Abstract
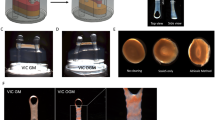
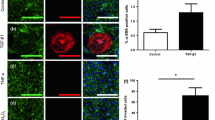
Calcific aortic valve disease (CAVD) results in impaired function through the inability of valves to fully open and close, but the causes of this pathology are unknown. Stiffening of the aorta is associated with CAVD and results in exposing the aortic valves to greater mechanical strain. Transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1) is enriched in diseased valves and has been shown to combine with strain to synergistically alter aortic valve interstitial cell (AVIC) phenotypes. Therefore, we investigated the role of strain and TGF-β1 on the calcification of AVICs. Following TGF-β1 pretreatment, strain induced intact monolayers to aggregate and calcify. Using a wound assay, we confirmed that TGF-β1 increases tension in the monolayer in parallel with α-smooth muscle actin (αSMA) expression. Continual exposure to strain accelerates aggregates to calcify into mature nodules that contain a necrotic core surrounded by an apoptotic ring. This phenotype appears to be mediated by strain inhibition of AVIC migration after the initial formation of aggregates. To better interpret the extent to which externally applied strain physically impacts this process, we modified the classical Lamé solution, derived using principles from linear elasticity, to reveal strain magnification as a novel feature occurring in a mechanical environment that supports nodule formation. These results indicate that strain can impact multiple points of nodule formation: by modifying tension in the monolayer, remodeling cell contacts, migration, apoptosis, and mineralization. Therefore, strain-induced nodule formation provides new directions for developing strategies to address CAVD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balachandran K, Konduri S, Sucosky P, Jo H, Yoganathan AP (2006) An ex vivo study of the biological properties of porcine aortic valves in response to circumferential cyclic stretch. Ann Biomed Eng 34(11): 1655–1665. doi:10.1007/s10439-006-9167-8
Balachandran K, Sucosky P, Jo H, Yoganathan AP (2009) Elevated cyclic stretch alters matrix remodeling in aortic valve cusps: implications for degenerative aortic valve disease. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 296(3): H756–H764. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00900.2008
Balachandran K, Sucosky P, Jo H, Yoganathan AP (2010) Elevated cyclic stretch induces aortic valve calcification in a bone morphogenic protein-dependent manner. Am J Pathol 177(1): 49–57. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2010.090631
Balestrini JL, Skorinko JK, Hera A, Gaudette GR, Billiar KL (2010) Applying controlled non-uniform deformation for in vitro studies of cell mechanobiology. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 9(3): 329–344. doi:10.1007/s10237-009-0179-9
Benton JA, Kern HB, Anseth KS (2008) Substrate properties influence calcification in valvular interstitial cell culture. J Heart Valve Dis 17(6): 689–699
Benton JA, Kern HB, Leinwand LA, Mariner PD, Anseth KS (2009) Statins block calcific nodule formation of valvular interstitial cells by inhibiting alpha-smooth muscle actin expression. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 29(11): 1950–1957. doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.109.195271
Chen JH, Chen WL, Sider KL, Yip CY, Simmons CA beta-catenin mediates mechanically regulated, transforming growth factor-beta1-induced myofibroblast differentiation of aortic valve interstitial cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 31(3):590–597. doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.110.220061
Chen JH, Simmons CA (2011) Cell-matrix interactions in the pathobiology of calcific aortic valve disease: critical roles for matricellular, matricrine, and matrix mechanics cues. Circ Res 108(12): 1510–1524. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.234237
Chen JH, Yip CY, Sone ED, Simmons CA (2009) Identification and characterization of aortic valve mesenchymal progenitor cells with robust osteogenic calcification potential. Am J Pathol 174(3): 1109–1119. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2009.080750
Cushing MC, Liao JT, Anseth KS (2005) Activation of valvular interstitial cells is mediated by transforming growth factor-beta1 interactions with matrix molecules. Matrix Biol 24(6): 428–437
David G, Humphrey JD (2004) Redistribution of stress due to a circular hole in a nonlinear anisotropic membrane. J Biomech 37(8): 1197–1203. doi:10.1016/j.jbiomech.2003.12.013
