Abstract
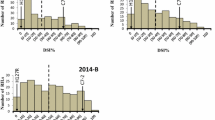
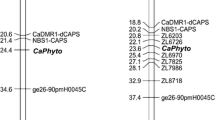
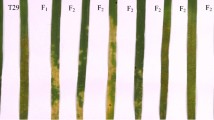
Stalk rots are destructive diseases in maize around the world, and are most often caused by the pathogen Pythium, Fusarium and other fungi. The most efficient management for controlling stalk rots is to breed resistant cultivars. Pythium stalk rot can cause serious yield loss on maize, and to find the resistance genes from the existing germplasm is the basis to develop Pythium-resistance hybrid lines. In this study, we investigated the genetic resistance to Pythium stalk rot in inbred line Qi319 using F2 and F2:3 population, and found that the resistance to Pythium inflatum in Qi319 was conferred by two independently inherited dominant genes, RpiQI319-1 and RpiQI319-2. Linkage analysis uncovered that the RpiQI319-1 co-segregated with markers bnlg1203, and bnlg2057 on chromosome 1, and that the RpiQI319-2 locus co-segregated with markers umc2069 and bnlg1716 on chromosome 10. The RpiQI319-1 locus was further mapped into a ~500-kb interval flanked by markers SSRZ33 and SSRZ47. These results will facilitate marker-assisted selection of Pythium stalk rot-resistant cultivars in maize breeding. To our knowledge, this is the first report on the resistance to P. inflatum in the inbred line Qi319, and is also the first description of two independently inherited dominant genes conferring the resistance of Pythium stalk rot in maize.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bahrini I, Ogawa T, Kobayashi F, Kawahigashi H, Handa H (2011) Overexpression of the pathogen-inducible wheat TaWRKY45 gene confers disease resistance to multiple fungi in transgenic wheat plants. Breed Sci 61:319–326
Chen SJ, Song TM (1999) Disease resistance of maize stalk rot simple genetics controlled by single gene. Acta China Agric Univ 4:56
Chung C-L, Poland J, Kump K, Benson J, Longfellow J, Walsh E, Balint-Kurti P, Nelson R (2011) Targeted discovery of quantitative trait loci for resistance to northern leaf blight and other diseases of maize. Theor Appl Genet 123:307–326
Danson J, Lagat M, Kimani M, Kuria A (2008) Quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for resistance to gray leaf spot and common rust diseases of maize. Afr J Biotechnol 7:3247–3254
Di Renzo MA, Bonamico NC, Díaz DG, Ibañez MA, Faricelli ME, BalzarinI MG, Salerno JC (2004) Microsatellite markers linked to QTL for resistance to Mal de Río Cuarto disease in Zea mays L. J Agric Sci 142:289–295
Kosambi DD (1944) The estimation of map distance from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–175
Lehmensiek A, Esterhuizen AM, van Staden D, Nelson SW, Retief AE (2001) Genetic mapping of gray leaf spot (GLS) resistance genes in maize. Theor Appl Genet 103:797–803
Li Q, Wan JM (2005) SSRHunter: development of a local searching software for SSR sites. Hereditas 27:808–810
Lincoln S, Daly M, Lander E (1992) Constructing genetic maps with Mapmaker/EXP30 Whitehead Institute Technical Report, 3rd edn. Whitehead Institute, Cambridge
Lu XW, Brewbaker JL (1999) Molecular mapping of QTLs conferring resistance to Sphacelotheca reiliana (Kühn) Clint. Maize Genet Coop Newsl 73:36
Lu GZ, Chen J, Liu WC, Zhou YL, Zhao TC, Liang JY, Bai QK (1995) The pathogens of corn stalk rot and variety resistance. Fungal Genet Biol 3:47–51
Luan J, Wang F, Li Y, Zhang B, Zhang J (2012) Mapping quantitative trait loci conferring resistance to rice black-streaked virus in maize (Zea mays L.). Theor Appl Genet 125:781–791
McCouch SR, Kochert G, Yu ZH, Wang ZY, Khush GS, Coffman WR, Tanksley SD (1988) Molecular mapping of rice chromosomes. Theor Appl Genet 76:815–829
Michelmore RW, Paran I, Kesseli RV (1991) Identification of markers linked to disease-resistance genes by bulked segregant analysis: a rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions by using segregating populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:9828–9832
