Abstract
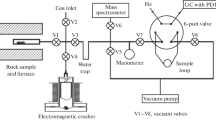
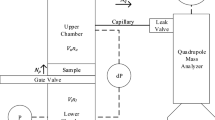
A helium leakage detection system was modified to measure gas permeability on extracted cores of nearly impermeable rock. The Helium-Mass-Spectrometry-Permeameter (HMSP) is duplicating the classic Darcy’s experiment with a constant pressure differential and steady-state flow through a sample using helium gas. Under triaxial stress condition, the newly developed HMSP can measure hydraulic permeability of rocks and geomaterials down to the nanoDarcy scale (10−21 m2). The extension of measuring the lower end of the permeability scale may help answer important questions regarding the permeability of rock at great depth where fractures may close completely under high lithostatic stress.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson RN, Zoback MD (1982) Permeability, underpressures, and convection in the oceanic crust near the Cost Rica rift, eastern equatorial Pacific. J Geophys Res 87:2860–2868
ASTM D4543 (1995) Standard practice for preparing rock core specimens and determining dimensional and shape tolerances. Am Soc Test Mater
Brace WF, Walsh JB, Frangos WT (1968) Permeability of granite under high pressure. J Geophys Res 73:2225–2236
Bredehoeft JD, Papadopulos SS (1980) A method for determining the hydraulic properties of tight formations. Water Resour Res 16:233–238
Haimson BC, Doe TW (1983) State of stress, permeability, and fractures in the Precambrian granite of northern Illinois. J Geophys Res 88:7355–7372
Heid JG, McMahon JJ, Nielson RF, Yuster ST (1950) Study of the permeability of rocks to homogeneous fluids. In: API Drilling and Production Practice, pp 230–244
Jones FO, Owens WW (1980) A laboratory study of low-permeability gas sands. J Pet Technol 32(9):1631–1640
Klinkenberg LJ (1941) The permeability of porous media to liquids and gases. In: Drilling and Production Practice. American Petroleum Institute, New York, pp 200–213
Kranz RL, Saltzman JS, Blacic JD (1990) Hydraulic diffusivity measurements on laboratory rock samples using an oscillating pore pressure method. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci Geomech Abstr 27:345–352
Morrow CA, Moore DE, Lockner DA (2001) Permeability reduction in granite under hydrothermal conditions. J Geophys Res 106:30551–30560
U.S. Department of Energy (2002) Carbon sequestration technology roadmap, National Energy Technology Laboratory
Wang JSY, Ellsworth D (1999) Permeability changes induced by excavation in fractured tuff. In: Amadei B et al (eds) Rock mechanics for industry. Balkema, Rotterdam, pp 751–757
Webb SW (1996) Gas-phase diffusion in porous media—evaluation of an advective-dispersive formulation and the Dusty-Gas model including comparison to data for binary mixtures, SAND96-1197. Sandia National Laboratories, Albuquerque
Xiao J, Wei J (1992) Diffusion mechanism of hydrocarbons in zeolites—I. Theory. Chem Eng Sci 47:1123–1141
Zoback MD, Byerlee JD (1975) The effect of microcrack dilatancy on the permeability of Westerly granite. J Geophys Res 80:752–755
Acknowledgments
Sandia National Laboratories is a multi-program laboratory managed and operated by Sandia Corporation, a wholly owned subsidiary of Lockheed Martin Corporation, for the US Department of Energy’s National Nuclear Security Administration under contract DE-AC04-94AL85000. The technical support received from Steve Webb and David Bronowski as part of this study is also gratefully appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, M.Y., Bauer, S.J. Development of Helium-Mass-Spectrometry-Permeameter for the Measurement of Permeability of Near-Impermeable Rock. Rock Mech Rock Eng 49, 4661–4665 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-016-1058-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-016-1058-1