Abstract
Aim
Specific interventions for overweight but not obese children have not been established yet. Therefore, we developed the methods, materials, and an evaluation protocol for a lifestyle intervention for overweight children based on an intervention for obese children.
Subjects and methods
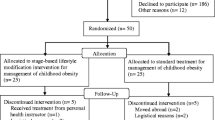
The 1-year lifestyle intervention “Obeldicks” for obese children, compromised of physical activity plans, nutritional education, and behavioural counselling, including individual psychological care for both children and their parents, was shortened, reducing the amount of exercise training and individual counselling by about 50%, forming a 6-month intervention (“Obeldicks light”).
Results
The evaluation protocol was based on guidelines and validated instruments with available German healthy normal-weight controls. As the ideal study design, a multicentre randomised controlled trail with the primary outcome change of weight status was identified. As secondary outcomes, improvement of body composition (skinfold thickness, bioimpedance analysis), cardiovascular risk factors (blood pressure, waist circumference), quality of life, dietary habits, eating, exercise, and sedentary behaviour were established. Potential influencing factors for treatment success were identified, such as parental BMI, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status. All proposed instruments were validated in the German representative KiGGS and DONALD study.
Conclusions
Adapting a well-established program for obese children to overweight children is an easy way to create a lifestyle intervention for overweight children. Our study protocol using instruments validated in German normal weight cohorts allows evaluating this new intervention.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anonymous (2004) The fourth report on the diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. Pediatrics 114:555–576
Baker JL, Olsen LW, Sorensen TI (2007) Childhood body-mass index and the risk of coronary heart disease in adulthood. N Engl J Med 357:2329–2337
Biro FM, Wien M (2010) Childhood obesity and adult morbidities. Am J Clin Nutr 91:1499S–1505S
Bös K, Heel J, Romahn N, Tittlbach SWAWT (2010) Untersuchungen zur Motorik im Rahmen des Kinder- und Jugendsurveys. Gesundheitswesen 64:80–87
Cole TJ (1990) The LMS method for constructing normalized growth standards. Eur J Clin Nutr 44:45–60
Ebbeling CB, Pawlak DB, Ludwig DS (2002) Childhood obesity: public-health crisis, common sense cure. Lancet 360:473–482
Finne E, Reinehr T, SchaeferA WK, Kolip P (2009) Overweight children and adolescents–is there a subjective need for treatment? Int J Public Health 54:112–116
Flodmark CE (2005) Management of the obese child using psychological-based treatments. Acta Paediatr Suppl 94:14–22
Haroun D, Croker H, Viner RM, Williams JE, Darch TS, Fewtrell MS, Eaton S, Wells JC (2009) Validation of BIA in Obese Children and Adolescents and Re-evaluation in a Longitudinal Study. Obesity (Silver Spring) 17:2245–2250
Hoffmeister U, Bullinger M, van Egmond-Fröhlich A, Goldapp C, Mann R, Ravens-Sieberer U, Reinehr T, Westenhöfer J, Wille N, Holl R (2010) Übergewicht und Adipositas in Kindheit und Jugend: Evaluation der ambulanten und stationären Versorgung in Deutschland in der “EvAKuJ-Studie”. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz, in press
http:www.a-g-a.de/Leitlinie.pdf (2011) Guidelines of the German working group on obese children and adolescents. Accessed 28 February 2011
I'Allemand D, Wiegand S, Reinehr T, Muller J, Wabitsch M, Widhalm K, Holl R (2008) Cardiovascular risk in 26,008 European overweight children as established by a multicenter database. Obesity (Silver Spring) 16:1672–1679
Kersting M, Alexy U, Clausen K (2005) Using the concept of Food Based Dietary Guidelines to Develop an Optimized Mixed Diet (OMD) for German children and adolescents. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 40:301–308
Kromeyer-Hauschild K, Wabitsch M, Geller F, Ziegler A, Geiss HC, Hesse V, von Hippel V, Jäger U, Johnson D, Korte W, Kunze D, Menner K, Müller G, Müller M, Niemann-Pilatus A, Remer T, Schäfer F, Wittchen H, Zabransky S, Zelnner K, Hebebrand J (2001) Percentiles of body mass index in children and adolescents evaluated from different regional German studies. Monatsschr Kinderheilkd 149:807–818
Kurth BM, Kamtsiuris P, Holling H, Schlaud M, Dolle R, Ellert U, Kahl H, Knopf H, Lange M, Mensink GB, Neuhauser H, Rosario AS, Scheidt-Nave C, Schenk L, Schlack R, Stolzenberg H, Thamm M, Thierfelder W, Wolf U (2008) The challenge of comprehensively mapping children's health in a nation-wide health survey: design of the German KiGGS-Study. BMC Public Health 8:196
Lampert T, Mensink GB, Romahn N, Woll A (2007a) Physical activity among children and adolescents in Germany. Results of the German Health Interview and Examination Survey for Children and Adolescents (KiGGS). Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz 50:634–642
Lampert T, Sygusch R, Schlack R (2007b) Use of electronic media in adolescence. Results of the German Health Interview and Examination Survey for Children and Adolescents (KiGGS). Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz 50:643–652
