Abstract
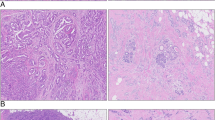
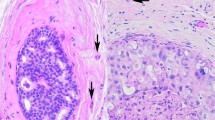
Breast carcinomas are graded according to the “Nottingham modification of the Bloom–Richardson system” (SBR). The system is hindered, however, by lack of precision in assessing all three parameters including nuclear grade, mitosis, and tubular formation, leading to an element of subjectivity. Our objective was to evaluate a new grading system [the nuclear grade plus proliferation (N+P) system] for subjectivity, ease, and better representation of tumor biology. Its components are nuclear grade and automated proliferation index. Invasive ductal carcinomas, consisting of 137 SBR grade I, 247 grade II, and 266 grade III, were re-evaluated by the N+P system. The two systems were compared with each other and correlated with patients’ overall survival, tumor size, angiolymphatic invasion, lymph node status, and biomarker status including estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, p53, epidermal growth factor receptor, BCL-2, and Her-2. Although there was an agreement between the two systems with histologic and prognostic parameters studied, there was 37% disagreement when grading individual tumors. Fifty-three percent of SBR grade II tumors were “down-graded” to N+P grade I, and 7% were “up-graded” to N+P grade III. Distinction among the different histologic grades for overall survival curves was better indicated by the N+P than the SBR system.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bane AL, Tjan S, Parkes RK, Andrulis I, O’Malley FP (2005) Invasive lobular carcinoma: to grade or not to grade. Mod Pathol 18:621–628
Black MM, Barclay THC, Hankey BF (1975) Prognosis in breast cancer utilizing histologic characteristics of the primary tumor. Cancer 36:2048–2055
Bloom HJG, Richardson WW (1957) Histologic grading in breast cancer: a study of 1,409 cases of which 359 have been followed for 15 years. Br J Cancer 11:359–377
Boiesen P, Bendahl PO, Anagnostaki L, Domanski H, Holm E, Idvall I, Johansson S, Ljungberg O, Ringberg A, Ostberg G, Ferno M (2000) Histologic grading in breast cancer—reproducibility between seven pathologic departments. South Sweden Breast Cancer Group. Acta Oncol 39:41–45
Brown RW, Allred CD, Clark GM, Osborne CK, Hilsenbeck SG (1996) Prognostic value of Ki-67 compared to S-phase fraction in axillary node-negative breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2:585–592
Cady B, Stone MD, Schuler JG, Thakur R, Wanner MA, Lavin PT (1996) The new era in breast cancer. Invasion, size and nodal involvement dramatically decreasing as a result of mammography screening. Arch Surg 131:301–308
Cattoretti G, Becker MH, Key G, Duchrow M, Schluter C, Galle J, Gerdes J (1992) Monoclonal antibodies against recombinant parts of the Ki-67 antigen (MIB-1 and MIB-3) detect proliferating cells in microwave-processed formalin-fixed paraffin sections. J Pathol 168:357–363
Chia SK, Speers CH, Bryce CJ, Hayes MM, Olivotto IA (2004) Ten-year outcomes in a population-based cohort of node-negative, lymphatic, and vascular invasion-negative early breast cancers without adjuvant systemic therapies. J Clin Oncol 22:1630–1637
Clahsen PC, van de Velde CJ, Duval C, Pallud C, Mandard AM, Delobelle-Deroide A, van den Broek L, van de Vijver MJ (1999) The utility of mitotic index, oestrogen receptor and Ki-67 measurements in the creation of novel prognostic indices for node-negative breast cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol 25:356–363
Dalton LW, Page DL, Dupont WD (1994) Histologic grading of breast carcinoma. A reproducibility study. Cancer 73:2765–2770
Dalton LW, Pinder SE, Elston CE, Page DL, Dupont WD, Blamey RW (2000) Histologic grading of breast cancer: linkage of patient outcome with level of pathologist agreement. Mod Pathol 13:730–735