Follonier L, Schaub S, Meister JJ, Hinz B (2008) Myofibroblast communication is controlled by intercellular mechanical coupling. J Cell Sci 121(Pt 20): 3305–3316. doi:10.1242/jcs.024521
Goffin JM, Pittet P, Csucs G, Lussi JW, Meister JJ, Hinz B (2006) Focal adhesion size controls tension-dependent recruitment of alpha-smooth muscle actin to stress fibers. J Cell Biol 172(2): 259–268. doi:10.1083/jcb.200506179
Goldbarg SH, Elmariah S, Miller MA, Fuster V (2007) Insights into degenerative aortic valve disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 50(13): 1205–1213. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2007.06.024
Gu X, Masters KS (2009) Role of the MAPK/ERK pathway in valvular interstitial cell calcification. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 296(6): H1748–1757. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00099.2009
Gu X, Masters KS (2010) Regulation of valvular interstitial cell calcification by adhesive peptide sequences. J Biomed Mater Res A 93(4): 1620–1630. doi:10.1002/jbm.a.32660
Gu X, Masters KS (2011) Role of the Rho pathway in regulating valvular interstitial cell phenotype and nodule formation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 300(2): H448–H458. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.01178.2009
Haskett D, Johnson G, Zhou A, Utzinger U, Vande Geest J (2010) Microstructural and biomechanical alterations of the human aorta as a function of age and location. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 9(6): 725–736. doi:10.1007/s10237-010-0209-7
Helske S, Kupari M, Lindstedt KA, Kovanen PT (2007) Aortic valve stenosis: an active atheroinflammatory process. Curr Opin Lipidol 18(5): 483–491. doi:10.1097/MOL.0b013e3282a66099
Hinz B, Mastrangelo D, Iselin CE, Chaponnier C, Gabbiani G (2001) Mechanical tension controls granulation tissue contractile activity and myofibroblast differentiation. Am J Pathol 159(3): 1009–1020. doi:10.1016/S0002-9440(10)61776-2
Hinz B, Pittet P, Smith-Clerc J, Chaponnier C, Meister JJ (2004) Myofibroblast development is characterized by specific cell-cell adherens junctions. Mol Biol Cell 15(9): 4310–4320. doi:10.1091/mbc.E04-05-0386
Hutcheson JD, Venkataraman R, Baudenbacher FJ, Merryman WD (2011) Intracellular Ca(2+) accumulation is strain-dependent and correlates with apoptosis in aortic valve fibroblasts. J Biomech doi:10.1016/j.jbiomech.2011.11.031
Jian B, Narula N, Li QY, Mohler ER, 3rd, Levy RJ (2003) Progression of aortic valve stenosis: TGF-beta1 is present in calcified aortic valve cusps and promotes aortic valve interstitial cell calcification calcification via apoptosis. Ann Thorac Surg 75(2):457–465; discussion 465–456
Kennedy JA, Hua X, Mishra K, Murphy GA, Rosenkranz AC, Horowitz JD (2009) Inhibition of calcifying nodule formation in cultured porcine aortic valve cells by nitric oxide donors. Eur J Pharmacol 602(1): 28–35. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.11.029
Merryman WD (2008) What modulates the aortic valve interstitial cell phenotype?. Future Cardiol 4(3): 247–252. doi:10.2217/14796678.4.3.247
Merryman WD (2009) Mechano-potential etiologies of aortic valve disease. J Biomech 43(1): 87–92. doi:10.1016/j.jbiomech.2009.09.013
Merryman WD, Huang HY, Schoen FJ, Sacks MS (2006) The effects of cellular contraction on aortic valve leaflet flexural stiffness. J Biomech 39(1): 88–96. doi:10.1016/j.jbiomech.2004.11.008
Merryman WD, Liao J, Parekh A, Candiello JE, Lin H, Sacks MS (2007) Differences in tissue-remodeling potential of aortic and pulmonary heart valve interstitial cells. Tissue Eng 13(9): 2281–2289. doi:10.1089/ten.2006.0324
Merryman WD, Lukoff HD, Long RA, Engelmayr GC Jr., Hopkins RA, Sacks MS (2007) Synergistic effects of cyclic tension and transforming growth factor-beta1 on the aortic valve myofibroblast. Cardiovasc Pathol 16(5): 268–276. doi:10.1016/j.carpath.2007.03.006
Merryman WD, Youn I, Lukoff HD, Krueger PM, Guilak F, Hopkins RA, Sacks MS (2006) Correlation between heart valve interstitial cell stiffness and transvalvular pressure: implications for collagen biosynthesis. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 290(1): H224–H231
Mohler ER 3rd, Chawla MK, Chang AW, Vyavahare N, Levy RJ, Graham L, Gannon FH (1999) Identification and characterization of calcifying valve cells from human and canine aortic valves. J Heart Valve Dis 8(3): 254–260
Mohler ER 3rd, Gannon F, Reynolds C, Zimmerman R, Keane MG, Kaplan FS (2001) Bone formation and inflammation in cardiac valves. Circulation 103(11): 1522–1528
Mori D, David G, Humphrey JD, Moore JE Jr. (2005) Stress distribution in a circular membrane with a central fixation. J Biomech Eng 127(3): 549–553
