Abstract
Objectives
To investigate the roles of fatty acid biosynthesis in carotenogenesis in the high-lipid accumulating aerial microalga Vischeria helvetica KGU-Y001, we cultured algal cells with fatty acid biosynthesis inhibitors.
Results
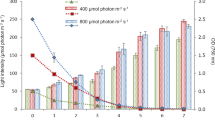
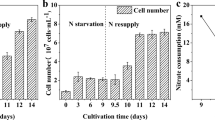
Under nitrogen-deficient, high-light (200 µmol photons m−2 s−1) conditions, the alga accumulated 6.2 mg carotenoids g−1 dry weight cells (DWC) after 1 week of culture. The total fatty acid content increased gradually, and reached 290 mg g−1 DWC after 9 weeks. When algal cells were cultured with a fatty acid biosynthesis inhibitor (molinate) under nitrogen-deficient, high-light conditions for 1 week, carotenoid accumulation was synergistically increased to 2.4 times that in algal cells cultured without the inhibitor in nitrogen-deficient, low-light conditions (40 µmol photons m−2 s−1). The synergistic induction of carotenogenesis was suppressed by an inhibitor of c-jun N-terminal kinase, a mitogen-activated protein kinase-like protein.
Conclusion
In a commercial context, carotenoid production could be increased by using fatty acid biosynthesis inhibitors to redirect metabolic flux to carotenoid biosynthesis instead of fatty acid synthesis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe K, Hattori H, Hirano M (2007) Accumulation and antioxidant activity of secondary carotenoids in the aerial microalga Coelastrella striolata var. multistriata. Food Chem 100:656–661
Aburai N, Ohkubo S, Miyashita H, Abe K (2013) Composition of carotenoids and identification of aerial microalgae isolated from the surface of rocks in mountainous districts of Japan. Algal Res 2:237–243
Augustin JM, Kusina V, Andersen SB, Bak S (2011) Molecular activities, biosynthesis and evolution of triterpenoid saponins. Phytochemistry 72:435–457
Bhosale P (2004) Environmental and cultural stimulants in the production of carotenoids from microorganisms. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 63:351–361
Casida JE (2009) Pest toxicology: the primary mechanisms of pesticide action. Chem Res Toxicol 22:609–619
Demmig-Adams B, Adams WW (2002) Antioxidants in photosynthesis and human nutrition. Science 298:2149–2153
Galhano V, Peixoto F, Gomes-Laranjo J, Fernández-Valiente E (2010) Comparative toxicity of bentazon and molinate on growth, photosynthetic pigments, photosynthesis, and respiration of the Portuguese ricefield cyanobacterium Nostoc muscorum. Environ Toxicol 25:147–156
García-Gómez C, Parages ML, Jiménez C, Palma A, Mata MT, Segovia M (2012) Cell survival after UV radiation stress in the unicellular chlorophyte Dunaliella tertiolecta is mediated by DNA repair and MAPK phosphorylation. J Exp Bot 63:5259–5274
Jiménez C, Berl T, Rivard CJ, Edelstein CL, Capasso JM (2004) Phosphorylation of MAP kinase-like proteins mediate the response of the halotolerant alga Dunaliella viridis to hypertonic shock. Biochim Biophys Acta 1644:61–69
Jiménez C, Cossío BR, Rivard CJ, Berl T, Capasso JM (2007) Cell division in the unicellular microalga Dunaliella viridis depends on phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs). J Exp Bot 58:1001–1011
Mendoza H, Martel A, Jiménez del Río M, García Reina G (1999) Oleic acid is the main fatty acid related with carotenogenesis in Dunaliella salina. J Appl Phycol 11:15–19
Moustafa K, AbuQamar S, Jarrar M, Al-Rajab AJ, Trémouillaux-Guiller J (2014) MAPK cascades and major abiotic stresses. Plant Cell Rep 33:1217–1225
Ōmura S (2011) Microbial metabolites: 45 years of wandering, wondering and discovering. Tetrahedron 67:6420–6459
Rabbani S, Beyer P, Lintig J, Hugueney P, Kleinig H (1998) Induced β-carotene synthesis driven by triacylglycerol deposition in the unicellular alga Dunaliella bardawil. Plant Physiol 116:1239–1248
Shaish A, Avron M, Pick U, Ben-Amotz A (1993) Are active oxygen species involved in induction of β-carotene in Dunaliella bardawil? Planta 190:363–368
Tran NP, Park JK, Kim Z, Lee CG (2009a) Influence of sodium Orthovanadate on the production of astaxanthin from green algae Haematococcus lacustris. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 14:322–329
Tran NP, Park JK, Lee CG (2009b) Proteomics analysis of proteins in green alga Haematococcus lacustris (Chlorophyceae) expressed under combined stress of nitrogen starvation and high irradiance. Enzyme Microb Technol 45:241–246
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Research Institute for Science and Technology of Kogakuin University for a special Grant-in-Aid to earn KAKENHI by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science. This study was supported in part by a grant from the Strategic Research Foundation Grant-aided Project for Private Universities from Ministry of Education, Culture, Sport, Science, and Technology, Japan (S1411005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aburai, N., Abe, K. Metabolic switching: synergistic induction of carotenogenesis in the aerial microalga, Vischeria helvetica, under environmental stress conditions by inhibitors of fatty acid biosynthesis. Biotechnol Lett 37, 1073–1080 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-015-1770-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-015-1770-z