Davis BW, Gelber R, Goldhirsch A, Hartmann WH, Hollaway L, Russell I, Rudenstam CM (1985) Prognostic significance of peritumoral vessel invasion in clinical trials of adjuvant therapy for breast cancer with axillary lymph node metastasis. Human Pathol 16:1212–1218
Delides GS, Garas G, Georgouli G, Jiortziotis D, Lecca J, Liva T, Elemenoglou J (1982) Intralaboratory variations in the grading of breast carcinoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med 106:126–128
Eisen T, Smith IE, Johnston S, Ellis PA, Prendiville J, Seymour MT, Walsh G, Ashley S (1998) Randomized phase II trial of infusional fluorouracil, epirubicin and cyclophosphamide versus infusional fluorouracil, epirubicin and cisplatin in patients with advanced breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 16:1350–1357
Ellis IO, Galea M, Broughton N, Locker A, Blamey RW, Elston CW (1992) Pathological prognostic factors in breast cancer. II. Histological type. Relationship with survival in a large study with long-term follow up. Histopathology 20:479–489
Elston CW, Ellis IO (1991) Pathological prognostic factors in breast cancer. I. The value of histological grade in breast cancer: experience from a large study with long-term follow up. Histopathology 19:403–410
Fisher B, Bryant J, Wolmark N, Mamounas E, Brown A, Fisher ER, Wickerham DL, Begovic M, DeCillis A, Robidoux A, Margolese RG, Cruz AB Jr, Hoehn JL, Lees AW, Dimitrov NV, Bear HD (1998) Effect of preoperative chemotherapy on the outcome of women with operable breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 16:2672–2685
Fisher ER, Redmond C, Fisher B (1980) Histologic grading of breast cancer. Pathol Annu 15:239–251
Frierson HF Jr, Wolber RA, Berean KW, Franquemont DW, Gaffey MJ, Boyd JC, Wilbur DC (1995) Interobserver reproducibility of the Nottingham modification of the Bloom and Richardson histologic grading scheme for infiltrating ductal carcinoma. Am J Clin Pathol 103:195–198
Gerdes J, Lemke H, Baisch H, Wacker H-H, Schwab U, Stein H (1984) Cell cycle analysis of a cell proliferation-associated human nuclear antigen defined by the monoclonal antibody Ki-67. J Immunol 133:1710–1715
Greenhough RB (1925) Varying degree of malignancy in cancer of the breast. J Cancer Res 9:453–463
Haagensen CD (1933) The basis for histologic grading of the breast. Am J Cancer 1:285–327
Haerslev T, Jacobsen GK, Zedeler K (1996) Correlation of growth fraction by Ki-67 and proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) immunohistochemistry with histopathological parameters and prognosis in primary breast carcinomas. Breast Cancer Res Treat 37:101-113
Harvey JM, de Klerk NH, Sterrett GF (1992) Histological grading in breast cancer. Interobserver agreement and relation to other prognostic factors including ploidy. Pathology 24:63–68
Hilbe W, Gachter A, Duba HC, Dirnhofer S, Eisterer W, Schmid T, Mildner A, Bodner J, Woll E (2003) Comparison of automated cellular imaging system and manual microscopy for immunohistochemically stained cryostat sections of lung cancer specimens applying p53, Ki-67 and p120. Oncol Rep 10:15–20
Hlupic L, Jakic-Razumovic J, Bozikov J, Coric M, Belev B, Vrbanec D (2004) Prognostic values of different factors in breast carcinoma. Tumori 90:112–119
Jansen RL, Hupperets PS, Arends JW, Joosten-Achjanie SR, Volovics A, Schouten HC, Hillen HF (1998) MIB-1 labeling index is an independent prognostic marker in primary breast cancer. Br J Cancer 78:460–465
Keshgegian AA, Cnaan A (1995) Proliferation markers in breast carcinoma. Mitotic figure count, S-phase fraction, proliferating cell nuclear antigen, Ki-67 and MIB-1. Am J Clin Pathol 104:42–49
