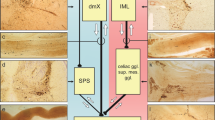
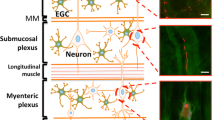
Abstract
Gastrointestinal dysfunction is a prominent non-motor feature of Parkinson’s disease (PD) that contributes directly to the morbidity of patients, complicates management of motor symptoms, and may herald incipient PD in patients without motor disability. Although PD has traditionally been considered a disease of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra, analyses of gastrointestinal samples from PD patients have consistently revealed pathology in the enteric nervous system. The relationship of PD pathology to GI dysmotility is poorly understood, and this lack of understanding has led to limited success in developing treatments for PD-related GI symptoms. We have quantitatively compared myenteric neuron density and relative abundance of NO, VIP, and catecholamine neurons between patients with PD and control individuals along the length of the GI tract. In addition, we have examined the frequency of GI α-synuclein neuritic pathology and its co-localization with the same neuronal markers. We have included a comparison with a small population of patients with incidental Lewy bodies found at autopsy. These data indicate that there is no neuronal loss in the myenteric plexus in PD. Lewy body pathology parallels parasympathetic autonomic input from the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus, not the distribution of extrinsic sympathetic input or intrinsic enteric neurons, and is only rarely co-localized with tyrosine hydroxylase. These data provide a critical background to which further analyses of the effect of PD on the GI tract may be compared and suggest that neuropathology in myenteric neurons is unlikely to be a causative factor in PD-related GI dysmotility.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott RD, Petrovitch H, White LR, Masaki KH, Tanner CM, Curb JD, Grandinetti A, Blanchette PL, Popper JS, Ross GW (2001) Frequency of bowel movements and the future risk of Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 57(3):456–462
Anderson G, Noorian AR, Taylor G, Anitha M, Bernhard D, Srinivasan S, Greene JG (2007) Loss of enteric dopaminergic neurons and associated changes in colon motility in an MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Exp Neurol 207(1):4–12
Anlauf M, Schafer MK, Eiden L, Weihe E (2003) Chemical coding of the human gastrointestinal nervous system: cholinergic, VIPergic, and catecholaminergic phenotypes. J Comp Neurol 459(1):90–111
Ashraf W, Wszolek ZK, Pfeiffer RF, Normand M, Maurer K, Srb F, Edwards LL, Quigley EM (1995) Anorectal function in fluctuating (on-off) Parkinson’s disease: evaluation by combined anorectal manometry and electromyography. Mov Disord 10(5):650–657
Aube AC, Cabarrocas J, Bauer J, Philippe D, Aubert P, Doulay F, Liblau R, Galmiche JP, Neunlist M (2006) Changes in enteric neurone phenotype and intestinal functions in a transgenic mouse model of enteric glia disruption. Gut 55(5):630–637. doi:10.1136/gut.2005.067595
Beach TG, Adler CH, Sue LI, Vedders L, Lue L, White Iii CL, Akiyama H, Caviness JN, Shill HA, Sabbagh MN, Walker DG (2010) Multi-organ distribution of phosphorylated alpha-synuclein histopathology in subjects with Lewy body disorders. Acta Neuropathol 119(6):689–702
Beach TG, White CL, Hamilton RL, Duda JE, Iwatsubo T, Dickson DW, Leverenz JB, Roncaroli F, Buttini M, Hladik CL, Sue LI, Noorigian JV, Adler CH (2008) Evaluation of alpha-synuclein immunohistochemical methods used by invited experts. Acta Neuropathol 116(3):277–288
Belai A, Burnstock G (1999) Distribution and colocalization of nitric oxide synthase and calretinin in myenteric neurons of developing, aging, and Crohn’s disease human small intestine. Dig Dis Sci 44(8):1579–1587
