Abstract
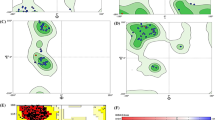
We report the results of a comparative molecular field analysis and comparative molecular similarity index analysis of the human farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase (FPPS) inhibition by nitrogen bisphosphonates (NBPs) taking into account their time-dependent inhibition efficacies. The 3D-QSAR models obtained provide steric, electrostatic and hydrophobic contour maps consistent with the interactions into the active site of human FPPS observed in available crystallographic structures. Furthermore, the 3D-QSAR models obtained provide accurately IC50 values of the NBPs of the training set. The predictive ability of these 3D-QSAR models was found to rely on the choice of biologically active conformations of the target molecules and on a careful examination of the protonation status of the NBPs in the training set. The best models obtained can be useful to predict biological values of a high number of NBPs that have been used for the treatment of different diseases as potential inhibitors of the activity of the FPPS enzyme.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fleisch H (1993) Editorial: prospective use of bisphosphonates in osteoporosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 76:1397–1398
Rodan GA (1998) Mechanisms of action of bisphosphonates. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 38:375–388
Martin MB, Arnold W, Heath HT III, Urbina JA, Oldfield E (1999) Nitrogen-containing bisphosphonates as carbocation transition state analogs for isoprenoid biosynthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 263:754–758
Coleman RE (2005) Bisphosphonates in breast cancer. Ann Oncol 16:687–695
Sicard H, Al Saati T, Delsol G, Fournié JJ (2001) Synthetic phosphoantigens enhance human Vγ9 Vδ2T lymphocytes killing of non-Hodgkin’s B lymphoma. Mol Med 7:711–722
Wilhelm M, Kunzmann V, Eckstein S, Reimer P, Weissinger F, Ruediger T, Tony HP (2003) γδT cells for immune therapy of patients with lymphoid malignancies. Blood 102:200–206
Stresing V, Daubiné F, Benzaid I, Mönkkönen H, Clézardin P (2007) Bisphosphonates in cancer therapy. Cancer Lett 257:16–35
Martin MB, Sanders JM, Kendrick H, Luca-Fradley K, Lewis JC, Grimley JS, Van Brussel EM, Olsen JR, Meints GA, Burzynska A, Kafarski P, Croft SL, Oldfield E (2002) Activity of bisphosphonates against trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense. J Med Chem 45:2904–2914
Dąbrowska E, Burzyńska A, Mucha A, Matczak-Jon E, Sawka-Dobrowolska W, Berlicki L, Kafarski P (2009) Insight into the mechanism of three component condensation leading to aminomethylenebisphosphonates. J Org Chem 694:3806–3813
Baojie Li B, Chau JFL, Wang X, Leong WF (2011) Bisphosphonates, specific inhibitors of osteoclast function and a class of drugs for osteoporosis therapy. J Cell Biochem 112:1229–1242
Dunford JE, Kwaasi AA, Rogers MJ, Barnett BL, Ebetino FH, Russell RGG, Oppermann U, Kavanagh KL (2008) Structure-activity relationships among the nitrogen containing bisphosphonates in clinical use and other analogues: time-dependent inhibition of human farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase. J Med Chem 51:2187–2195
Zhang FL, Casey PJ (1996) Protein prenylation: molecular mechanisms and functional consequences. Annu Rev Biochem 65:241–269
Sinensky M (2000) Recent advances in the study of prenylated proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta 1484:93–106
Shipman CM, Rogers MJ, Apperley JF, Russell RG, Croucher PI (1997) Bisphosphonates induce apoptosis in human myeloma cell lines; a novel anti-tumour activity. Br J Haematol 98:665–672
Russell RG, Xia Z, Dunford JE, Oppermann U, Kwaasi A, Hulley PA, Davanagh KL, Triffitt JT, Lundy MW, Phipps RJ, Barnett BL, Coxon FP, Rogers MJ, Watts NB, Ebetino FH (2007) Bisphosphonates: an update on mechanisms of action and how these relate to clinical efficacy. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1117:209–257
Zhang Y, Cao R, Yin F, Hudock MP, Guo R-T, Krysiak K, Mukherjee S, Gao Y-G, Robinson J, Song Y, No JH, Bergan K, Leon A, Cass L, Goddard A, Chang T-K, Lin F-Y, Van Beek E, Papapoulos S, Wang AH-J, Kubo T, Ochi M, Mukkamala D, Oldfield E (2009) Lipophilic bisphosphonates as dual farnesyl/geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase inhibitors: an X-ray and NMR investigation. J Am Chem Soc 131:5153–5162
