Abstract
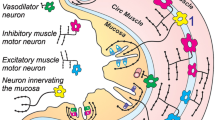
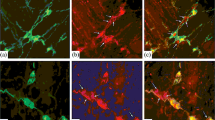
The continuing and even expanding use of genetically modified mice to investigate the normal physiology and development of the enteric nervous system and for the study of pathophysiology in mouse models emphasises the need to identify all the neuron types and their functional roles in mice. An investigation that chemically and morphologically defined all the major neuron types with cell bodies in myenteric ganglia of the mouse small intestine was recently completed. The present study was aimed at the submucosal ganglia, with the purpose of similarly identifying the major neuron types with cell bodies in these ganglia. We found that the submucosal neurons could be divided into three major groups: neurons with vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) immunoreactivity (51% of neurons), neurons with choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) immunoreactivity (41% of neurons) and neurons that expressed neither of these markers. Most VIP neurons contained neuropeptide Y (NPY) and about 40% were immunoreactive for tyrosine hydroxylase (TH); 22% of all submucosal neurons were TH/VIP. VIP-immunoreactive nerve terminals in the mucosa were weakly immunoreactive for TH but separate populations of TH- and VIP-immunoreactive axons innervated the arterioles in the submucosa. Of the ChAT neurons, about half were immunoreactive for both somatostatin and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP). Calretinin immunoreactivity occurred in over 90% of neurons, including the VIP neurons. The submucosal ganglia and submucosal arterioles were innervated by sympathetic noradrenergic neurons that were immunoreactive for TH and NPY; no VIP and few calretinin fibres innervated submucosal neurons. We conclude that the submucosal ganglia contain cell bodies of VIP/NPY/TH/calretinin non-cholinergic secretomotor neurons, VIP/NPY/calretinin vasodilator neurons, ChAT/CGRP/somatostatin/calretinin cholinergic secretomotor neurons and small populations of cholinergic and non-cholinergic neurons whose targets have yet to be identified. No evidence for the presence of type-II putative intrinsic primary afferent neurons was found.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdu F, Hicks GA, Hennig G, Allen JP, Grundy D (2002) Somatostatin sst2 receptors inhibit peristalsis in the rat and mouse jejunum. Am J Physiol 282:G624–G633
Accili EA, Dhatt N, Buchan AMJ (1995) Neural somatostatin, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide and substance P in canine and human jejunum. Neurosci Lett 185:37–40
Banks MR, Farthing MJG, Robberecht P, Burleigh DE (2005) Antisecretory actions of a novel vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) antagonist in human and rat small intestine. Br J Pharmacol 144:994–1001
Bian X, Ren J, DeVries M, Schnegelsberg B, Cockayne DA, Ford APDW, Galligan JJ (2003) Peristalsis is impaired in the small intestine of mice lacking the P2X3 subunit. J Physiol (Lond) 551:309–322
Brehmer A (2006) Structure of enteric neurons. Adv Anat 186:1–94
Brehmer A (2007) The value of neurofilament-immunohistochemistry for identifying enteric neuron types—special reference to intrinsic primary afferent (sensory) neurons. In: Arlen RK (ed) New research on neurofilament proteins. Nova Science, New York, pp 99–114
Chiocchetti R, Grandis A, Bombardi C, Clavenzani P, Costerbosa GL, Lucchi ML, Furness JB (2004) Characterisation of neurons expressing calbindin immunoreactivity in the ileum of the unweaned and mature sheep. Cell Tissue Res 318:289–303
Clarke CM, Plata C, Cole B, Tsuchiya K, La Spada AR, Kapur RP (2007) Visceral neuropathy and intestinal pseudo-obstruction in a murine model of a nuclear inclusion disease. Gastroenterology 133:1971–1978
Costa M, Furness JB (1984) Somatostatin is present in a subpopulation of noradrenergic nerve fibres supplying the intestine. Neuroscience 13:911–919
Cox HM, Rudolph A, Gschmeissner S (1994) Ultrastructural co-localization of neuropeptide Y and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in neurosecretory vesicles of submucous neurons in the rat jejunum. Neuroscience 59:469–476
Cox HM, Pollock EL, Tough IR, Herzog H (2001) Multiple Y receptors mediate pancreatic polypeptide responses in mouse colon mucosa. Peptides 22:445–452
De Jonge F, Van Nassauw L, Adriaensen D, Van Meir F, Miller HRP, Van Marck E, Timmermans J-P (2003a) Effect of intestinal inflammation on capsaicin-sensitive afferents in the ileum of Schistosoma mansoni-infected mice. Histochem Cell Biol 119:477–484