Bernard CE, Gibbons SJ, Gomez-Pinilla PJ, Lurken MS, Schmalz PF, Roeder JL, Linden D, Cima RR, Dozois EJ, Larson DW, Camilleri M, Zinsmeister AR, Pozo MJ, Hicks GA, Farrugia G (2009) Effect of age on the enteric nervous system of the human colon. Neurogastroenterol Motil 21(7):746-e46
Bernardini N, Segnani C, Ippolito C, De Giorgio R, Colucci R, Faussone-Pellegrini MS, Chiarugi M, Campani D, Castagna M, Mattii L, Blandizzi C, Dolfi A (2012) Immunohistochemical analysis of myenteric ganglia and interstitial cells of Cajal in ulcerative colitis. J Cell Mol Med 16(2):318–327. doi:10.1111/j.1582-4934.2011.01298.x
Braak H, de Vos RA, Bohl J, Del Tredici K (2006) Gastric alpha-synuclein immunoreactive inclusions in Meissner’s and Auerbach’s plexuses in cases staged for Parkinson’s disease-related brain pathology. Neurosci Lett 396(1):67–72
Brehmer A, Schrodl F, Neuhuber W (2006) Morphology of VIP/nNOS-immunoreactive myenteric neurons in the human gut. Histochem Cell Biol 125(5):557–565
Derkinderen P, Rouaud T, Lebouvier T, Bruley des Varannes S, Neunlist M, De Giorgio R (2011) Parkinson disease: the enteric nervous system spills its guts. Neurology 77(19):1761–1767. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e318236ef60
Djaldetti R, Ziv I, Melamed E (1996) Impaired absorption of oral levodopa: a major cause for response fluctuations in Parkinson’s disease. Isr J Med Sci 32(12):1224–1227
Edwards LL, Quigley EM, Pfeiffer RF (1992) Gastrointestinal dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease: frequency and pathophysiology. Neurology 42(4):726–732
Ekblad E, Alm P, Sundler F (1994) Distribution, origin and projections of nitric oxide synthase-containing neurons in gut and pancreas. Neuroscience 63(1):233–248
Ekblad E, Mulder H, Uddman R, Sundler F (1994) NOS-containing neurons in the rat gut and coeliac ganglia. Neuropharmacology 33(11):1323–1331
Forsyth CB, Shannon KM, Kordower JH, Voigt RM, Shaikh M, Jaglin JA, Estes JD, Dodiya HB, Keshavarzian A (2011) Increased intestinal permeability correlates with sigmoid mucosa alpha-synuclein staining and endotoxin exposure markers in early Parkinson’s disease. PLoS ONE 6(12):e28032. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0028032
Furness JB (2006) The enteric nervous system. Blackwell, Malden
Ganns D, Schrodl F, Neuhuber W, Brehmer A (2006) Investigation of general and cytoskeletal markers to estimate numbers and proportions of neurons in the human intestine. Histol Histopathol 21(1):41–51
Goetze O, Nikodem AB, Wiezcorek J, Banasch M, Przuntek H, Mueller T, Schmidt WE, Woitalla D (2006) Predictors of gastric emptying in Parkinson’s disease. Neurogastroenterol Motil 18(5):369–375
Goetze O, Wieczorek J, Mueller T, Przuntek H, Schmidt WE, Woitalla D (2005) Impaired gastric emptying of a solid test meal in patients with Parkinson’s disease using 13C-sodium octanoate breath test. Neurosci Lett 375(3):170–173
Greene JG, Noorian AR, Srinivasan S (2009) Delayed gastric emptying and enteric nervous system dysfunction in the rotenone model of Parkinson’s disease. Exp Neurol 218(1):154–161
Hanani M, Fellig Y, Udassin R, Freund HR (2004) Age-related changes in the morphology of the myenteric plexus of the human colon. Auton Neurosci 113(1–2):71–78. doi:10.1016/j.autneu.2004.05.007
Hoff S, Zeller F, von Weyhern CW, Wegner M, Schemann M, Michel K, Ruhl A (2008) Quantitative assessment of glial cells in the human and guinea pig enteric nervous system with an anti-Sox8/9/10 antibody. J Comp Neurol 509(4):356–371
Ippolito C, Segnani C, De Giorgio R, Blandizzi C, Mattii L, Castagna M, Moscato S, Dolfi A, Bernardini N (2009) Quantitative evaluation of myenteric ganglion cells in normal human left colon: implications for histopathological analysis. Cell Tissue Res 336(2):191–201