Lange M, Kamtsiuris P, Lange C, Schaffrat Rosario A, Stolzenberg H, Lampert T (2007) Sociodemographic characteristics in the German Health Interview and Examination Survey for Children and Adolescents (KiGGS)—operationalisation and public health significance, taking as an example the assessment of general state of health. Bundesgesundheitsblatt 50:578–589
Lorenz MW, Markus HS, Bots ML, Rosvall M, Sitzer M (2007) Prediction of clinical cardiovascular events with carotid intima-media thickness: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Circulation 115:459–467
Monasta L, Batty GD, Macaluso A, Ronfani L, Lutje V, Bavcar A, van Lenthe FJ, Brug J, Cattaneo A (2010) Interventions for the prevention of overweight and obesity in preschool children: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Obes Rev. doi:10.1111/j.1467-789X.2010.00774.x. Accessed 22 JUN 2010
Oude LH, Baur L, Jansen H, Shrewsbury VA, O'Malley C, Stolk RP, Summerbell CD (2009) Interventions for treating obesity in children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev CD001872
Ravens-Sieberer U, Erhart M, Wille N, Bullinger M (2008) Health-related quality of life in children and adolescents in Germany: results of the BELLA study. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 17(Suppl 1):148–156
Reinehr T, Andler W, Denzer C, Siegried W, Mayer H, Wabitsch M (2005a) Cardiovascular risk factors in overweight German children and adolescents: relation to gender, age and degree of overweight. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 15:181–187
Reinehr T, Kersting M, Wollenhaupt A, Alexy U, Kling B, Strobele K, Andler W (2005b) Evaluation of the training program "OBELDICKS" for obese children and adolescents. Klin Pädiatr 217:1–8
Reinehr T, de Sousa G, Toschke AM, Andler W (2006) Long-term follow-up of cardiovascular disease risk factors in children after an obesity intervention. Am J Clin Nutr 84:490–496
Reinehr T, Dobe M, Kersting M (2010a) Therapie der Adipositas im Kindes- und Jugendalter: Schulung Obeldicks und Obeldicks Light. 2. Auflage edn Hogrefe Verlag
Reinehr T, Kleber M, Lass N, Toschke AM (2010b) Body mass index patterns over 5 y in obese children motivated to participate in a 1-year lifestyle intervention: age as a predictor of long-term success. Am J Clin Nutr 91:1165–1171
Reinehr T, Schaefer A, Winkel K, Finne E, Toschke AM, Kolip P (2010c) An effective lifestyle intervention in overweight children: findings from a randomized controlled trial on “Obeldicks light”. Clin Nutr 29:331–336
Sallis J, Saelens B (2000) Assessment of physical activity by self-report: status, limitations, and future directions. Res Q Exerc Sport 71:1–14
Schenk L, Ellert U, Neuhauser H (2007) Kinder und Jugendliche mit Migrationshintergrund in Deutschland. Bundesgesundheitsblatt 50:590–599
Sichert-Hellert W, Kersting M, Manz F (2001) Changes in time-trends of nutrient intake from fortified and non-fortified food in German children and adolescents—15 year results of the DONALD study. Dortmund Nutritional and Anthropometric Longitudinally Designed Study. Eur J Nutr 40:49–55
Slaughter M, Lohmann T, Boileau R, Horswill C, Stillmann R, Bemben D (1998) Skinfold equations for estimation of body fatness in children and youth. Hum Biol 60:709–723
Stunkard AJ, Messick S (1985) The three-factor eating questionnaire to measure dietary restraint, disinhibition and hunger. J Psychosom Res 29:71–83
Verplanken B, Orbell S (2003) Reflections on past behavior: a self-report index of habit strength. J Appl Soc Psychol 33:1313–1330
WestenhoeferJ PV (1989) Fragebogen zum Eßverhalten (FEV). Hogrefe, Göttingen
Wille N, Erhart M, Petersen C, Ravens-Sieberer U (2008) The impact of overweight and obesity on health-related quality of life in childhood–results from an intervention study. BMC Public Health 8:421
Wunsch R, de Sousa G, Toschke AM, Reinehr T (2006) Intima-media thickness in obese children before and after weight loss. Pediatrics 118:2334–2340
Acknowledgements
AS, TR, and KW developed the lifestyle intervention; TR, EF, and PK performed the evaluation study; AS, KW, EF, PK, and TR prepared the discussion; TR wrote the first version of the manuscript.
The “Obeldicks light” intervention was initiated by the health insurances Techniker Krankenkasse (TK), Kaufmänische Krankenkasse/Allianz (KKH Allianz), Deutsche Angestellten Krankenkassen (DAK), and the Vestische Kinder- und Jugendklinik Datteln.
This study was funded by the German Federal Ministry of Research (grant nos. 01EL619 and 01EL0603)
Conflict of interest
All authors have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study is registered at clinicaltrials.gov (NCT00422916).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reinehr, T., Schaefer, A., Winkel, K. et al. Development and evaluation of the lifestyle intervention “Obeldicks light” for overweight children and adolescents. J Public Health 19, 377–384 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10389-011-0410-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10389-011-0410-x