Abstract
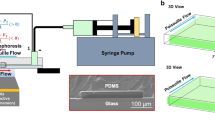
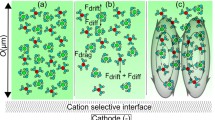
This work demonstrates by direct visualization using confocal laser scanning microscopy that the application of electrical fields to a single-fixed, ion-permselective glass bead produces a remarkable complexity in both the coupled mass and charge transport through the bead and the coupled electrokinetics and hydrodynamics in the adjoining bulk electrolyte. The visualization approach enables the acquisition of a wealth of information, forming the basis for a detailed analysis of the underlying effects (e.g., ion-permselectivity, concentration polarization, nonequilibrium electroosmotic slip) and an understanding of electrohydrodynamic phenomena at charge-selective interfaces under more general conditions. The device used for fixing single beads in a microfluidic channel is flexible and allows to investigate the electrohydrodynamics in both transient and stationary regimes under the influence of bead shape, pore size and surface charge density, mobile phase composition, and applied volume forces. This insight is relevant for the design of microfluidic/nanofluidic interconnections and addresses the ionic conductance of discrete nanochannels, as well as nanoporous separation and preconcentration units contained as hybrid configurations, membranes, packed beds, or monoliths in lab-on-a-chip devices.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barany S (1998) Complex electrosurface investigations of dispersed microphases. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 75:45–78
Barany S, Mishchuk NA, Prieve DC (1998) Superfast electrophoresis of conducting dispersed particles. J Colloid Interface Sci 207:240–250
Belova EI, Lopatkova GY, Pismenskaya ND, Nikonenko VV, Larchet C, Pourcelly G (2006) Effect of anion-exchange membrane surface properties on mechanisms of overlimiting mass transfer. J Phys Chem B 110:13458–13469
Ben Y, Chang HC (2002) Nonlinear Smoluchowski slip velocity and micro-vortex generation. J Fluid Mech 461:229–238
Ben Y, Demekhin EA, Chang HC (2004) Nonlinear electrokinetics and “superfast” electrophoresis. J Colloid Interface Sci 276:483–497
Chang H, Venkatesan BM, Iqbal SM, Andreadakis G, Kosari F, Vasmatzis G, Peroulis D, Bashir R (2006) DNA counterion current and saturation examined by a MEMS-based solid state nanopore sensor. Biomed Microdevices 8:263–269
Chatterjee AN, Cannon DM, Gatimu EN, Sweedler JV, Aluru NR, Bohn PW (2005) Modeling and simulation of ionic currents in three-dimensional microfluidic devices with nanofluidic interconnects. J Nanopart Res 7:507–516
Chen Z, Wang P, Chang HC (2005) An electroosmotic micropump based on monolithic silica for microflow analysis and electrosprays. Anal Bioanal Chem 382:817–824
Choi JH, Kim SH, Moon SH (2001a) Heterogeneity of ion-exchange membranes: the effects of membrane heterogeneity on transport properties. J Colloid Interface Sci 241:120–126
Choi JH, Lee HJ, Moon SH (2001b) Effects of electrolytes on the transport phenomena in a cation-exchange membrane. J Colloid Interface Sci 238:188–195
Choudhary G, Horváth C (1997) Dynamics of capillary electrochromatography: experimental study of the electroosmotic flow and conductance in open and packed capillaries. J Chromatogr A 781:161–183
Cui H, Horiuchi K, Dutta P, Ivory CF (2005) Multistage isoelectric focusing in a polymeric microfluidic chip. Anal Chem 77:7878–7886
Daiguji H, Yang P, Majumdar A (2004) Ion transport in nanofluidic channels. Nano Lett 4:137–142
Deyl Z, Svec F (2001) Capillary electrochromatography. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Dittmann MM, Wienand K, Bek F, Rozing GP (1995) Theory and practice of capillary electrochromatography. LC GC 13:800–814
Dhopeshwarkar R, Sun L, Crooks RM (2005) Electrokinetic concentration enrichment within a microfluidic device using a hydrogel plug. Lab Chip 5:1148–1154
Dukhin SS (1991) Electrokinetic phenomena of the second kind and their applications. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 35:173–196
Eijkel JCT, van den Berg A (2006) Nanotechnology for membranes, filters, and sieves. Lab Chip 6:19–23
Foote RS, Khandurina J, Jacobson SC, Ramsey JM (2005) Preconcentration of proteins in microfluidic devices using porous silica membranes. Anal Chem 77:57–63
Ghosal S (2006) Electrokinetic flow and dispersion in capillary electrophoresis. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 38:309–338
