Abstract
Background
In cases with a tumor-positive resection margin after endoscopic resection of early gastric cancer (EGC), not all patients are found to have residual or recurrent tumor. The aim of this study was to identify risk factors associated with residual/recurrent tumor in patients with incomplete endoscopic resection of EGC.
Methods
A retrospective analysis was performed on consecutive patients who underwent endoscopic resection of EGC at a single institution in South Korea. Patients with a tumor-positive resection margin in the specimen were divided into two groups, with and without residual/recurrent tumor, and the clinicopathologic characteristics were compared.
Results
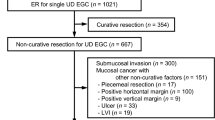
A total of 102 patients with a tumor-positive lateral or vertical resection margin after endoscopic mucosal resection (n = 10) or submucosal dissection (n = 92) were enrolled. Overall, the rate of residual/recurrent tumor was 33.3 % (34/102): 17 residual tumors in 46 patients who immediately underwent additional endoscopic or surgical resection, and 17 recurrent tumors in 56 patients who were initially followed up with regular endoscopy during a median period of 17 (range = 2–70) months. Univariate analysis showed that the presence of ulcer, the direction of the tumor-positive resection margin, and length of lateral resection margin involvement by the tumor were associated with the incidence of residual/recurrent tumor. In multivariate analysis, total length (cm) of lateral resection margin involvement was the only independent risk factor for residual/recurrent tumor (OR 2.05; 95 % CI 1.22–3.44, p = 0.006).
Conclusions
Patients with extensive tumor involvement of a lateral resection margin after endoscopic resection of EGC should consider additional endoscopic or surgical resection due to a high risk of residual/recurrent tumor.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Takenaka R, Kawahara Y, Okada H, Hori K, Inoue M, Kawano S, Tanioka D, Tsuzuki T, Yagi S, Kato J, Uemura M, Ohara N, Yoshino T, Imagawa A, Fujiki S, Takata R, Yamamoto K (2008) Risk factors associated with local recurrence of early gastric cancers after endoscopic submucosal dissection. Gastrointest Endosc 68:887–894
Jang JS, Choi SR, Qureshi W, Kim MC, Kim SJ, Jeung JS, Han SY, Noh MH, Lee JH, Lee SW, Baek YH, Kim SH, Choi PJ (2009) Long-term outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection in gastric neoplastic lesions at a single institution in South Korea. Scand J Gastroenterol 44:1315–1322
Isomoto H, Shikuwa S, Yamaguchi N, Fukuda E, Ikeda K, Nishiyama H, Ohnita K, Mizuta Y, Shiozawa J, Kohno S (2009) Endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer: a large-scale feasibility study. Gut 58:331–336
Isomoto H, Ohnita K, Yamaguchi N, Fukuda E, Ikeda K, Nishiyama H, Akiyama M, Ozawa E, Nakao K, Kohno S, Shikuwa S (2010) Clinical outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection in elderly patients with early gastric cancer. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 22:311–317
Ryu KW, Choi IJ, Doh YW, Kook MC, Kim CG, Park HJ, Lee JH, Lee JS, Lee JY, Kim YW, Bae JM (2007) Surgical indication for non-curative endoscopic resection in early gastric cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 14:3428–3434
Jung H, Bae JM, Choi MG, Noh JH, Sohn TS, Kim S (2011) Surgical outcome after incomplete endoscopic submucosal dissection of gastric cancer. Br J Surg 98:73–78
Bae SY, Jang TH, Min BH, Lee JH, Rhee PL, Rhee JC, Kim JJ (2012) Early additional endoscopic submucosal dissection in patients with positive lateral resection margins after initial endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer. Gastrointest Endosc 75:432–436
Song KY, Hyung WJ, Kim HH, Han SU, Cho GS, Ryu SW, Lee HJ, Kim MC (2008) Is gastrectomy mandatory for all residual or recurrent gastric cancer following endoscopic resection? A large-scale Korean multi-center study. J Surg Oncol 98:6–10
Ono H, Kondo H, Gotoda T, Shirao K, Yamaguchi H, Saito D, Hosokawa K, Shimoda T, Yoshida S (2001) Endoscopic mucosal resection for treatment of early gastric cancer. Gut 48:225–229
Kojima T, Parra-Blanco A, Takahashi H, Fujita R (1998) Outcome of endoscopic mucosal resection for early gastric cancer: review of the Japanese literature. Gastrointest Endosc 48:550–554 discussion 554–555
Inoue H, Takeshita K, Hori H, Muraoka Y, Yoneshima H, Endo M (1993) Endoscopic mucosal resection with a cap-fitted panendoscope for esophagus, stomach, and colon mucosal lesions. Gastrointest Endosc 39:58–62
Kang HY, Kim SG, Kim JS, Jung HC, Song IS (2010) Clinical outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection for undifferentiated early gastric cancer. Surgical Endosc 24:509–516
Japanese Gastric Cancer Association (1998) Japanese Classification of Gastric Carcinoma - 2nd English Edition. Gastric Cancer 1:10–24
Nakamura Y, Yasuoka H, Tsujimoto M, Kurozumi K, Nakahara M, Nakao K, Kakudo K (2006) Importance of lymph vessels in gastric cancer: a prognostic indicator in general and a predictor for lymph node metastasis in early stage cancer. J Clin Pathol 59:77–82
Soetikno R, Kaltenbach T, Yeh R, Gotoda T (2005) Endoscopic mucosal resection for early cancers of the upper gastrointestinal tract. J Clin Oncol 23:4490–4498
Choi J, Kim SG, Im JP, Kim JS, Jung HC, Song IS (2011) Endoscopic prediction of tumor invasion depth in early gastric cancer. Gastrointest Endosc 73:917–927
Choi J, Kim SG, Im JP, Kim JS, Jung HC, Song IS (2010) Is endoscopic ultrasonography indispensable in patients with early gastric cancer prior to endoscopic resection? Surg Endosc 24:3177–3185
Gotoda T, Yamamoto H, Soetikno RM (2006) Endoscopic submucosal dissection of early gastric cancer. J Gastroenterol 41:929–942
Yamaguchi N, Isomoto H, Fukuda E, Ikeda K, Nishiyama H, Akiyama M, Ozawa E, Ohnita K, Hayashi T, Nakao K, Kohno S, Shikuwa S (2009) Clinical outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer by indication criteria. Digestion 80:173–181
Park JC, Lee SK, Seo JH, Kim YJ, Chung H, Shin SK, Lee YC (2010) Predictive factors for local recurrence after endoscopic resection for early gastric cancer: long-term clinical outcome in a single-center experience. Surgical Endosc 24:2842–2849
Disclosures
Drs. H. Yoon, S. G. Kim, J. Choi, J. P. Im, J. S. Kim, W. H. Kim, and H. C. Jung have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoon, H., Kim, S.G., Choi, J. et al. Risk factors of residual or recurrent tumor in patients with a tumor-positive resection margin after endoscopic resection of early gastric cancer. Surg Endosc 27, 1561–1568 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-012-2627-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-012-2627-3