Irwin DA (1931) The anatomy of Auerbach’s plexus. Am J Anat 49:141–166
Johnson LR (2001) Gastrointestinal physiology. The Mosby Physiology Monograph Series, 6th edn. Mosby, Inc., St. Louis
Kupsky WJ, Grimes MM, Sweeting J, Bertsch R, Cote LJ (1987) Parkinson’s disease and megacolon: concentric hyaline inclusions (Lewy bodies) in enteric ganglion cells. Neurology 37(7):1253–1255
Kurlan R, Rothfield KP, Woodward WR, Nutt JG, Miller C, Lichter D, Shoulson I (1988) Erratic gastric emptying of levodopa may cause “random” fluctuations of parkinsonian mobility. Neurology 38(3):419–421
Lebouvier T, Chaumette T, Damier P, Coron E, Touchefeu Y, Vrignaud S, Naveilhan P, Galmiche JP, Bruley des Varannes S, Derkinderen P, Neunlist M (2008) Pathological lesions in colonic biopsies during Parkinson’s disease. Gut 57(12):1741–1743
Lebouvier T, Chaumette T, Paillusson S, Duyckaerts C, Bruley des Varannes S, Neunlist M, Derkinderen P (2009) The second brain and Parkinson’s disease. Eur J Neurosci 30(5):735–741
Lebouvier T, Neunlist M, Bruley des Varannes S, Coron E, Drouard A, N’Guyen JM, Chaumette T, Tasselli M, Paillusson S, Flamand M, Galmiche JP, Damier P, Derkinderen P (2010) Colonic biopsies to assess the neuropathology of Parkinson’s disease and its relationship with symptoms. PLoS ONE 5(9):e12728
Li ZS, Pham TD, Tamir H, Chen JJ, Gershon MD (2004) Enteric dopaminergic neurons: definition, developmental lineage, and effects of extrinsic denervation. J Neurosci 24(6):1330–1339
Murphy EM, Defontgalland D, Costa M, Brookes SJ, Wattchow DA (2007) Quantification of subclasses of human colonic myenteric neurons by immunoreactivity to Hu, choline acetyltransferase and nitric oxide synthase. Neurogastroenterol Motil 19(2):126–134
Neunlist M, Aubert P, Toquet C, Oreshkova T, Barouk J, Lehur PA, Schemann M, Galmiche JP (2003) Changes in chemical coding of myenteric neurones in ulcerative colitis. Gut 52(1):84–90
Neunlist M, Coquenlorge S, Aubert P, Duchalais-Dassonneville E, des Varannes SB, Meurette G, Coron E (2011) Colonic endoscopic full-thickness biopsies: from the neuropathological analysis of the myenteric plexus to the functional study of neuromuscular transmission. Gastrointest Endosc 73(5):1029–1034. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2011.01.041
Noorian AR, Taylor GM, Annerino DM, Greene JG (2011) Neurochemical phenotypes of myenteric neurons in the rhesus monkey. J Comp Neurol 519(17):3387–3401
Orimo S, Uchihara T, Nakamura A, Mori F, Kakita A, Wakabayashi K, Takahashi H (2008) Axonal alpha-synuclein aggregates herald centripetal degeneration of cardiac sympathetic nerve in Parkinson’s disease. Brain 131(Pt 3):642–650
Pascale A, Gusev PA, Amadio M, Dottorini T, Govoni S, Alkon DL, Quattrone A (2004) Increase of the RNA-binding protein HuD and posttranscriptional up-regulation of the GAP-43 gene during spatial memory. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 101(5):1217–1222
Pfeiffer RF (2003) Gastrointestinal dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol 2(2):107–116
Pfeiffer RF, Quigley EM (1999) Gastrointestinal motility problems in patients with Parkinson’s disease: epidemiology, pathophysiology, and guidelines for management. CNS Drugs 11:435–448
Phillips RJ, Hargrave SL, Rhodes BS, Zopf DA, Powley TL (2004) Quantification of neurons in the myenteric plexus: an evaluation of putative pan-neuronal markers. J Neurosci Methods 133(1–2):99–107
Pimont S, Bruley Des Varannes S, Le Neel JC, Aubert P, Galmiche JP, Neunlist M (2003) Neurochemical coding of myenteric neurones in the human gastric fundus. Neurogastroenterol Motil 15(6):655–662
Porter AJ, Wattchow DA, Brookes SJ, Costa M (1997) The neurochemical coding and projections of circular muscle motor neurons in the human colon. Gastroenterology 113(6):1916–1923