Hatch AV, Herr AE, Throckmorton DJ, Brennan JS, Singh AK (2006) Integrated preconcentration SDS-PAGE of proteins in microchips using photopatterned cross-linked polyacrylamide gels. Anal Chem 78:4976–4984
Helfferich F (1995) Ion exchange. Dover, New York
Hlushkou D, Seidel-Morgenstern A, Tallarek U (2005) Numerical analysis of electroosmotic flow in regular and random arrays of impermeable, nonconducting spheres. Langmuir 21:6097–6112
Höltzel A, Tallarek U (2007) Ionic conductance of nanopores in microscale analysis systems: where microfluidics meets nanofluidics. J Sep Sci 30:1398–1419
Hu YD, Lee JSH, Werner C, Li DQ (2006) Electrokinetically controlled concentration gradients in micro-chambers in microfluidic systems. Microfluid Nanofluid 2:141–153
Ibanez R, Stamatialis DF, Wessling M (2004) Role of membrane surface in concentration polarization at cation exchange membranes. J Memb Sci 239:119–128
Jung B, Bharadwaj R, Santiago JG (2006) On-chip millionfold sample stacking using transient isotachophoresis. Anal Chem 78:2319–2327
Kang YJ, Yang C, Huang XY (2005) Analysis of electroosmotic flow in a microchannel packed with microspheres. Microfluid Nanofluid 1:168–176
Kelly RT, Woolley AT (2005) Electric field gradient focusing. J Sep Sci 28:1985–1993
Kim SM, Burns MA, Hasselbrink EF (2006) Electrokinetic protein preconcentration using a simple glass/poly(dimethylsiloxane) microfluidic chip. Anal Chem 78:4779–4785
Kirby BJ, Hasselbrink EF (2004) Zeta potential of microfluidic substrates: 1. Theory, experimental techniques, and effects on separations. Electrophoresis 25:187–202
Kuo TC, Cannon DM, Chen Y, Tulock JJ, Shannon MA, Sweedler JV, Bohn PW (2003) Gateable nanofluidic interconnects for multilayered microfluidic separation systems. Anal Chem 75:1861–1867
Laser DJ, Santiago JG (2004) A review of micropumps. J Micromech Microeng 14:R35–R64
Li D (2004) Electrokinetics in microfluidics. Elsevier, Burlington
Li QL, Fang YF, Green ME (1983) Turbulent light-scattering fluctuation spectra near a cation electrodialysis membrane. J Colloid Interface Sci 91:412–417
Leinweber FC, Tallarek U (2004) Nonequilibrium electrokinetic effects in beds of ion-permselective particles. Langmuir 20:11637–11648
Leinweber FC, Tallarek U (2005) Concentration polarization-based nonlinear electrokinetics in porous media: induced-charge electroosmosis. J Phys Chem B 109:21481–21485
Leinweber FC, Pfafferodt M, Seidel-Morgenstern A, Tallarek U (2005) Electrokinetic effects on the transport of charged analytes in biporous media with discrete ion-permselective regions. Anal Chem 77:5839–5850
Lyklema J (1995) Fundamentals of colloid and interface science, vol II: solid–liquid interfaces. Academic, San Diego
Manzanares JA, Kontturi K, Mafé S, Aguilella VM, Pellicer J (1991) Polarization effects at the cation-exchange–membrane solution interface. Acta Chem Scand 45:115–121
Manzanares JA, Murphy WD, Mafé S, Reiss H (1993) Numerical simulation of the nonequilibrium diffuse double layer in ion-exchange membranes. J Phys Chem 97:8524–8530
Mishchuk NA, Dukhin SS (2002) Electrokinetic phenomena of the second kind. In: Delgado AV (ed) Interfacial electrokinetics and electrophoresis. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 241–275
Mishchuk NA, Takhistov PV (1995) Electroosmosis of the second kind. Colloids Surf A 95:119–131
Mishchuk NA, Gonzalez-Caballero F, Takhistov P (2001) Electroosmosis of the second kind and current through curved interface. Colloids Surf A 181:131–144
Mulligan CN, Yong RN, Gibbs BF (2001) Remediation technologies for metal-contaminated soils and groundwater: an evaluation. Eng Geol 60:193–207
Nischang I, Tallarek U (2007) Fluid dynamics in capillary and chip electrochromatography. Electrophoresis 28:611–626
Nischang I, Chen G, Tallarek U (2006a) Electrohydrodynamics in hierarchically structured monolithic and particulate fixed beds. J Chromatogr A 1109:32–50
Nischang I, Spannmann K, Tallarek U (2006b) Key to analyte migration and retention in electrochromatography. Anal Chem 78:3601–3608
Probstein RF (1994) Physicochemical hydrodynamics. Wiley, New York
Pumera M (2005) Microchip-based electrochromatography: designs and applications. Talanta 66:1048–1062
Raats MHM, van Diemen AJG, Lavèn J, Stein HN (2002) Full scale electrokinetic dewatering of waste sludge. Colloids Surf A 210:231–241
