–328 (2012)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the MRSEC program of the National Science Foundation (DMR-1121262). A portion of the work done by DBB and RPHC was also supported by the U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Science, Office of Basic Energy Sciences under Award Number DE-FG02-06ER46320. Portions of this work were performed at the DuPont-Northwestern-Dow Collaborative Access Team (DND-CAT) located at Sector 5 of the Advanced Photon Source (APS). DND-CAT is supported by E.I. DuPont de Nemours & Co., The Dow Chemical Company and Northwestern University. Use of the APS, an Office of Science User Facility operated for the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science by Argonne National Laboratory, was supported by the U.S. DOE under Contract No. DE-AC02-06CH11357. This work made use of the J.B.Cohen X-Ray Diffraction Facility supported by the MRSEC program of the National Science Foundation (DMR-1121262) at the Materials Research Center of Northwestern University. DEP acknowledges support of an NSF Graduate Research Fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Proffit, D.E., Philippe, T., Emery, J.D. et al. Thermal stability of amorphous Zn-In-Sn-O films. J Electroceram 34, 167–174 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-014-9967-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-014-9967-4