Abstract
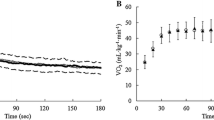
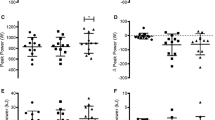
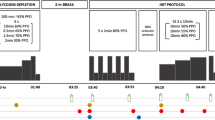
The relationship between work rate (W˙) and time to exhaustion (t) during intense exercise is commonly described by either a hyperbolic function (NLin), t=W ′/(W˙−W˙ cp), or by its linear equivalent (LinW) W lim =W ′+W˙ cp(t). The parameter W˙<INF </INF>cp (critical power) has been described as an inherent characteristic of the aerobic energy system, while W ′ has been shown to be a ralid estimate of anaerobic work capacity. Recent studies have demonstrated that oral supplementation of creatine monohydrate (CrH2O) increases total muscle creatine stores, and have linked these increases to improved performances in intense intermittent exercise. This study was conducted to determine the effect of CrH2O supplementation on estimates of W ′ and W˙<INF </INF>cp derived from the NLin and LinW equations, and to determine the effect of CrH2O on t in exhaustive constant power exercise of different intensities. Fifteen active but untrained university students completed three phases of testing on a cycle ergometer: (1) familiarization, three learning trials, (2) baseline determination of W ′ and W˙<INF </INF>cp, four bouts performed at a W˙ selected to elicit fatigue in 90–600 s, and (3) experimental determination of W ′ and W˙ cp, four bouts performed at the same W˙ as baseline, but performed after 5 days of ingesting either a placebo (4 × 6 g of glucose/day) or CrH2O (4 × 5 g of CrH2O and 1 g glucose/day). Testing was administered in a double-blind manner. Analyses of covariance revealed a significant effect for CrH2O on both estimates of W ′ (NLin, P=0.04; LinW, P<0.01), but not on estimates of W˙ cp (NLin, P=0.37; LinW; P=0.30). Within groups, t was significantly different for only CrH2O at the two highest W˙s (P=0.04). It is concluded that oral ingestion of CrH2O increases estimates of W ′ due to an improved t at the shorter, more intense exercise bouts.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Accepted: 1 September 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smith, J., Stephens, D., Hall, E. et al. Effect of oral creatine ingestion on parameters of the work rate-time relationship and time to exhaustion in high-intensity cycling. Eur J Appl Physiol 77, 360–365 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004210050345
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004210050345