Abstract
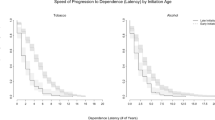
We examined early social influences across stages of smoking within the context of a twin study using an environmental exposure specific to smoking: whether twins started smoking at the same time (“simultaneous smoking initiation”: SSI). We expected that SSI would be a good index of shared social influences on smoking initiation. Rates of SSI were indeed significantly higher in MZ twins and in twins who shared peers and classes, as well as in male twins. With the exception of regular smoking in females, we found no significant difference in estimates of genetic and environmental parameters between SSI and non-SSI pairs for any of the smoking measures that we examined (DSM-IV and Fagerstrom HSI measures of nicotine dependence; DSM-IV nicotine withdrawal; heavy smoking; and in males, regular smoking). For regular smoking in females, allowing for additional shared environmental influences associated with SSI only modestly reduced our estimates of additive genetic variance (56% vs. 68%). These results indicate the important social influences that may occur for smoking initiation do not appear to seriously bias estimates of genetic effects on later stages of smoking.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association (1994). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (Fourth Edition). Washington, DC, American Psychiatric Association
Bucholz K. K., Cadoret R., Cloninger C. R., et al. (1994). A new semi-structured psychiatric interview for use in genetic linkage studies: A report of the reliability of the SSAGA. J. Studies Alcohol, 55:149–158
Center for Disease Control and Prevention (1998). Selected cigarettes smoking initiation and quitting behaviors among high school students—United States, 1997. Morb. Mortal. Wkly., 47 (19):386–389
Center for Disease Control and Prevention (2002). Annual smoking-attributable mortality, years of potential life lost, and economic costs- United States, 1995–1999. Morb. Mortal. Wkly., 51 (14):300–302
Center for Disease Control and Prevention (2004). Cigarette use among high school students- United States, 1991–2003. Morb. Mortal. Wkly., 53 (23):499–502
Center for Disease Control and Prevention (2005). Annual smoking-attributable mortality, years of potential life lost, and economic costs- United States, 1997–2001. Morb. Mortal. Wkly., 54 (25):625–628
Cleveland H. H., Wiebe R. P., Rowe D. C. (2005). Sources of exposure to smoking and drinking friends among adolescents: a behavioral-genetic evaluation. J. Genetic Psychol., 166(2):153–169
Cottler L. B., Robins L. N., Grant B. F., et al. (1991). The CIDI-core substance abuse and dependence questions: Cross-cultural and nosological issues. The WHO/ADAMHA field trial. Br. J. Psychiatry, 159:653–658
Eaves, L. J., Last, K. A., Young, P. A. Martin, N. G. (1978). Model-fitting approaches to the analysis of human behavior. Heredity 41: 249–320
Heath A. C., Cates R., Martin N. G., Meyer J., Hewitt J. K., Neale M. C., Eaves L. J. (1993). Genetic contribution to risk of smoking initiation: Comparison across birth cohorts and across cultures. J. Subst. Abuse 5: 221–246
Heath A. C., Howells W., Kirk K. M., Madden P. A. F., Bucholz K. K., Nelson E. C., Slutske W. S., Statham D. J., Martin N. G. (2001). Predictors of non-response to a questionnaire survey of a volunteer twin panel: findings from the Australian 1989 twin cohort. Twin Res. 4(2): 73–80
Heath A. C., Madden P. A. F. (1995). Genetic influences on smoking behaviors. In: Turner J.R., Cardon L.R., Hewitt J.K. (eds). Behavior Genetic Approaches in Behavioral Medicine. Plenum, New York, pp. 45–66
Heath A. H., Martin N. G., Lynskey M. T., Todorov A. A., Madden P. A. F. (2002). Estimating two-stage models for genetic influences on alcohol, tobacco or drug use initiation and dependence vulnerability in twin and family data. Twin Res. 5 (2): 113–124
Heatherton T. F., Kozlowski L. T., Frecker R. C., Fagerstrom K. O. (1991). The Fagerstrom Test for Nicotine Dependence: a revision of the Fagerstrom Tolerance Questionnaire. Br. J. Addict. 86(9):1119–1127
Heatherton T. F., Kozlowski L. T., Frecker R. C., Rickert W., Robinson J. (1989). Measuring the heaviness of smoking: using self-reported time to the first cigarette of the day and number of cigarettes smoked per day. Br. J. Addict. 84(7):791–799