Frith JC, Mönkkönen J, Blackburn M, Russell RGG, Rogers MJ (1997) Clodronate and liposome-encapsulated clodronate are metabolized to a toxic ATP analog, adenosine 5`-(β, γ-dichloromethylene) triphosphate, by mammalian Cells in vitro. J Bone Miner Res 12:1358–1367
Tarshis LC, Yan M, Poulter CD, Sacchettini JC (1994) Crystal structure of recombinant farnesyl diphosphate synthase at 2.6-Å resolution. Biochemistry 33:10871–10877
Tarshis LC, Proteau P, Poulter CD, Sacchettini JC (1996) Regulation of product chain length by isoprenyl diphosphate synthases. Proc Natl Acad Sci 93:15018–15023
Gabelli SB, McLellan JS, Montalvetti A, Oldfield E, Docampo R, Amzel LM (2005) Structure and mechanism of the farnesyl diphosphate synthase from Trypanosoma cruzi: implications for drug design. Proteins 62:80–88
Kavanagh KL, Guo K, Dunford JE, Wu X, Knapp S, Ebetino FH, Rogers MJ, Russell RG, Oppermann U (2006) The molecular mechanism of nitrogen-containing bisphosphonates as antiosteoporosis drugs. Proc Natl Acad Sci 103:7829–7834
Rondeau JM, Bitsch F, Bourgier E, Geiser M, Hemming R, Kroemer M, Lehmann S, Ramage P, Rieffel S, Strauss A, Green JR, Jahnke W (2006) Structural basis for the exceptional in vivo efficacy of bisphosphonate drugs. ChemMedChem 1:267–273
Lin YS, Park J, De Schutter JW, Huang XF, Berghuis AM, Sebag M, Tsantrizos YS (2012) Design and synthesis of active site inhibitors of the human farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase: apoptosis and inhibition of ERK phosphorylation in multiple myeloma cells. J Med Chem 55:3201–3215
Szabo CM, Martin MB, Oldfield E (2002) An investigation of bone resorption and Dictyostelium discoideum growth inhibition by bisphosphonate drugs. J Med Chem 45:2894–2903
Sanders JM, Gómez AO, Mao J, Meints GA, Van Brussel EM, Burzynska A, Kafarski P, González-Pacanoska D, Oldfiel E (2003) 3D-QSAR investigation of the inhibition of leishmania major farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase by bisphosphonates. J Med Chem 46:5171–5183
Whitaker M, Guo J, Kehoe T, Benson G (2012) Perspective: bisphosphonates for osteoporosis - where do we go from here? N Engl J Med 366:2048–2051
Hess LM, Jeter JM, Benham-Hutchins M, Alberts DS (2008) Factors associated with osteonecrosis of the jaw among bisphophonates users. Am J Med 121:475–483
Bauss F, Pfister T, Papapoulos S (2008) Ibandronate uptake in the jaw is similar to long bones and vertebrae in the rat. J Bone Miner Metab 26:406–408
Ruggiero SL, Mehrotra B (2009) Bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: diagnosis, prevention, and management. Annu Rev Med 60:85–96
Park-Wyllie LP, Mamdani MM, Juurlink DN, Hawker GA, Gunraj N, Austin PC, Whelan DB, Weiler JP, Laupacis A (2011) Bisphosphonate use and the risk of subtrochanteric or femoral shaft fractures in older women. JAMA 305:783–789
Cramer RD III, Patterson DE, Bunce JD (1988) Comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA). 1. Effect of shape on binding of steroids to carrier proteins. J Am Chem Soc 110:5959–5967
Klebe G, Abraham U, Mietzner T (1994) Molecular similarity indices in a comparative analysis (CoMSIA) of drug molecules to correlate and predict their biological activity. J Med Chem 37:4130–4146
Kotsikorou E, Oldfield E (2003) A quantitative structure-activity relationship and pharmacophore modelling investigation of aryl-X and heterocyclic bisphosphonate as bone resorption agents. J Med Chem 46:2932–2944
Clark M, Cramer RD III, Van Opdenbosch N (1989) Validation of the general purpose Tripos 5.2 force field. J Comp Chem 10:982–1012
SYBYL 8.0 Tripos Inc., 1699 South Hanley Rd. St. Louis, Missouri, 63144-2917
NBO Version 3.1, Glendening ED, Reed AE, Carpenter JE, Weinhold F
Reed AE, Weinstock RB, Weinhold F (1985) Natural-population analysis. J Chem Phys 83:735–746
Reed AE, Curtiss LA, Weinhold F (1988) Intermolecular interactions from a natural bond orbital, donor-acceptor viewpoint. Chem Rev 88:899–926