Rubinstein I, Zaltzman B (1999) Electroconvective mechanisms in concentration polarization at electrodialysis membranes. In: Sørensen TS (ed) Surface chemistry and electrochemistry of membranes. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 591–621
Rubinstein I, Zaltzman B (2000) Electroosmotically induced convection at a permselective membrane. Phys Rev E 62:2238–2251
Rubinstein I, Zaltzman B, Pretz J, Linder C (2002) Experimental verification of the electroosmotic mechanism of overlimiting conductance through a cation exchange electrodialysis membrane. Russ J Electrochem 38:853–863
Rubinstein I, Zaltzman B, Lerman I (2005) Electroconvective instability in concentration polarization and nonequilibrium electroosmotic slip. Phys Rev E 72:011505
Saichek RE, Reddy KR (2005) Electrokinetically enhanced remediation of hydrophobic organic compounds in soils: a review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 35:115–192
Schmuhl R, Nijdam W, Sekulić J, Roy Chowdhury S, van Rijn CJM, van den Berg A, ten Elshof JE, Blank DHA (2005) Si-supported mesoporous and microporous oxide interconnects as electrophoretic gates for application in microfluidic devices. Anal Chem 77:178–184
Schmuhl R, van den Berg A, Blank DHA, ten Elshof JE (2006) Surfactant-modulated switching of molecular transport in nanometer-sized pores of membrane gates. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 45:3341–3345
Sinton D (2004) Microscale flow visualization. Microfluid Nanofluid 1:2–21
Siwy ZS (2006) Ion-current rectification in nanopores and nanotubes with broken symmetry. Adv Funct Mater 16:735–746
Smeets RMM, Keyser UF, Krapf D, Wu MY, Dekker NH, Dekker C (2006) Salt dependence of ion transport and DNA translocation through solid-state nanopores. Nano Lett 6:89–95
Stachowiak TB, Svec F, Fréchet JMJ (2004) Chip electrochromatography. J Chromatogr A 1044:97–111
Stone HA, Stroock AD, Ajdari A (2004) Engineering flows in small devices: microfluidics toward a lab-on-a-chip. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 36:381–411
Svec F (2005) Recent developments in the field of monolithic stationary phases for capillary electrochromatography. J Sep Sci 28:729–745
Tallarek U, Pačes M, Rapp E (2003) Perfusive flow and intraparticle distribution of a neutral analyte in capillary electrochromatography. Electrophoresis 24:4241–4253
Verpoorte E, de Rooij N (2003) Microfluidics meets MEMS. Proc IEEE 91:930–953
Virkutyte J, Sillanpaa M, Latostenmaa P (2002) Electrokinetic soil remediation: critical overview. Sci Total Environ 289:97–121
Volodina E, Pismenskaya N, Nikonenko V, Larchet C, Pourcelly G (2005) Ion transfer across ion-exchange membranes with homogeneous and heterogeneous surfaces. J Colloid Interface Sci 285:247–258
Wang SC, Lai YW, Ben Y, Chang HC (2004) Microfluidic mixing by dc and ac nonlinear electrokinetic vortex flows. Ind Eng Chem Res 43:2902–2911
Wang YC, Stevens AL, Han J (2005) Million-fold preconcentation of proteins and peptides by nanofluidic filter. Anal Chem 77:4293–4299
Wang P, Chen ZL, Chang HC (2006) A new electroosmotic pump based on silica monoliths. Sens Actuators B 113:500–509
Wong PK, Wang TH, Deval JH, Ho CM (2004) Electrokinetics in micro devices for biotechnology applications. IEEE ASME Trans Mechatron 9:366–376
Yao SH, Myers AM, Posner JD, Rose KA, Santiago JG (2006) Electroosmotic pumps fabricated from porous silicon membranes. J Microelectromech Syst 15:717–728
Yu A, Lee SB, Martin CR (2003) Electrophoretic protein transport in gold nanotube membranes. Anal Chem 75:1239–1244
Zabolotsky VI, Manzanares JA, Nikonenko VV, Lebedev KA, Lovtsov EG (2002) Space charge effect on competitive ion transport through ion-exchange membranes. Desalination 147:387–392
Zabolotsky VI, Lebedev KA, Lovtsov EG (2006) Mathematical model for the overlimiting state of an ion-exchange membrane system. Russ J Electrochem 42:836–846
Zilberstein GV, Baskin EM, Bukshpan S (2003) Parallel processing in the isoelectric focusing chip. Electrophoresis 24:3735–3744
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (Bonn, Germany) under grants TA 268/2 and HL 56/1, as well as by the Fonds der Chemischen Industrie (Frankfurt a.M., Germany).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ehlert, S., Hlushkou, D. & Tallarek, U. Electrohydrodynamics around single ion-permselective glass beads fixed in a microfluidic device. Microfluid Nanofluid 4, 471–487 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-007-0200-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-007-0200-5