Kendler K. S., Gardner C. O. Jr. (1998). Twin studies of adult psychiatric and substance dependence disorders: are they biased by differences in the environmental experiences of monozygotic and dizygotic twins in childhood and adolescence? Psychol. Med. 28(3): 625–633
Kendler K. S., Neale M. C., Sullivan P., Corey L. A., Gardner C. O., Prescott C. A. (1999). A population-based twin study in women of smoking initiation and nicotine dependence. Psychol. Med. 29: 299–308
Knopik V. S., Heath A. C., Madden P. A. F., Bucholz K. K., Slutske W. S., Nelson E. C., Statham D., Whitfield J. B., Martin N. G. (2004). Genetic effects on alcohol dependence risk: re-evaluating the importance of psychiatric and other heritable risk factors. Psychol. Med. 34(8): 1519–1530
Koopmans J. R., Slutske W. S., Heath A. C., Neale M. C., Boomsma D. I. (1999). The genetics of smoking initiation and quantity smoked in Dutch adolescent and young adult twins. Behav. Genet. 29(6): 383–393
Lessov C. N., Martin N. G., Statham D. J., Todorov A. A., Slutske W. S., Bucholz K. K., Heath A. C., Madden P. A. F. (2004). Defining nicotine dependence for genetic research: evidence from Australian twins. Psychol. Med. 34: 865–879
Li M. D., Cheng R., Ma J. Z., Swan G. E. (2003). A meta-analysis of estimated genetic and environmental effects on smoking behavior in male and female twins. Addiction 98: 23–31
Madden P. A. F., Heath A. C., Pedersen N. L., Kaprio J. K., Koskenvuo M. J., Martin N. G. (1999). The genetics of smoking persistence in men and women: a multicultural study. Behav. Genet. 29: 421–429
Madden P. A. F., Pedersen N. L., Kaprio J., Koskenvou M. J., Martin N. G. (2004). The epidemiology and genetics of smoking initiation and persistence: crosscultural comparisons of twin study results. Twin Res. 7 (1): 82–97
Maes H. H., Sullivan P. F., Bulik C. M., Neale M. C., Prescott C. A., Eaves L. J., Kendler K. S. (2004). A twin study of genetic and environmental influences on tobacco initiation, regular tobacco use and nicotine dependence. Psychol. Med. 34: 1251–1261
Merikangas K. R., Risch N. (2003). Genomic priorities and public health. Science 302: 599–601
Neale M. C., Boker S. M., Xie G., Maes H. H. (2002). MX: Statisical Modeling. Department of Psychiatry, Medical College of Virginia, Richmond, VA 6th Edition
Peto R., Darby S., Deo H., Silcocks P., Whitley E., Doll R. (2000). Smoking, smoking cessation, and lung cancer in the UK since 1950: combination of national statistics with two case–control studies. Br. Med. J. 321: 323–329
Pomerleau O. F., Collins A. C., Shiffman S., Pomerleau C. S. (1993). Why some people smoke and others do not: New perspectives. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 61: 723–732
SAS Institute Inc. (1999). SAS® Procedures Guide, Version 8. Cary, NC: SAS Institute Inc
Simons-Morton B. G. (2002). Prospective analysis of peer and parent influences on smoking initiation among early adolescents. Prev. Sci. 3 (4): 275–283
Slomkowski C., Rende R., Novak S., Lloyd-Richardson E., Niaura R. (2005). Sibling effects on smoking in adolescence: evidence for social influence from a genetically informative design. Addiction 100(4): 430–438
StataCorp (2003). Stata statistical software, Release 8.0. College Station, TX: Stata Corporation
Thomson C. C., Fisher L. B., Winickoff J. P., Colditz G. A., Camargo C. A., Jr., King C., III, Frazier A. L. (2004). State tobacco excise taxes and adolescent smoking behaviors in the United States. J. Public Health Manage. Practice 10 (6): 490–496
Vink J. M., Willemsen G., Boomsma D. I. (2003). The association of current smoking behavior with the smoking behavior of parents, siblings, friends and spouses. Addiction 98(7): 923–931
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful for Support from the following NIH Grants: AA07728, AA11998, and AA13321 (A.C.H.), DA12540 and DA12854 (P.A.F.M), DA019951 and AA07535 (M.L.P), and the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council. The authors are also thankful to the twins and their families for participation in this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pergadia, M.L., Heath, A.C., Agrawal, A. et al. The Implications of Simultaneous Smoking Initiation for Inferences about the Genetics of Smoking Behavior from Twin Data. Behav Genet 36, 567–576 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-005-9042-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-005-9042-7