Pe ME, Gianfranceschi L, Taramino G, Tarchini R, Angelini P, Dani M, Binelli G (1993) Mapping quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for resistance to Gibberella zeae infection in maize. Mol Gen Genet 241:11–16
Pronczuk M, Pronczuk S, Messyasz M (1991) Pathogenicity of Fusarium SPP. contributing to the stalk rot of Maize in Poland. Mycotoxin Research 7(2) Supplement: 2, 97–101
Ramsey MD (1990) Etiology of coot and stalk rots of maize in north Queensland: 2. Pathogenicity of fungi, including Pyrenochaeta indica, a new record. Australas Plant Pathol 19:52–55
Robertson-Hoyt LA, Jines MP, Balint-Kurti PJ, Kleinschmidt CE, White DG, Payne GA, Maragos CM, Molnár TL, Holland JB (2006) QTL mapping for Fusarium ear rot and fumonisin contamination resistance in two maize populations. Crop Sci 46:1734–1743
Toman J, White DG (1993) Inheritance of resistance to anthracnose stalk rot of corn. Phytopathology 83:981–986
Wang X, Zhang Y, Xu X, Li H, Wu X, Zhang S, Li X (2014) Evaluation of maize inbred lines currently used in Chinese breeding programs for resistance to six foliar diseases. The Crop Journal 2:213–222
White DG (1999) Compendium of corn diseases, 3rd edn. APS Press, St Paul USA
Wisser RJ, Kolkman JM, Patzoldt ME, Holland JB, Yu J, Krakowsky M, Nelson RJ, Balint-Kurti PJ (2011) Multivariate analysis of maize disease resistances suggests a pleiotropic genetic basis and implicates a GST gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:7339–7344
Wu QA, Zhu XY, Lin HX, Jin TJ, Wang GY (1997) Methodological study on the isolation and determination of infectious ability of the pathogen for maize stalk rot. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica 27:29–35
Yang DE, Wang YG, Cheng CX, Wang B, Zhang CL, Chen SJ (2002a) Review of maize stalk rot in China. J Maize Sci 10:88–90
Yang DE, Zhang CL, Cheng CX, Wang YG, Wang B, Chen SJ (2002b) Genetics analysis of gene resistant to pathogen Fusarium graminearum in maize. Acta Agronomica Sinica 28:389–393
Yang DE, Zhang CL, Zhang DS, Jin DM, Weng ML, Chen SJ, Nguyen H, Wang B (2004) Genetic analysis and molecular mapping of maize (Zea mays L.) stalk rot resistant gene Rfg1. Theor Appl Genet 108:706–711
Yang DE, Jin DM, Wang B, Zhang DS, Nguyen HT, Zhang CL, Chen SJ (2005) Characterization and mapping of Rpi1, a gene that confers dominant resistance to stalk rot in maize. Mol Genet Genomics 274:229–234
Yang Q, Yin G, Guo Y, Zhang D, Chen S, Xu M (2010) A major QTL for resistance to Gibberella stalk rot in maize. Theor Appl Genet 121:673–687
Zambrano JL, Jones MW, Brenner E, Francis DM, Tomas A, Redinbaugh MG (2014) Genetic analysis of resistance to six virus diseases in a multiple virus-resistant maize inbred line. Theor Appl Genet 127:867–880
Zhang D, Liu Y, Guo Y, Yang Q, Ye J, Chen S, Xu M (2012) Fine-mapping of qRfg2, a QTL for resistance to Gibberella stalk rot in maize. Theor Appl Genet 124:585–596
Acknowledgments
We thank Hai Wang, Biotechnology Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, for revision and helpful comments on the manuscript. This work was funded by the China Agriculture Research System (Maize) from the Ministry of Agriculture of China (CARS-02), the Public Welfare Special Fund from Institute of Crop Science, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (2060302-2-13), and the Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program from Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by J. Lai.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, FJ., Xiao, MG., Duan, CX. et al. Two genes conferring resistance to Pythium stalk rot in maize inbred line Qi319. Mol Genet Genomics 290, 1543–1549 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-015-1019-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-015-1019-5