Abstract
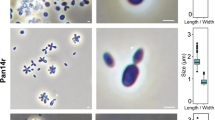
During attempts to obtain axenic the cultures of the marine dinoflagellate Prorocentrum micans, a microorganism with peculiar features was isolated. This contaminant resisted the physical and antibiotic treatments performed. Subsequent characterization showed that in agar plates this microorganism develops round granular pink colonies. It is a salt-dependent mesophilic and chemoheterotrophic Gram negative bacterium with a rod to ovoid shape, presenting cell motility in young cultures. Cell division occurs by cell budding. The bacterium forms aggregates with a variable number of cells that are stacked by fibrillar glycoproteic material, the holdfast. A tuft of numerous short glycoproteic fimbriae emerges from one pole of the cell. Preeminent granular inclusions, also of glycoproteic nature, are present in the cytoplasm. Several structural and compositional aspects of the cell envelope and cytoplasm are provided. The production of fibrillar material and the existence of the polar appendages suggest that this microorganism should occur in aquatic environments bound to substrates and could be associated with P. micans in natural marine habitats. Based on the characteristics displayed, this microorganism is a member of the Planctomycetes, order Planctomycetales.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barlaan EA, Furukawa S, Takeuchi K (2007) Detection of bacteria associated with harmful algal blooms from coastal and microcosm environments using electronic microarrays. Environ Microbiol 9(3):690–702
Bell W, Mitchell R (1972) Chemotactic and growth responses of marine bacteria to algal extracellular products. Biol Bull 143(2):265–277
Bengtsson MM, Sjotun K, Ovreås L (2010) Seasonal dynamics of bacterial biofilms on the kelp Laminaria hyperborea. Aquat Microb Ecol 60(1):71–83
Berland BR, Bonin DJ, Maestrini SY (1970) Study of bacteria associated with marine algae in culture III organic substrates supporting growth. Mar Biol 5(1):68–76
Biegala IC, Kennaway G, Alverca E, Lennon J, Vaulot D, Simon N (2002) Identification of bacteria associated with dinoflagellates (Dinophyceae) Alexandrium spp. using tyramide signal amplification–fluorescent in situ hybridization and confocal microscopy. J Phycol 38:404–411
Bockelmann U, Manz W, Neu TR, Szewzyk U (2000) Characterization of the microbial community of lotic organic aggregates (‘river snow’) in the Elbe River of Germany by cultivation and molecular methods. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 33(2):157–170
Brümmer IH, Felske AD, Wagner-Dobler I (2004) Diversity and seasonal changes of uncultured Planctomycetales in river biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol 70(9):5094–5101
Burke C, Thomas T, Lewis M, Steinberg P, Kjelleberg S (2011) Composition, uniqueness and variability of the epiphytic bacterial community of the green alga Ulva australis. ISME J 5(4):590–600
Chipman L, Podgorski D, Green S, Kostka J, Cooper W, Huettel M (2010) Decomposition of plankton-derived dissolved organic matter in permeable coastal sediments. Limnol Oceanogr 55(2):857–871
Cole JJ (1982) Interactions between bacteria and algae in aquatic ecosystems. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 13(1):291–314
Cole JJ, Caraco NF, Strayer DL, Ochs C, Nolan SS (1989) A detailed carbon budget as an ecosystem-level calibration of bacterial respiration in an oligotrophic lake during mid-summer. Limnol Oceanogr 34:286–296
Córdova JL, Escudero C, Bustamante J (2003) Bloom inside the bloom: intracellular bacteria multiplication within toxic dinoflagellates. Rev Biol Mar Oceanogr 38:57–67
