Abstract
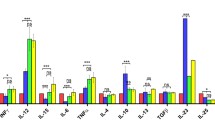
Resistance and susceptibility to different parasitic diseases have been associated with the predominance of Th1- or Th2-type immune responses. In experimental murine cysticercosis a Th1 response seems to be involved in resistance, whereas Th2 activity is associated with heavy parasite intensities. To test this notion the roles of Th1- and Th2-type cytokines in infected mice were studied after treatment with anticytokine monoclonal antibodies or with recombinant murine cytokines during early stages of infection. Mice receiving anti-interleukin 10 (IL-10) carried lower parasite intensities than did control mice and developed a strong Th1-type response, whereas mice receiving anti-interferon gamma (IFN-γ) showed a dramatic increase in susceptibility. Treatment with recombinant cytokines confirmed these results; mice receiving IFN-γ and IL-2 showed low parasite numbers, whereas IL-10 induced a significant increase in parasite loads. Thus, the Th1-type immune response plays a fundamental role in protection against Taenia crassiceps cysticercosis, whereas Th2, at least through IL-10, favors parasite establishment.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 29 May 1998 / Accepted: 3 July 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Terrazas, L., Cruz, M., Rodríguez-Sosa, M. et al. Th1-type cytokines improve resistance to murine cysticercosis caused by Taenia crassiceps . Parasitol Res 85, 135–141 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004360050522
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004360050522