Kronqvist P, Montironi R, Kuopio T, Collan YU (1997) Subjective breast cancer grading. Analyses of reproducibility after application of Bayesian belief networks. Anal Quant Cytol Histol 19:423–429
Lakhani SR, Jacquemier J, Sloane JP, Gusterson BA, Anderson TJ, van de Vijver MJ, Farid LM, Venter D, Antoniou A, Storfer-Isser A, Smyth E, Steel CM, Haites N, Scott RJ, Goldgar D, Neuhausen S, Daly PA, Ormiston W, McManus R, Scherneck S, Ponder BA, Ford D, Peto J, Stoppa-Lyonnet D, Bignon YJ, Struewing JP, Spurr NK, Bishop DT, Klijn JG, Devilee P, Cornelisse CJ, Lasset C, Lenoir G, Barkardottir RB, Egilsson V, Hamann U, Chang-Claude J, Sobol H, Weber B, Stratton MR, Easton DF (1998) Multifactorial analysis of differences between sporadic breast cancer and cancers involving BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations. J Natl Cancer Inst 90:1138–1145
Le Doussal V, Tubiana-Hulin M, Friedman S, Hacene K, Spyratos F, Brunet M (1989) Prognostic value of histologic grade nuclear components of Scarff–Bloom–Richardson (SBR). An improved score modification based on a multivariate analysis of 1262 invasive ductal breast carcinomas. Cancer 64:1914–1921
Lehr HA, Hansen DA, Kussick S, Li M, Hwang H, Krummenauer F, Trouet S, Gown AM (1999) Assessment of proliferative activity in breast cancer: MIB-1 immunohistochemistry versus mitotic figure count. Human Pathol 30:1314–1320
Leonardi E, Girlando S, Serio G, Mauri FA, Perrone G, Scampini S, Dalla Palma P, Barbareschi M (1992) PCNA and Ki67 expression in breast carcinoma: correlations with clinical and biological variables. J Clin Pathol 45:416–419
Marchetti E, Querzoli P, Marzola A, Bagni A, Ferretti S, Fabris G, Nenci I (1990) Assessment of proliferative rate of breast cancer by Ki-67 monoclonal antibody. Mod Pathol 3:31–35
Mengel M, von Wasielewski R, Wiese B, Rudiger T, Muller-Hermelink HK, Kreipe H (2002) Inter-laboratory and inter-observer reproducibility of immunohistochemical assessment of the Ki-67 labeling index in large multi-centre trial. J Pathol 198:292–299
Meyer JS, Alvarez C, Milikowski C, Olson N, Russo I, Russo J, Glass A, Zehnbauer BA, Lister K, Parwaresch R, Cooperative Breast Cancer Tissue Resource (2005) Breast carcinoma malignancy grading by Bloom–Richardson system vs. proliferation index: reproducibility of grade and advantages of proliferation index. Mod Pathol 18:1067–1078
Offersen BV, Sorensen FB, Knoop A, Overgaard J, Danish Breast Cancer Cooperative Tumour Biology Committee (2003) The prognostic relevance of estimates of proliferative activity in early breast cancer. Histopathology 43:573–582
Page DL, Ellis IO, Elston CW (1995) Histologic grading of breast cancer. Let’s do it. Am J Clin Pathol 103:123–124
Patey DH, Scarff RW (1928) The position of histology in the prognosis of the breast. Lancet 1:801–804
Petit T, Wilt M, Velten M, Millon R, Rodier JF, Borel C, Mors R, Haegele P, Eber M, Ghnassia JP (2004) Comparative value of tumour grade, hormonal receptors, Ki-67, HER-2 and topoisomerase II alpha status as predictive markers in breast cancer patients with neoadjuvant anthracycline based chemotherapy. Eur J Cancer 40:205–211
Pinder SE, Murray S, Ellis IO, Trihia H, Elston CW, Gelber RD, Goldhirsch A, Lindtner J, Cortes-Funes H, Simoncini E, Byrne MJ, Golouh R, Rudenstam CM, Castiglione-Gertsch M, Gusterson BA (1998) The importance of histologic grade in invasive breast carcinoma and response to chemotherapy. Cancer 83:1529–1539
Pinder SE, Wencyk P, Sibbering DM, Bell JA, Elston CW, Nicholson R, Robertson JF, Blamey RW, Ellis IO (1995) Assessment of the new proliferation marker MIB-1 in breast carcinoma using image analysis: associations with other prognostic factors and survival. Br J Cancer 71:146–149
