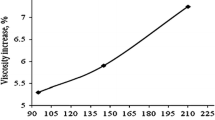
Abstract
Dielectric behaviors of titanium dioxide (TiO2)-based electrorheological (ER) suspensions with different particle concentrations and TiO2 polymorphs were investigated in the frequency range of 40 Hz to 110 MHz. Two relaxations in kilohertz and megahertz frequency range were attributed to interface polarization between TiO2 and silicone oil and ion pair polarization between dissociated counterions and fixed charges on TiO2 surfaces, respectively. Dipolar coefficient D, which is related to the construction or structure of the colloid, changes after critical volume fraction \(\phi _{\rm c} \approx \) 0.05, indicating that chain-like or network structures are formed by particles. Based on percolation model, the values of critical exponent suggest that particles may form two-dimensional percolation network. Furthermore, the effective dielectric mismatch parameter, \(\beta _{\rm eff}\), was calculated based on the obtained phase parameters. We found that rutile should have better ER activity than anatase. The main reason for weak ER activity of pure TiO2 ER suspensions may due to poor conductivity properties of TiO2 crystals.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balberg I, Binenbaum M, Wagner N (1984) Percolation thresholds in the three-dimensional sticks system. Phys Rev Lett 52:1465
Cheng QL, Pavlinek V, He Y, Li CZ, Saha P (2008) Structural and electrorheological properties of mesoporous silica modified with triethanolamine. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 318:169–174
Cheng QL, Pavlinek V, He Y, Li CZ, Saha P (2009) Electrorheological characteristics of polyaniline/titanate composite nanotube suspensions. Colloid Polym Sci 287:435–441
Cheng Z, Russel WB, Chalkin PM (1999) Controlled growth of hard-sphere colloidal crystals. Nature 401:893–895
Cole KS, Cole RH (1941) Dispersion and absorption in dielectrics. I. Alternating current characteristics. J Chem Phys 9:341–351
Dukhin SS, Shilov VN (1974) Dielectric phenomena and the double layer in disperse systems and polyelectrolytes. Wiley, New York
Espin MJ, Delgado AV, González-Caballero F, Rejon L (2007) Rheological properties of a model colloidal suspension under large electric fields of different waveforms. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 146:125–135
Grosse C, Shilov VN (2007) Dependence of the dielectric properties of suspensions on the volume fraction of suspended particles. J Colloid Interface Sci 309:283–288
Hanai T, Imakita A, Koizumi N (1977) Systematic analysis to determine of dielectric phase parameters from dielectric relaxations caused by diphasic structure of disperse systems. Bull Inst Chem Res Kyoto Univ 55:4
Hao T (2001) Electrorheological fluids. Adv Mater 13(2001):1847–1857
Hao T (2002) Electrorheological suspensions. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 9:71–35
Hao T, Kawai A, Ikazaki F (2001) Direct differentiation of the types of polarization responsible for the electrorheological effect by a dielectric method. J Colloid Interface Sci 239:106–112
Havriliak S, Negami S (1967) A complex plane representation of dielectric and mechanical relaxation processes in some polymers. Polymer 8:161–210
Hunt A, Ewing R (2009) Percolation theory for flow in porous media. Springer, Berlin, p 43
Ikazaki F, Kawai A, Kawakami T (1998) Mechanisms of electrorheology: the effect of the dielectric property. J Phys D Appl Phys 31:336
Klass DL, Martinek TW (1967) Electroviscous fluids. I. Rheological properties. J Appl Phys 38:67
Kitahara A (1984) Nonaqueous systems. In: Kitahara A, Watanabe A (eds) Electrical phenomena at interfaces. Marcel Dekker, New York, p 119
Labat F, Baranek P, Domain C, Minot C, Adamo C (2007) Density functional theory analysis of the structural and electronic properties of TiO2 rutile and anatase polytypes: performances of different exchange-correlation functionals. J Chem Phys 154703:126
Lee BH, Jeon Y, Zawadzki K, Qi WJ, Lee J (1999) Effects of interfacial layer growth on the electrical characteristic of thin titanium oxide films on silicon. Appl Phys Lett 74:3143
Liu AJ, Nagel SR (1998) Jamming is not just cool anymore. Nature 396:21–22
Liu FH, Xu GJ, Wu JH, Cheng YC, Guo JJ, Cui P (2010) Synthesis and electrorheological properties of oxalate group-modified amorphous titanium oxide nanoparticles. Colloid Polym Sci 288:739–1744
Parthasarathy M, Klingenberg DJ (1996) Electrorheology: mechanisms and models. Mater Sci Eng R 17:57–103
Safran SA, Webman I, Grest GS (1995) Percolation in interacting colloids. Phys Rev A 32:506–511
Schönhals A, Goeing H, Costa FR, Wagenknecht U, Heinrich G (2009) Dielectric properties of nanocomposites based on polyethylene and layered double hydroxide. Macromolecules 42:4165–4174
Schwan HP (1963) Determination of biological impedance. In: Nastuk WL (ed) Physical techniques in biological research, vol 6. Academic, New York, p 373
Stangroom JE (1983) Electrorheological fluids. Phys Technol 14:290
Stauffer D (1985) Introduction to percolation theory. Taylor & Francis, London
Trappe V, Prasad V, Cipelletti L, Segre PN, Weitz DA (2001) Jamming phase diagram for attractive particles. Nature 411:772–775
Van Beek LKH (1967) Dielectric behaviour of heterogeneous systems. In: Birks JB (ed) Progress in dielectrics, vol 7. Heywood Books, London, pp 69–114
Wang BX, Zhao Y, Zhao XP (2007) The wettability, size effect and electrorheological activity of modified titanium oxide nanoparticles. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 295:27–33
Wang HT, Xu S, Gordon RG (2010) Low temperature epitaxial growth of high permittivity rutile TiO2 on SnO2. Electrochem Solid-State Lett 13(9):G75–G78
Wen WJ, Ma HR, Tam WY, Sheng P (2000) Frequency-induced structure variation in electrorheological fluids. Appl Phys Lett 77:3821–3823
Winslow WM (1949) Induced fibration of suspensions. J Appl Phys 20:1137
Yang WL, Marino J, Monson A, Wolden CA (2006) An investigation of annealing on the dielectric performance of TiO2 thin films. Semicond Sci Technol 21:1573–1579
Yin JB, Zhao XP (2002) Preparation and electrorheological activity of mesoporous rare-earth-doped TiO2. Chem Mater 14:4633–4640
Yin JB, Zhao XP (2004) Giant electrorheological activity of high surface area mesoporous cerium-doped TiO2 templated by block copolymer. Chem Phys Lett 398:393–399
Yin JB, Zhao XP (2006) Enhanced electrorheological activity of mesoporous Cr-doped TiO2 from activated pore wall and high surface area. J Phys Chem B 110:12916–12925
Zhao KS, Asami K, Lei JP (2002) Dielectric analysis of chitosan microsphere suspensions: study on its ion adsorption. Colloid Polym Sci 280:1038–1044
Acknowledgment
Financial support of this work by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (nos. 21173025 and 20976015) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Zhao, K. & Zhang, L. Dielectric analysis of TiO2-based electrorheological suspensions. Rheol Acta 52, 115–125 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-012-0666-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-012-0666-2