Abstract
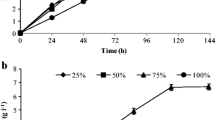
Olive mill wastewater (OMW) characteristics make it a suitable resource to be used as a microbial culture media to produce value-added compounds, such as enzymes. In this work, the ability of the novel species Aspergillus ibericus to discolor OMW and produce lipase was studied. An initial screening on plates containing an OMW-based agar medium and an emulsified olive oil/rhodamine-B agar medium was employed to select the strain A. ibericus MUM 03.49. Then, experiments in conical flasks with liquid OMW-based media showed that the fungus could growth on undiluted OMW, with a chemical oxygen demand (COD) of 97 ± 2 g/L, and to produce up to 2,927 ± 54 U/L of lipase. When pure OMW was used in the media, the maximum COD and color reduction achieved were 45 and 97 %, respectively. When OMW diluted to 10 % was used, A. ibericus was able to reduce phenolic and aromatic compounds by 37 and 39 %, respectively. Additionally, lipase production was found to be promoted by the addition of mineral nutrients. When the fermentations were scaled up to a 2-L bioreactor, A. ibericus produced up to 8,319 ± 33 U/L of lipase, and the maximum COD and color reduction were 57 and 24 %, respectively.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
FAO (2010) Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Statistics. http://faostat.fao.org/site/636/DesktopDefault.aspx?PageID=636#ancor. Accessed 15 Apr 2012
IOC (2012) International Olive Oil Council series of world statistics on production, imports, exports and consumption. http://www.internationaloliveoil.org/estaticos/view/131-world-olive-oil-figures. Accessed 15 Apr 2012
Caputo AC, Scacchia F, Pelagagge PM (2003) Disposal of by-products in olive oil industry: waste-to-energy solutions. Appl Therm Eng 23:197–214
Paraskeva P, Diamadopoulos E (2006) Technologies for olive mill wastewater (OMW) treatment: a review. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 81:1475–1485
Gonçalves C, Pereira C, Alves M, Belo I (2010) Olive mill wastewater as a renewable resource. Environ Eng Manag J 9:319–325
Niaounakis M, Halvadakis CP (2006) Olive processing waste management: literature review and patent survey. Pergamon Press, Oxford, UK
IMPEL (2003) IMPEL Olive oil project report. http://impel.eu/wp-content/uploads/2010/02/2003-03-olive-oil-FINAL-REPORT.pdf. Accessed 15 Apr 2012
INE (2010) Portuguese type of oil press unit and type of extraction system. http://www.ine.pt/xportal/xmain?xpid=INE&xpgid=ine_indicadores&indOcorrCod=0000702&contexto=bd&selTab=tab2. Accessed 15 Apr 2012
Roig A, Cayuela ML, Sanchez-Monedero MA (2006) An overview on olive mill wastes and their valorisation methods. Waste Manag 26:960–969
Morillo J, Antizar-Ladislao B, Monteoliva-Sánchez M, Ramos-Cormenzana A, Russell N (2009) Bioremediation and biovalorisation of olive-mill wastes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 82:25–39
Fenice M, Sermanni GG, Federici F, D’Annibale A (2003) Submerged and solid-state production of laccase and Mn-peroxidase by Panus tigrinus on olive mill wastewater-based media. J Biotechnol 100:77–85
Sayadi S, Ellouz R (1995) Roles of lignin peroxidase and manganese peroxidase from Phanerochaete chrysosporium in the decolorization of olive mill wastewaters. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:1098–1103
Federici F, Montedoro G, Servili M, Petruccioli M (1988) Pectic enzyme production by Cryptococcus albidus var. albidus on olive vegetation waters enriched with sunflower calathide meal. Biol Wastes 25:291–301
Aissam H, Errachidi F, Penninckx MJ, Merzouki M, Benlemlih M (2005) Production of tannase by Aspergillus niger HA37 growing on tannic acid and olive mill waste waters. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 21:609–614
D’Annibale A, Sermanni GG, Federici F, Petruccioli M (2006) Olive-mill wastewaters: a promising substrate for microbial lipase production. Bioresour Technol 97:1828–1833
Lotti M, Monticelli S, Luis Montesinos J, Brocca S, Valero F, Lafuente J (1998) Physiological control on the expression and secretion of Candida rugosa lipase. Chem Phys Lipids 93:143–148
Gonçalves C, Lopes M, Ferreira JP, Belo I (2009) Biological treatment of olive mill wastewater by non-conventional yeasts. Bioresour Technol 100:3759–3763
Lopes M, Araujo C, Aguedo M, Gomes N, Gonçalves C, Teixeira JA, Belo I (2009) The use of olive mill wastewater by wild type Yarrowia lipolytica strains: medium supplementation and surfactant presence effect. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 84:533–537
