Abstract
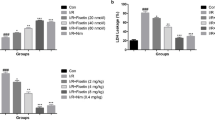
We previously found that xanthotoxol, one of the major active ingredients in Cnidium monnieri (L.) Cusson, exerts protective effects in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by alleviating brain edema, inhibiting the neutrophil infiltration, and decreasing the expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) and E-selectin. The present study was designed to further determine the possible mechanisms of action of neuroprotective properties of xanthotoxol after cerebral ischemia. Transient focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion model in male Sprague–Dawley rats was induced by 2-h middle cerebral artery occlusion followed by 24-h reperfusion. Xanthotoxol (5 and 10 mg/kg) or vehicle were administered intraperitoneally at 1 and 12 h after the onset of ischemia. At 24 h after reperfusion, we assessed the effect of xanthotoxol on the blood–brain barrier (BBB) permeability, the production of pro-inflammatory mediators such as interleukin (IL)-1β, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, IL-8, nitric oxide (NO), inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), and the p65 subunit of the transcription factor, nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) in the cortex after ischemic insult. The results showed that xanthotoxol treatment significantly attenuated BBB disruption, reduced the IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-8 and NO level, and attenuated the iNOS activity compared with vehicle-treated animals. Further, xanthotoxol treatment also significantly prevented the ischemia/reperfusion-induced increase in the protein expression of iNOS, COX-2, and the nuclear NF-κB p65. These results, taken together with those of our previous study, suggest that the neuroprotection may be attributed to the ability of xanthotoxol to attenuate the expression of pro-inflammatory mediators and thereby inhibit the inflammatory response after cerebral ischemia.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amantea D, Nappi G, Bernardi G, Bagetta G, Corasaniti MT (2009) Post-ischemic brain damage: pathophysiology and role of inflammatory mediators. FEBS J 276(1):13–26
Candelario-Jalil E, González-Falcón A, García-Cabrera M, León OS, Fiebich BL (2007) Post-ischaemic treatment with the cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor nimesulide reduces blood-brain barrier disruption and leukocyte infiltration following transient focal cerebral ischaemia in rats. J Neurochem 100(4):1108–1120
Collino M, Aragno M, Mastrocola R, Gallicchio M, Rosa AC, Dianzani C, Danni O, Thiemermann C, Fantozzi R (2006) Modulation of the oxidative stress and inflammatory response by PPAR-gamma agonists in the hippocampus of rats exposed to cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. Eur J Pharmacol 530(1–2):70–80
Danielisova V, Burda J, Nemethova M, Gottlieb M (2011) Aminoguanidine administration ameliorates hippocampal damage after middle cerebral artery occlusion in rat. Neurochem Res 36(3):476–486
del Zoppo G, Ginis I, Hallenbeck JM, Iadecola C, Wang X, Feuerstein GZ (2000) Inflammation and stroke: putative role for cytokines, adhesion molecules and iNOS in brain response to ischemia. Brain Pathol 10(1):95–112
He W, Chen WW, Ye HY, Zhou YM, Huang XH (2009) Inhibitory effects of xanthotoxol on neutrophil infiltration and brain edema induced by focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Chin Pharmacol Bull 25(5):668–672
Huang J, Upadhyay UM, Tamargo RJ (2006) Inflammation in stroke and focal cerebral ischemia. Surg Neurol 66(3):232–245
Jin R, Yang G, Li G (2010) Inflammatory mechanisms in ischemic stroke: role of inflammatory cells. J Leukoc Biol 87(5):779–789
Khan M, Sekhon B, Jatana M, Giri S, Gilg AG, Sekhon C, Singh I, Singh AK (2004) Administration of N-acetylcysteine after focal cerebral ischemia protects brain and reduces inflammation in a rat model of experimental stroke. J Neurosci Res 76(4):519–527