El-Ghazaly G, Jensen WA (1987) Development of wheat (Triticum aestivum) polen. II. Histochemical differentiation of wall and Ubisch bodies during development. Am J Bot 74:1396–1418
Fuerst JA (1995) The planctomycetes: emerging models for microbial ecology, evolution and cell biology. Microbiology 141:1493–1506
Fuerst JA, Sagulenko E (2012) Keys to eukaryality: planctomycetes and ancestral evolution of cellular complexity. Front Microbiol 3:167
Fuerst JA, Sagulenko E (2013) Nested bacterial boxes: nuclear and other intracellular compartments in Planctomycetes. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 23(1–2):95–103
Fuerst JA, William HG, Lindsay M, Lichanska A, Belcher C, Vickers JE, Hugenholtz P (1997) Isolation and molecular identification of planctomycete bacteria from postlarvae of the giant tiger prawn, Penaeus monodon. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:254–262
Fukunaga Y, Kurahashi M, Sakiyama Y, Ohuchi M, Tokota A, Harayama S (2009) Phycisphaera mikurensis gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from a marine alga, and proposal of Phycisphaeraceae fam. nov., Phycisphaerales ord. nov. and Phycisphaerae classis nov. in the phylum Planctomycetes. J Gen Appl Microbiol 55:267–275
Gade D, Stuhrmann T, Reinhardt R, Rabus R (2005) Growth phase dependent regulation of protein composition in Rhodopirellula baltica. Environ Microbiol 7(8):1074–1084
Glockner FO, Fuchs BM, Amann R (1999) Bacterioplankton compositions of lakes and oceans: a first comparison based on fluorescence in situ hybridization. Appl Environ Microbiol 65(8):3721–3726
Godon JJ, Zumstein E, Dabert P, Habouzit F, Moletta R (1997) Molecular microbial diversity of an anaerobic digestor as determined by small-subunit rDNA sequence analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol 63(7):2802–2813
Harrison PJ, Waters RE, Taylor FJR (1980) A broad spectrum artificial seawater medium for coastal and open ocean phytoplankton. J Phycol 16(1):28–35
Hasegawa Y, Martin JL, Giewat MW, Rooney-Varga JN (2007) Microbial community diversity in the phycosphere of natural populations of the toxic alga Alexandrium fundyense. Environ Microbiol 9(12):3108–3121
Hold GL, Smith EA, Rappé MS, Maas EW, Moore ERB, Stroempl C, Stephen JR, Prosser JI, Birkbeck TH, Gallacher S (2001) Characterisation of bacterial communities associated with toxic and non-toxic dinoflagellates: Alexandrium spp. and Scrippsiella trochoidea. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 37(2):161–173
Hu Y, Fu C, Yin Y, Cheng G, Lei F, Yang X, Li J, Ashforth EJ, Zhang L, Zhu B (2010) Construction and preliminary analysis of a deep-sea sediment metagenomic fosmid library from Qiongdongnan Basin South China Sea. Mar Biotechnol 12(6):719–727
Kodama M, Doucette GJ, Green DH (2006) Relationships between bacteria and harmful algae. In: Granéli E, Turner J (eds) Ecology of Harmful Algae Ecological Studies, vol 189. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, New York, pp 243–255
König E, Schlesner H, Hirsch P (1984) Cell wall studies on budding bacteria of the Planctomyces/Pasteuria group and on a Prosthecomicrobium sp. Arch Microbiol 138:200–205
Lachnit T, Meske D, Wahl M, Harder T, Schmitz R (2011) Epibacterial community patterns on marine macroalgae are host-specific but temporally variable. Environ Microbiol 13(3):655–665
Lafay B, Ruimy R, de Traubenberg CR, Breittmayer V, Gauthier MJ, Christen R (1995) Roseobacter algicola sp. nov., a new marine bacterium isolated from the phycosphere of the toxin-producing dinoflagellate Prorocentrum lima. Int J Syst Bacteriol 45(2):290–296
Lage OM, Bondoso J (2011) Planctomycetes diversity associated with macroalgae. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 78(2):366–375