Piper C, Bergemann R, Schulte HD, Koerfer R, Horstkotte D (2003) Can progression of valvar aortic stenosis be predicted accurately?. Ann Thorac Surg 76(3):676–680; discussion 680
Pittet P, Lee K, Kulik AJ, Meister JJ, Hinz B (2008) Fibrogenic fibroblasts increase intercellular adhesion strength by reinforcing individual OB-cadherin bonds. J Cell Sci 121(Pt 6): 877–886. doi:10.1242/jcs.024877
Rajamannan NM (2010) Mechanisms of aortic valve calcification: the LDL-density-radius theory: a translation from cell signaling to physiology. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 298(1): H5–H15. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00824.2009
Rajamannan NM, Evans FJ, Aikawa E, Grande-Allen KJ, Demer LL, Heistad DD, Simmons CA, Masters KS, Mathieu P, O’Brien KD, Schoen FJ, Towler DA, Yoganathan AP, Otto CM (2011) Calcific aortic valve disease: not simply a degenerative process: a review and agenda for research from the National Heart and Lung and Blood Institute Aortic Stenosis Working Group. Executive summary: calcific aortic valve disease-2011 update . Circulation 124(16): 1783–1791. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.006767
Robicsek F, Thubrikar MJ (2002) Mechanical stress as cause of aortic valve disease. Presentation of a new aortic root prosthesis. Acta Chir Belg 102(1): 1–6
Rodriguez KJ, Masters KS (2009) Regulation of valvular interstitial cell calcification by components of the extracellular matrix. J Biomed Mater Res A 90(4): 1043–1053. doi:10.1002/jbm.a.32187
Roger VL, Go AS, Lloyd-Jones DM, Adams RJ, Berry JD, Brown TM, Carnethon MR, Dai S, de Simone G, Ford ES, Fox CS, Fullerton HJ, Gillespie C, Greenlund KJ, Hailpern SM, Heit JA, Ho PM, Howard VJ, Kissela BM, Kittner SJ, Lackland DT, Lichtman JH, Lisabeth LD, Makuc DM, Marcus GM, Marelli A, Matchar DB, McDermott MM, Meigs JB, Moy CS, Mozaffarian D, Mussolino ME, Nichol G, Paynter NP, Rosamond WD, Sorlie PD, Stafford RS, Turan TN, Turner MB, Wong ND, Wylie-Rosett J (2011) Heart disease and stroke statistics–2011 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 123(4): e18–e209. doi:10.1161/CIR.0b013e3182009701
Simmons CA, Nikolovski J, Thornton AJ, Matlis S, Mooney DJ (2004) Mechanical stimulation and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling independently regulate osteogenic differentiation and mineralization by calcifying vascular cells. J Biomech 37(10): 1531–1541. doi:10.1016/j.jbiomech.2004.01.006
Tomasek JJ, Gabbiani G, Hinz B, Chaponnier C, Brown RA (2002) Myofibroblasts and mechano-regulation of connective tissue remodelling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3(5): 349–363. doi:10.1038/nrm809
Walker GA, Masters KS, Shah DN, Anseth KS, Leinwand LA (2004) Valvular myofibroblast activation by transforming growth factor-beta: implications for pathological extracellular matrix remodeling in heart valve disease. Circ Res 95(3): 253–260. doi:10.1161/01.RES.0000136520.07995.aa
Weinberg EJ, Kaazempur Mofrad MR (2007) Transient, three-dimensional, multiscale simulations of the human aortic valve. Cardiovasc Eng 7(4): 140–155. doi:10.1007/s10558-007-9038-4
Weinberg EJ, Mack PJ, Schoen FJ, Garcia-Cardena G, Kaazempur Mofrad MR (2010) Hemodynamic environments from opposing sides of human aortic valve leaflets evoke distinct endothelial phenotypes in vitro. Cardiovasc Eng 10(1): 5–11. doi:10.1007/s10558-009-9089-9
Weinberg EJ, Schoen FJ, Mofrad MR (2009) A computational model of aging and calcification in the aortic heart valve. PLoS One 4(6): e5960. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0005960
Wipff PJ, Rifkin DB, Meister JJ, Hinz B (2007) Myofibroblast contraction activates latent TGF-β1 from the extracellular matrix. J Cell Biol 179(6): 1311–1323. doi:10.1083/jcb.200704042
Yip CY, Chen JH, Zhao R, Simmons CA (2009) Calcification by valve interstitial cells is regulated by the stiffness of the extracellular matrix. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 29(6): 936–942. doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.108.182394
Yip CY, Simmons CA (2011) The aortic valve microenvironment and its role in calcific aortic valve disease. Cardiovasc Pathol 20(3): 177–182. doi:10.1016/j.carpath.2010.12.001
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Charles I. Fisher and Joseph Chen were co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fisher, C.I., Chen, J. & Merryman, W.D. Calcific nodule morphogenesis by heart valve interstitial cells is strain dependent. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 12, 5–17 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10237-012-0377-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10237-012-0377-8