Gaussian 09, Revision B.1, Frisch MJ, Trucks GW, Schlegel HB, Scuseria GE, Robb MA, Cheeseman JR, Scalmani G, Barone V, Mennucci B, Petersson GA, Nakatsuji H, Caricato M, Li X, Hratchian HP, Izmaylov AF, Bloino J, Zheng G, Sonnenberg JL, Hada M, Ehara M, Toyota K, Fukuda R, Hasegawa J, Ishida M, Nakajima T, Honda Y, Kitao O, Nakai H, Vreven T, Montgomery Jr. JA, Peralta JE, Ogliaro F, Bearpark M, Heyd JJ, Brothers E, Kudin KN, Staroverov VN, Kobayashi R, Normand J, Raghavachari K, Rendell A, Burant J. C, Iyengar SS, Tomasi J, Cossi M, Rega N, Millam JM, Klene M, Knox JE, Cross JB, Bakken V, Adamo C, Jaramillo J, Gomperts R, Stratmann RE, Yazyev O, Austin AJ, Cammi R, Pomelli C, Ochterski JW, Martin RL, Morokuma K, Zakrzewski VG, Voth GA, Salvador P, Dannenberg JJ, Dapprich S, Daniels AD, Farkas Ö, Foresman JB, Ortiz JV, Cioslowski J, Fox DJ. Gaussian, Inc., Wallingford CT, 2009
Weinhold FA (1997) Nature of H-bonding in clusters, liquids, and enzymes: an ab initio, natural bond orbital perspective. J Mol Struct (Theochem) 398:181–197
Kubinyi H (1998) Comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA). In: Schleyer PvR, Allinger NL, Clark T, Gasteiger J, Kollman PA, Schaefer III HF, Schreiner PR (eds) The encyclopedia of computational chemistry, vol 1. Wiley, Chichester, p 448–460
Viswanadhan VN, Ghose AK, Revankar GR, Robins RK (1989) Atomic physicochemical parameters for three dimensional structure directed quantitative structure-activity relationships. 4. Additional parameters for hydrophobic and dispersive interactions and their application for an automated superposition of certain naturally occurring nucleoside antibiotics. J Chem Inf Comput Sci 29:163–172
Geladi P, Kowalski B (1986) Partial least-squares regression: a tutorial. Anal Chim Acta 185:1–17
Hasegawa K, Funatsu K (2000) Partial least squares modelling and genetic algorithm optimization in quantitative structure-activity relationships. SAR QSAR Environ Res 11:189–209
Wold S (1978) Cross-validatory estimation of the number of components in factor and principal components models. Technometrics 20:397–406
MarvinSketch 5.7, Calculator Plugin and Chemical Terms Demo Copyright © 1999–2012 ChemAxon Ltd
SPARC Performs Automated Reasoning in Chemistry. Sparc v4.6
Haynes WM (2012) CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics 93th edn. Taylor & Francis Group
Walba H, Isensee RW (1961) Acidity constants of some arylimidazoles and their cations. J Org Chem 26:289–2791
Golbraikh A, Tropsha A (2002) Beware of q2! J Mol Graph Model 20:267–276
Gasteiger J, Marsili M (1980) Iterative partial equalization of orbital electronegativity: a rapid access to atomic charges. Tetrahedron 36:3219–3228
Marsili M, Gasteiger J (1980) π Charge distribution from molecular topology and π orbital electronegativity. Croat Chem Acta 53:601–614
Montgomery JA Jr, Frisch MJ, Ochterski JW, Petersson GA (1999) A complete basis set model chemistry. VI. Use of density functional geometries and frequencies. J Chem Phys 110:2822–2827
Montgomery JA Jr, Frisch MJ, Ochterski JW, Petersson GA (2000) A complete basis set model chemistry. VII. Use of the minimum population localization method. J Chem Phys 112:6532–6542
Singh UC, Kollman PA (1984) An approach to computing electrostatic charges for molecules. J Comp Chem 5:129–145
Besler BH, Merz KM Jr, Kollman PA (1990) Atomic charges derived from semiempirical methods. J Comp Chem 11:431–439
Breneman CM, Wiberg KB (1990) Determining atom-centered monopoles from molecular electrostatic potentials. The need for high sampling density in formamide conformational analysis. J Comp Chem 11:361–373
Ohno K, Mori K, Orita M, Takeuchi M (2011) Computational insights into binding of bisphosphates to farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase. Curr Med Chem 18:220–233
Sanz-Rodríguez CE, Concepción JL, Pekerar S, Oldfield E, Urbina JA (2007) Bisphosphonates as inhibitors of trypanosoma cruzi hexokinase: kinetic and metabolic studies. J Biol Chem 282:12377–12387
Feng-Lei W, Rong-Xin Y, Ji-Min X (2011) 4-[2-(Hydrogen phosphonate)-2-hydroxy-2-phosphonoethyl]pyridinium. Acta Cryst. E 67:o1025
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fernández, D., Ortega-Castro, J. & Frau, J. Human farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase inhibition by nitrogen bisphosphonates: a 3D-QSAR study. J Comput Aided Mol Des 27, 739–754 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10822-013-9674-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10822-013-9674-2