Kleinig TJ, Vink R (2009) Suppression of inflammation in ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke: therapeutic options. Curr Opin Neurol 22(3):294–301
Lian QS, Zhang ZZ, Shangguan Z, Zhou L, Pi RB, Xiang RD, Han Y, Zhang XY (1996) Studies on the anti-arrhythmic effect of xanthotoxol in experimental animals. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs 27(6):347–349
Lian QS, Zhang ZZ, Hu X, Zhou L, Ye HY, He W, Zhu ZP (1998) Studies on the anti-inflammatory effect of xanthotoxol in experimental animals. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs 29(2):102–104
Liu J, Lian Q, Zhou L, Zhou Q, He W, Zhu Z, Lai F (2005) Calcium antagonistic effect of xanthotoxol on isolated guinea pig atria. Zhong Yao Cai 28(4):319–321
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, Cummins R (1989) Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke 20(1):84–91
Ng TB, Liu F, Wang ZT (2000) Antioxidative activity of natural products from plants. Life Sci 66(8):709–723
Nogawa S, Zhang F, Ross ME, Iadecola C (1997) Cyclo-oxygenase-2 gene expression in neurons contributes to ischemic brain damage. J Neurosci 17(8):2746–2755
Nogawa S, Forster C, Zhang F, Nagayama M, Ross ME, Iadecola C (1998) Interaction between inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 after cerebral ischemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95(18):10966–10971
Rodríguez-Yáñez M, Castillo J (2008) Role of inflammatory markers in brain ischemia. Curr Opin Neurol 21(3):353–357
Salvemini D, Misko TP, Masferrer JL, Seibert K, Currie MG, Needleman P (1993) Nitric oxide activates cyclooxygenase enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90(15):7240–7244
Sethi OP, Anand KK, Gulati OD (1992) Evaluation of xanthotoxol for central nervous system activity. J Ethnopharmacol 36(3):239–247
Shangguan Z, Lian QS, Zeng J, Zhou Q, Pi RB, Liu JX, Yang JG (1997) Studies on the analgesic effect of xanthotoxol in experimental animals. Tradit Chin Drug Res Clin Pharmacol 8(1):45–46
Tas SW, Vervoordeldonk MJ, Tak PP (2009) Gene therapy targeting nuclear factor-kappaB: towards clinical application in inflammatory diseases and cancer. Curr Gene Ther 9(3):160–170
Toda N, Ayajiki K, Okamura T (2009) Cerebral blood flow regulation by nitric oxide: recent advances. Pharmacol Rev 61(1):62–97
Vane JR, Bakhle YS, Botting RM (1998) Cyclooxygenases 1 and 2. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 38:97–120
Villa P, Triulzi S, Cavalieri B, Di Bitondo R, Bertini R, Barbera S, Bigini P, Mennini T, Gelosa P, Tremoli E, Sironi L, Ghezzi P (2007) The interleukin-8 (IL-8/CXCL8) receptor inhibitor reparixin improves neurological deficits and reduces long-term inflammation in permanent and transient cerebral ischemia in rats. Mol Med 13(3–4):125–133
Wang Q, Tang XN, Yenari MA (2007) The inflammatory response in stroke. J Neuroimmunol 184(1–2):53–68
Xiang RD, Fu XH (1984) Studies on the chemical constituents of common cnidium(cnidium monnieri)(I). Chin Tradit Herb Drugs 15(9):14–15
Zeng J, Lian Q, Zhou Q, Zhou L, Ye H, Huang X (2003) Effect of xanthotoxol on contraction of rabbit thoracic aortic strips. Zhong Yao Cai 26(11):809–811
Zhang W, Potrovita I, Tarabin V, Herrmann O, Beer V, Weih F, Schneider A, Schwaninger M (2005) Neuronal activation of NF-kappaB contributes to cell death in cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 25(1):30–40
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Grants (to Wei He) from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC, 81060269) and from the Science and Technology Foundation of Educational Department of Jiangxi Province of China (GJJ08391).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, W., Chen, W., Zhou, Y. et al. Xanthotoxol Exerts Neuroprotective Effects Via Suppression of the Inflammatory Response in a Rat Model of Focal Cerebral Ischemia. Cell Mol Neurobiol 33, 715–722 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-013-9939-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-013-9939-2