Lage OM, Bondoso J, Viana F (2012) Isolation and characterization of Planctomycetes from the sediments of a fish farm wastewater treatment tank. Arch Microbiol 194(10):879–885
Lage OM, Bondoso J, Lobo-da-Cunha A (2013) Insights into the ultrastructural morphology of novel Planctomycetes. Anto Leeuw. doi:10.1007/s10482-013-9969-2
Lee SY, Bollinger J, Bezdicek D, Ogram A (1996) Estimation of the abundance of an uncultured soil bacterial strain by a competitive quantitative PCR method. Appl Environ Microbiol 62(10):3787–3793
Liesack W, Stackebrandt E (1992) Occurrence of novel groups of the domain bacteria as revealed by analysis of genetic material isolated from an Australian terrestrial environment. J Bacteriol 174(15):5072–5078
Liesack W, König E, Schlesner H, Hirsch P (1986) Chemical composition of the peptidoglycan-free cell envelopes of budding bacteria of the Pirella/Planctomyces group. Arch Microbiol 145:361–366
Lindsay MR, Webb RI, Fuerst JA (1997) Pirellulosomes: a new type of membrane-bounded cell compartment in planctomycete bacteria of the genus Pirellula. Microbiology 143:739–748
Lindsay MR, Webb RI, Strous M, Jetten MSM, Butler MK, Forde RJ, Fuerst JA (2001) Cell compartmentalisation in planctomycetes: novel types of structural organisation for the bacterial cell. Arch Microbiol 175(6):413–429
Mayali X, Franks PJS, Burton RS (2011) Temporal attachment dynamics by distinct bacterial taxa during a dinoflagellate bloom. Aquat Microb Ecol 63(2):111–122
Miranda LN, Hutchison K, Grossman AR, Brawley SH (2013) Diversity and abundance of the bacterial community of the red macroalga Porphyra umbilicalis: did bacterial farmers produce macroalgae? PLoS ONE 8(3):e58269
Morris RM, Longnecker K, Giovannoni SJ (2006) Pirellula and OM43 are among the dominant lineages identified in an Oregon coast diatom bloom. Environ Microbiol 8(8):1361–1370
Musat N, Werner U, Knittel K, Kolb S, Dodenhof T, van Beusekom JEE, de Beer D, Dubilier N, Amann R (2006) Microbial community structure of sandy intertidal sediments in the North Sea, Sylt-Rømø Basin Wadden Sea. Syst Appl Microbiol 29(4):333–348
Pimentel-Elardo S, Wehrl M, Friedrich AB, Jensen PR, Hentschel U (2003) Isolation of planctomycetes from Aplysina sponges. Aquat Microb Ecol 33:239–245
Prokic I, Brummer F, Brigge T, Gortz HD, Gerdts G, Schutt C, Elbrachter M, Muller WE (1998) Bacteria of the genus Roseobacter associated with the toxic dinoflagellate Prorocentrum lima. Protist 149(4):347–357
Rausch de Traubenberg C, Lassus P (1991) Dinoflagellate toxicity: are marine bacteria involved? Evidence from the literature. Marine Microbial Food Webs 5:205–226
Rusch A, Huettel M, Reimers CE, Taghon GL, Fuller CM (2003) Activity and distribution of bacterial populations in Middle Atlantic Bight shelf sands. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 44(1):89–100
Ryter A, Kellenberger E (1958) Étude aux microscope électronique de plasmas contenent de l’acid désoxyribonucéique. I. Les nucléoïdes des bacteries en croissance actives. Z Naturforsch 13B:597–605
Santarella-Mellwig R, Pruggnaller S, Roos N, Mattaj IW, Devos DP (2013) Three-dimensional reconstruction of bacteria with a complex Endomembrane system. PLoS Biol 11(5):e1001565
Sapp M, Schwaderer AS, Wiltshire KH, Hoppe HG, Gerdts G, Wichels A (2007) Species-specific bacterial communities in the phycosphere of microalgae? Microb Ecol 53(4):683–699
Schlesner H (1994) The development of media suitable for the microorganisms morphologically resembling Planctomyces spp., Pirellula spp., and other Planctomycetales from various aquatic habitats using dilute media. Syst Appl Microbiol 17(1):135–145
Schmidt JM, Starr MP (1979) Morphotype V of the Blastocaulis-Planctomyces group of budding and appendaged bacteria: Planctomyces guttaeformis Hortobágyi (sensu Hajdu). Curr Microbiol 2:195–200