Powles TJ, Hickish TF, Makris A, Ashley SE, O’Brien ME, Tidy VA, Casey S, Nash AG, Sacks N, Cosgrove D et al (1995) Randomized trial of chemoendocrine therapy started before and after surgery for treatment of primary breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 13:547–552
Raabe NK, Schistad O, Sauer T, Bofin A, Kaaresen R, Fossaa SD (1997) Prognosis of radically operated breast carcinoma patients. A retrospective study of 167 consecutive patients with emphasis on histopathological grading, reproducibility and mean nuclear area. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand APMIS 105:363–370
Robbins P, Pinder S, de Klerk N, Dawkins H, Harvey J, Sterrett G, Ellis I, Elston C (1995) Histological grading of breast carcinomas: a study of interobserver agreement. Human Pathol 26:873–879
Rudolph P, MacGrogan G, Bonichon F, Frahm SO, de Mascarel I, Trojani M, Durand M, Avril A, Coindre JM, Parwaresch R (1999) Prognostic significance of Ki-67 and topoisomerase II alpha expression in infiltrating ductal carcinoma of the breast. Breast Cancer Res Treat 55:61–71
Sediman JD, Schnaper LA, Aisner SC (1995) Relationship of the size of the invasive component of the primary breast carcinoma to axillary lymph node metastasis. Cancer 75:65–71
Sikka M, Agarwal S, Bhatia A (1999) Interobserver agreement of the Nottingham histologic grading scheme for infiltrating duct carcinoma breast. Indian J Cancer 36:149–153
Sinha PS, Bendall S, Bates T (2000) Does routine grading of invasive lobular cancer of the breast have the same prognostic significance as for ductal cancers? Eur J Surg Oncol 26:733–737
Spyratos F, Ferrero-Pous M, Trassard M, Hacene K, Phillips E, Tubiana-Hulin M, Le Doussal V (2002) Correlation between MIB-1 and other proliferation markers: clinical implications of the MIB-1 cutoff value. Cancer 94:2151–2159
Stenkvist B, Bengtsson E, Eriksson O, Jarkrans T, Nordin B, Westman-Naeser S (1982) Histopathological systems of breast classification: reproducibility and clinical significance. J Clin Pathol 36:392–398
Tavassoli FA, Devilee P (eds) (2003) World Health Organization classification of tumours. Pathology and genetics. Tumours of the breast and female genital organs. Chapter 1. IARC, Lyon, France, pp 9–112
Tawfik O, Davis MK, Clark J, Fan F, Damjanov I, Namiq A, Thomas P, Kimler BF (2006) A newly proposed semi-automated method of grading ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast. 19 (Suppl):43A (abstract 187)
Theissig F, Kunze KD, Haroske G, Meyer W (1990) Histological grading of breast cancer. Interobserver, reproducibility and prognostic significance. Pathol Res Pract 186:732–736
Tot T (2006) The limited prognostic value of measuring and grading small invasive breast carcinomas: the whole sick lobe versus the details within it. Med Sci Monit 12:RA170–RA175
Trihia H, Murray S, Price K, Gelber RD, Golouh R, Goldhirsch A, Coates AS, Collins J, Castiglione-Gertsch M, Gusterson BA, International Breast Cancer Study Group (2003) Ki-67 expression in breast carcinoma. Its association with grading systems, clinical parameters, and other prognostic factors—a surrogate marker? Cancer 97:1321–1331
Von Hansemann D (1892) Ueber die Anaplasie der Geschwulstzellen und die asymmetrische mitose. Virchows Arch Pathol Anat 129:436–449
Warnberg F, Nordgren H, Bergkvist L, Holmberg L (2001) Tumour markers in breast carcinoma correlate with grade rather than with invasiveness. Br J Cancer 85:869–874
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tawfik, O., Kimler, B.F., Davis, M. et al. Grading invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast: advantages of using automated proliferation index instead of mitotic count. Virchows Arch 450, 627–636 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-007-0400-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-007-0400-0