Asses N, Ayed L, Bouallagui H, Ben Rejeb I, Gargouri M, Hamdi M (2009) Use of Geotrichum candidum for olive mill wastewater treatment in submerged and static culture. Bioresour Technol 100:2182–2188
D’Annibale A, Brozzoli V, Crognale S, Gallo AM, Federici F, Petruccioli M (2006) Optimisation by response surface methodology of fungal lipase production on olive mill wastewater. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 81:1586–1593
Serra R, Cabañes FJ, Perrone G, Castellá G, Venâncio A, Mulè G, Kozakiewicz Z (2006) Aspergillus ibericus: a new species of section Nigri isolated from grapes. Mycologia 98:295–306
Nielsen KF, Mogensen JM, Johansen M, Larsen TO, Frisvad JC (2009) Review of secondary metabolites and mycotoxins from the Aspergillus niger group. Anal Bioanal Chem 395:1225–1242
Peterson RA, Bradner JR, Roberts TH, Nevalainen KMH (2009) Fungi from koala (Phascolarctos cinereus) faeces exhibit a broad range of enzyme activities against recalcitrant substrates. Lett Appl Microbiol 48:218–225
APHA, AWWA, WPCF (1989) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association, Washington
Gonçalves C, Rodriguez-Jasso RM, Gomes N, Teixeira JA, Belo I (2010) Adaptation of dinitrosalicylic acid method to microtiter plates. Anal Methods 2:2046–2048
Singleton VL, Orthofer R, Lamuela-Raventós RM (1999) Analysis of total phenols and other oxidation substrates and antioxidants by means of folin–ciocalteu reagent. In: Lester P (ed) Methods in enzymology—oxidants and antioxidants Part A. Academic Press, San Diego
Weishaar JL, Aiken GR, Bergamaschi BA, Fram MS, Fujii R, Mopper K (2003) Evaluation of specific ultraviolet absorbance as an indicator of the chemical composition and reactivity of dissolved organic carbon. Environ Sci Technol 37:4702–4708
Ben Othman N, Ayed L, Assas N, Kachouri F, Hammami M, Hamdi M (2008) Ecological removal of recalcitrant phenolic compounds of treated olive mill wastewater by Pediococcus pentosaceus. Bioresour Technol 99:2996–3001
Gomes N, Gonçalves C, Garcia-Roman M, Teixeira JA, Belo I (2011) Optimization of a colorimetric assay for yeast lipase activity in complex systems. Anal Methods 3:1008–1013
Lanciotti R, Gianotti A, Baldi D, Angrisani R, Suzzi G, Mastrocola D, Guerzoni ME (2005) Use of Yarrowia lipolytica strains for the treatment of olive mill wastewater. Bioresour Technol 96:317–322
Papagianni M (2004) Fungal morphology and metabolite production in submerged mycelial processes. Biotechnol Adv 22:189–259
Aissam H, Penninckx M, Benlemlih M (2007) Reduction of phenolics content and COD in olive oil mill wastewaters by indigenous yeasts and fungi. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 23:1203–1208
García GI, Peña JPR, Venceslada BJL, Martín MA, Santos MMA, Gómez RE (2000) Removal of phenol compounds from olive mill wastewater using Phanerochaete chrysosporium, Aspergillus niger, Aspergillus terreus and Geotrichum candidum. Process Biochem 35:751–758
Crognale S, D’Annibale A, Federici F, Fenice M, Quaratino D, Petruccioli M (2006) Olive oil mill wastewater valorisation by fungi. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 81:1547–1555
Hamdi M, Bouhamed H, Ellouz R (1991) Optimization of the fermentation of olive mill waste-waters by Aspergillus niger. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 36:285–288
Hamdi M, Khadir A, Garcia JL (1991) The use of Aspergillus niger for the bioconversion of olive mill waste-waters. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 34:828–831
Ramos JT, Barends S, Verhaert R, de Graaff L (2011) The Aspergillus niger multicopper oxidase family: analysis and overexpression of laccase-like encoding genes. Microb Cell Factories 10:78
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the Portuguese Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia (FCT) for the financial support through the Project PTDC/AMB/69379/2006 and Grants SFRH/BPD/43922/2008, PTDC/AMB/69379/2006 and SFRH/BD/27915/2006.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abrunhosa, L., Oliveira, F., Dantas, D. et al. Lipase production by Aspergillus ibericus using olive mill wastewater. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 36, 285–291 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-012-0783-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-012-0783-4