De Jonge F, Van Nassauw L, De Man JG, De Winter BY, Van Meir F, Depoortere I, Peeters TL, Pelckmans PA, Van Marck E, Timmermans J-P (2003b) Effects of Schistosoma mansoni infection on somatostatin and somatostatin receptor 2A expression in mouse ileum. Neurogastroenterol Motil 15:149–159
Ekblad E, Håkanson R, Sundler F (1984) VIP and PHI coexist with an NPY-like peptide in intramural neurones of the small intestine. Regul Pept 10:47–55
Fairman CL, Clagett Dame M, Lennon VA, Epstein ML (1995) Appearance of neurons in the developing chick gut. Dev Dyn 204:192–201
Furness JB (2006) The enteric nervous system. Blackwell, Oxford
Furness JB, Costa M (1979) Projections of intestinal neurons showing immunoreactivity for vasoactive intestinal polypeptide are consistent with these neurons being the enteric inhibitory neurons. Neurosci Lett 15:199–204
Furness JB, Costa M, Emson PC, Håkanson R, Moghimzadeh E, Sundler F, Taylor IL, Chance RE (1983) Distribution, pathways and reactions to drug treatment of nerves with neuropeptide Y- and pancreatic polypeptide-like immunoreactivity in the guinea-pig digestive tract. Cell Tissue Res 234:71–92
Furness JB, Costa M, Keast JR (1984) Choline acetyltransferase and peptide immunoreactivity of submucous neurons in the small intestine of the guinea-pig. Cell Tissue Res 237:329–336
Furness JB, Costa M, Gibbins IL, Llewellyn Smith IJ, Oliver JR (1985) Neurochemically similar myenteric and submucous neurons directly traced to the mucosa of the small intestine. Cell Tissue Res 241:155–163
Furness JB, Costa M, Rökaeus Å, McDonald TJ, Brooks BD (1987) Galanin-immunoreactive neurons in the guinea-pig small intestine: their projections and relationships to other enteric neurons. Cell Tissue Res 250:607–615
Furness JB, Lloyd KCK, Sternini C, Walsh JH (1990) Projections of substance P, vasoactive intestinal peptide and tyrosine hydroxylase immunoreactive nerve fibres in the canine intestine, with special reference to the innervation of the circular muscle. Arch Histol Cytol 53:129–140
Furness JB, Clerc N, Lomax AEG, Bornstein JC, Kunze WAA (2000) Shapes and projections of tertiary plexus neurons of the guinea-pig small intestine. Cell Tissue Res 300:383–387
Furness JB, Alex G, Clark MJ, Lal VV (2003) Morphologies and projections of defined classes of neurons in the submucosa of the guinea-pig small intestine. Anat Rec 272A:475–483
Furness JB, Jones C, Nurgali K, Clerc N (2004a) Intrinsic primary afferent neurons and nerve circuits within the intestine. Prog Neurobiol 72:143–164
Furness JB, Robbins HL, Xiao J, Stebbing MJ, Nurgali K (2004b) Projections and chemistry of Dogiel type II neurons in the mouse colon. Cell Tissue Res 317:1–12
Hens J, Schrödl F, Brehmer A, Adriaensen D, Neuhuber W, Scheuermann DW, Schemann M, Timmermans J-P (2000) Mucosal projections of enteric neurons in the porcine small intestine. J Comp Neurol 421:426–436
Hens J, Vanderwinden J-M, De Laet MH, Scheuermann DW, Timmermans J-P (2001) Morphological and neurochemical identification of enteric neurones with mucosal projections in the human small intestine. J Neurochem 76:464–471
Hoard JL, Hoover DB, Mabe AM, Blakely RD, Feng N, Paolocci N (2008) Cholinergic neurons of mouse intrinsic cardiac ganglia contain noradrenergic enzymes, norepinephrine transporters, and the neurotrophin receptors tropomyosin-related kinase A and p75. Neuroscience 156:129–142
Hoyle CHV, Burnstock G (1989) Neuronal populations in the submucous plexus of the human colon. J Anat 166:7–22
Kummer W, Gibbins IL, Stefan P, Kapoor V (1990) Catecholamines and catecholamine-synthesizing enzymes in guinea-pig sensory ganglia. Cell Tissue Res 261:595–606
Li ZS, Pham TD, Tamir H, Chen JJ, Gershon MD (2004) Enteric dopaminergic neurons: definition, developmental lineage, and effects of extrinsic denervation. J Neurosci 24:1330–1339
Lundgren O (2002) Enteric nerves and diarrhoea. Pharmacol Toxicol 90:109–120
Maccarrone C, Jarrott B (1985) Differences in regional brain concentrations of neuropeptide Y in spontaneously hypertensive SH and Wistar Kyoto WKY rats. Brain Res 345:165–169
Mao Y, Wang B, Kunze W (2006) Characterization of myenteric sensory neurons in the mouse small intestine. J Neurophysiol 96:998–1010
Mashimo H, Kjellin A, Goyal RK (2000) Gastric stasis in neuronal nitric oxide synthase-deficient knockout mice. Gastroenterology 119:766–773
Pham TD, Gershon MD, Rothman TP (1991) Time of origin of neurons in the murine enteric nervous system: sequence in relation to phenotype. J Comp Neurol 314:789–798
Porter AJ, Wattchow DA, Brookes SJ, Costa M (1999) Projections of nitric oxide synthase and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-reactive submucosal neurons in the human colon. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 14:1180–1187