Porter AJ, Wattchow DA, Brookes SJ, Costa M (2002) Cholinergic and nitrergic interneurones in the myenteric plexus of the human colon. Gut 51(1):70–75
Pouclet H, Lebouvier T, Coron E, Neunlist M, Derkinderen P (2012) Lewy pathology in gastric and duodenal biopsies in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 27(6):708. doi:10.1002/mds.24993
Qu ZD, Thacker M, Castelucci P, Bagyanszki M, Epstein ML, Furness JB (2008) Immunohistochemical analysis of neuron types in the mouse small intestine. Cell Tissue Res 334(2):147–161
Shannon KM, Keshavarzian A, Mutlu E, Dodiya HB, Daian D, Jaglin JA, Kordower JH (2012) Alpha-synuclein in colonic submucosa in early untreated Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 27(6):709–715
Singaram C, Ashraf W, Gaumnitz EA, Torbey C, Sengupta A, Pfeiffer R, Quigley EM (1995) Dopaminergic defect of enteric nervous system in Parkinson’s disease patients with chronic constipation. Lancet 346(8979):861–864
Ueki A, Otsuka M, Otsuka M (2004) Life style risks of Parkinson’s disease: association between decreased water intake and constipation. J Neurol 251(Suppl 7):vII18–vII23
Wakabayashi K, Mori F, Tanji K, Orimo S, Takahashi H (2010) Involvement of the peripheral nervous system in synucleinopathies, tauopathies and other neurodegenerative proteinopathies of the brain. Acta Neuropathol 120(1):1–12
Wakabayashi K, Takahashi H, Ohama E, Ikuta F (1989) Tyrosine hydroxylase-immunoreactive intrinsic neurons in the Auerbach’s and Meissner’s plexuses of humans. Neurosci Lett 96(3):259–263
Wakabayashi K, Takahashi H, Ohama E, Ikuta F (1990) Parkinson’s disease: an immunohistochemical study of Lewy body-containing neurons in the enteric nervous system. Acta Neuropathol 79:581–583
Wakabayashi K, Takahashi H, Takeda S, Ohama E, Ikuta F (1988) Parkinson’s disease: the presence of Lewy bodies in Auerbach’s and Meissner’s plexuses. Acta Neuropathol 76(3):217–221
Wakabayashi K, Takahashi H, Takeda S, Ohama E, Ikuta F (1989) Lewy bodies in the enteric nervous system in Parkinson’s disease. Arch Histol Cytol 52(Suppl):191–194
Wedel T, Busing V, Heinrichs G, Nohroudi K, Bruch HP, Roblick UJ, Bottner M (2010) Diverticular disease is associated with an enteric neuropathy as revealed by morphometric analysis. Neurogastroenterol Motil 22(4):407–414 (e93–4). doi:10.1111/j.1365-2982.2009.01445.x
Wedel T, Roblick U, Gleiss J, Schiedeck T, Bruch HP, Kuhnel W, Krammer HJ (1999) Organization of the enteric nervous system in the human colon demonstrated by wholemount immunohistochemistry with special reference to the submucous plexus. Ann Anat 181(4):327–337
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research (JGG). We are grateful to the Banner Sun Health Research Institute Brain and Body Donation Program of Sun City, Arizona for the provision of the human specimens. The Brain and Body Donation Program is supported by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (National Brain and Tissue Resource for Parkinson’s Disease and Related Disorders), the National Institute on Aging (P30 AG19610 Arizona Alzheimer’s Disease Core Center), the Arizona Department of Health Services (contract 211002, Arizona Alzheimer’s Research Center), the Arizona Biomedical Research Commission (contracts 4001, 0011, and 05-901 to the Arizona Parkinson’s Disease Consortium) and the Prescott Family Initiative of the Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Annerino, D.M., Arshad, S., Taylor, G.M. et al. Parkinson’s disease is not associated with gastrointestinal myenteric ganglion neuron loss. Acta Neuropathol 124, 665–680 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-012-1040-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-012-1040-2