Silva MT (1984) The use of transmission electron microscopy of ultrathin sections for the characterization of the ultrastructure of normal and damaged bacterial membranes. In: Burton R, Guerra F (eds) Biomembranes, NATO ASI Series, vol 76. Springer, New York, pp 1–36
Silva ES (1990) Intracellular bacteria: the origin of dinoflagellate toxicity. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol 10(3):124–128
Speth DR, van Teeseling MC, Jetten MS (2012) Genomic analysis indicates the presence of an asymmetric bilayer outer membrane in planctomycetes and verrucomicrobia. Front Microbiol 3:304
Spurr AP (1969) A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. Journal of Ultrastruture Resolution 26:31–43
Stackebrandt E, Wehmeyer U, Liesack W (1986) 16S ribosomal RNA- and cell wall analysis of Gemmata obscuriglobus, a new member of the order Planctomycetales. FEMS Microbiol Lett 37:289–292
Starr MP, Short KA, Schmidt JM (1984) Exclusion of the filamentous and rosette-forming bacterium “Planctomyces gracilis” Hortobiigyi 1965 from the Blastocaulis-Planctomyces group. Int J Bact 34:465–469
Tekniepe BL, Schmid M, Starr MP (1981) Life cycle of a budding and appendage bacterium belonging to morphotype IV of the Blastocaulis-Planctomyces group. Curr Microbiol 5:1–6
Thiéry JP (1967) Mise en évidence des polysaccharides sur coupes fines en microscopie électronique. Journal of Microscopie 6:987–1018
van Niftrik L, Geerts WJ, van Donselaar EG, Humbel BM, Webb RI, Harhangi HR, Camp HJ, Fuerst JA, Verkleij AJ, Jetten MS, Strous M (2009) Cell division ring, a new cell division protein and vertical inheritance of a bacterial organelle in anammox planctomycetes. Mol Microbiol 73(6):1009–1019
Wagner M, Horn M (2006) The Planctomycetes, Verrucomicrobia, Chlamydiae and sister phyla comprise a superphylum with biotechnological and medical relevance. Curr Opin Biotechnol 17(3):241–249
Watson SW, Bock E, Valois FW, Waterbury JB, Schlosser U (1986) Nitrospira marina gen. nov. sp. nov: a chemolithotrohic nitrite-oxidizing bacterium. Arch Microbiol 144(1):1–7
Webster NS, Bourne D (2007) Bacterial community structure associated with the Antarctic soft coral. Alcyonium antarcticum. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 59(1):81–94
Zarda B, Hahn D, Chatzinotas A, Schönhuber W, Neef A, Amann RI, Zeyer J (1997) Analysis of bacterial community structure in bulk soil by in situ hybridization. Arch Microbiol 168(3):185–192
ZoBell CE (1946) Marine microbiology a monograph on hydrobacteriology. Chronica Botanica Co, Waltham
Acknowledgments
I am grateful to Mrs M. Andrea Costa for excellent technical assistance and to Damien Devos for his encouragement and helpful comments. My special thoughts go to Ana Maria Parente, my supervisor during my PhD that shared with me the discovery of this fascinating group of bacteria.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10482_2013_9991_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Online resource 1 Cell section showing details of the cell envelope; (CW) cell wall, (CM) cytoplasmic membrane, (P) periplasm, (F) fimbriae
10482_2013_9991_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Online resource 2 Electron micrographs of thin sections of IP1 labeled after Thiéry procedure. (H) holdfast, (F) fimbriae, (Gl) glycogen-like reserve bodies
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lage, O.M. Characterization of a planctomycete associated with the marine dinoflagellate Prorocentrum micans Her. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 104, 499–508 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-013-9991-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-013-9991-4