Qu Z-D, Thacker M, Castelucci P, Bagyánszki M, Epstein ML, Furness JB (2008) Immunohistochemical analysis of neuron types in the mouse small intestine. Cell Tissue Res 334:147–161
Ren J, Bian X, DeVries M, Schnegelsberg B, Cockayne DA, Ford APDW, Galligan JJ (2003) P2X2 subunits contribute to fast synaptic excitation in myenteric neurons of the mouse small intestine. J Physiol (Lond) 552:809–821
Sanders KM, Smith TK (1986) Motoneurones of the submucous plexus regulate electrical activity of the circular muscle of the canine proximal colon. J Physiol (Lond) 380:293–310
Sang Q, Young HM (1996) Chemical coding of neurons in the myenteric plexus and external muscle of the small and large intestine of the mouse. Cell Tissue Res 284:39–53
Sang Q, Young HM (1998) The identification and chemical coding of cholinergic neurons in the small and large intestine of the mouse. Anat Rec 251:185–199
Sang Q, Williamson S, Young HM (1997) Projections of chemically identified myenteric neurons of the small and large intestine of the mouse. J Anat 190:209–222
Timmermans J-P, Scheuermann DW, Barbiers M, Adriaensen D, Stach W, Van Hee R, De Groodt Lasseel MHA (1992) Calcitonin gene-related peptide-like immunoreactivity in the human small intestine. Acta Anat 143:48–53
Timmermans J-P, Adriaensen D, Cornelissen W, Scheuermann DW (1997) Structural organization and neuropeptide distribution in the mammalian enteric nervous system, with special attention to those components involved in mucosal reflexes. Comp Biochem Physiol [A] 118:331–340
Timmermans J-P, Hens J, Adriaensen D (2001) Outer submucous plexus: an intrinsic nerve network involved in both secretory and motility processes in the intestine of large mammals and humans. Anat Rec 262:71–78
Van Nassauw L, Hens J, Bogers J, Van Marck E, Timmermans J-P (2000) Retrograde DiI tracing of enteric neurons projecting to the mucosa in the murine small intestine. In: Krammer H-J, Singer MV (eds) Neurogastroenterology, from the basics to the clinics. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, pp 92–95
Van Op Den Bosch J, Lantermann K, Torfs P, Van Marck E, Van Nassauw L, Timmermans J-P (2008) Distribution and expression levels of somatostatin and somatostatin receptors in the ileum of normal and acutely Schistosoma mansoni-infected SSTR2 knockout/lacZ knockin mice. Neurogastroenterol Motil 20:798–807
Vanner S, MacNaughton WK (2004) Submucosal secretomotor and vasodilator reflexes. Neurogastroenterol Motil 16s1:39–43
Wedel T, Roblick U, Gleiss J, Schiedeck T, Bruch H-P, Kühnel W, Krammer H-J (1999) Organization of the enteric nervous system in the human colon demonstrated by wholemount immunohistochemistry with special reference to the submucous plexus. Ann Anat 181:327–337
Weihe E, Tao Cheng JH, Schäfer MKH, Erickson JD, Eiden LE (1996) Visualization of the vesicular acetylcholine transporter in cholinergic nerve terminals and its targeting to a specific population of small synaptic vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:3547–3552
Weihe E, Schütz B, Hartschuh W, Anlauf M, Schäfer MK, Eiden LE (2005) Coexpression of cholinergic and noradrenergic phenotypes in human and nonhuman autonomic nervous system. J Comp Neurol 492:370–379
Williamson S, Pompolo S, Furness JB (1996) GABA and nitric oxide synthase immunoreactivities are colocalized in a subset of inhibitory motor neurons of the guinea-pig small intestine. Cell Tissue Res 284:29–37
Wilson AJ, Llewellyn Smith IJ, Furness JB, Costa M (1987) The source of the nerve fibres innervating the circular muscle and forming the deep muscular plexus in the guinea-pig small intestine. Cell Tissue Res 247:497–504
Wong V, Blennerhassett M, Vanner S (2008) Electrophysiological and morphological properties of submucosal neurons in the mouse distal colon. Neurogastroenterol Motil 20:725–734
Young HM, Ciampoli D (1998) Transient expression of neuronal nitric oxide synthase by neurons of the submucous plexus of the mouse small intestine. Cell Tissue Res 291:395–401
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by a grant from the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia (grant no. 400020) and an Australian Research Council international linkage grant (no. LZ0882269) for collaboration between the Melbourne and Bologna laboratories.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mongardi Fantaguzzi, C., Thacker, M., Chiocchetti, R. et al. Identification of neuron types in the submucosal ganglia of the mouse ileum. Cell Tissue Res 336, 179–189 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-009-0773-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-009-0773-2