Abstract
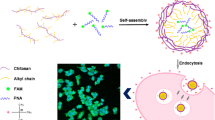
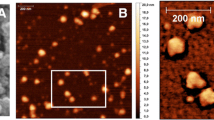
In this paper, a novel chitosan-g-(-O-methyl poly (ethylene glycol))-g-(-N-Tat peptide) (CS-mPEG-Tat) copolymer was synthesized. The synthesized intermediates and final products were characterized and confirmed by Fourier transform infrared spectrum, 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum, and X-ray diffraction, respectively. The particle sizes, size distributions, and zeta potentials can also be determined by dynamic light scattering. Agarose gel electrophoresis study showed effective DNA-binding ability of CS-mPEG-Tat. In vitro cytotoxicity assay indicated that CS-mPEG-Tat copolymers were low toxic and cell compatible as the polymer concentration was smaller than 5 mg/ml. This work provides a facile approach to prepare biocompatible PEG-peptide-chitosan copolymer nanoparticles with controllable performances. In conclusion, the obtained CS-mPEG-Tat copolymer might be attractive cationic polymers for nonviral gene therapy.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jin ML, Zhao K, Huang QS, Xu CL, Shang P (2012) Isolation, structure and bioactivities of the polysaccharides from Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels: a review. Carbohydr Polym 89(3):713–722. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.04.049
Crini G (2005) Recent developments in polysaccharide-based materials used as adsorbents in wastewater treatment. Prog Polym Sci 30(1):38–70. doi:10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2004.11.002
Liu L, Li YP, Li Y, Fang YE (2004) Rapid N-phthaloylation of chitosan by microwave irradiation. Carbohydr Polym 57(1):97–100. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2004.04.009
Mao C, Yuan J, Mei H, Zhu AP, Shen J, Lin S (2004) Introduction of photocrosslinkable chitosan to polyethylene film by radiation grafting and its blood compatibility. Materials Science & Engineering C-Biomimetic and Supramolecular Systems 24(4):479–485. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2003.09.168
Mao SR, Sun W, Kissel T (2010) Chitosan-based formulations for delivery of DNA and siRNA. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 62(1):12–27. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2009.08.004
Mao SR, Shuai XT, Unger F, Simon M, Bi DZ, Kissel T (2004) The depolymerization of chitosan: effects on physicochemical and biological properties. Int J Pharm 281(1–2):45–54. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2004.05.019
Ouchi T, Nishizawa H, Ohya Y (1998) Aggregation phenomenon of PEG-grafted chitosan in aqueous solution. Polymer 39(21):5171–5175. doi:10.1016/s0032-3861(97)10020-9
Pillai CKS, Paul W, Sharma CP (2009) Chitin and chitosan polymers: chemistry, solubility and fiber formation. Prog Polym Sci 34(7):641–678. doi:10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2009.04.001
Sieval AB, Thanou M, Kotze AF, Verhoef JE, Brussee J, Junginger HE (1998) Preparation and NMR characterization of highly substituted N-trimethyl chitosan chloride. Carbohydr Polym 36(2–3):157–165. doi:10.1016/s0144-8617(98)00009-5
Yi SS, Noh JM, Lee YS (2009) Amino acid modified chitosan beads: improved polymer supports for immobilization of lipase from Candida rugosa. J Mol Catal B-Enzymatic 57(1–4):123–129. doi:10.1016/j.molcatb.2008.08.002
Baumann H, Faust V (2001) Concepts for improved regioselective placement of O-sulfo, N-sulfo, N-acetyl, and N-carboxymethyl groups in chitosan derivatives. Carbohydr Res 331(1):43–57. doi:10.1016/s0008-6215(01)00009-x
Miao J, Chen GH, Gao CJ, Lin CG, Wang D, Sun MK (2006) Preparation and characterization of N, O-carboxymethyl chitosan (NOCC)/polysulfone (PS) composite nanofiltration membranes. J Membr Sci 280(1–2):478–484. doi:10.1016/j.memsci.2006.02.003
Kong XY, Li XY, Wang XH, Liu TT, Gu YC, Guo G, Luo F, Zhao X, Wei YQ, Qian ZY (2010) Synthesis and characterization of a novel MPEG-chitosan diblock copolymer and self-assembly of nanoparticles. Carbohydr Polym 79(1):170–175. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2009.07.037
Ohya Y, Cai R, Nishizawa H, Hara K, Ouchi T (2000) Preparation of PEG-grafted chitosan nanoparticles as peptide drug carriers. Stp Pharma Sciences 10(1):77–82
Bhattarai N, Ramay HR, Gunn J, Matsen FA, Zhang MQ (2005) PEG-grafted chitosan as an injectable thermosensitive hydrogel for sustained protein release. J Control Release 103(3):609–624. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2004.12.019
Chan P, Kurisawa M, Chung JE, Yang YY (2007) Synthesis and characterization of chitosan-g-poly(ethylene glycol)-folate as a non-viral carrier for tumor-targeted gene delivery. Biomaterials 28(3):540–549. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2006.08.046
Pasut G, Veronese FM (2009) PEG conjugates in clinical development or use as anticancer agents: an overview. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 61(13):1177–1188. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2009.02.010
Lin WJ, Lee HG (2003) Design of a microporous controlled delivery system for theophylline tablets. J Control Release 89(2):179–187. doi:10.1016/s0168-3659(03)00090-7
Heitz F, Morris MC, Divita G (2009) Twenty years of cell-penetrating peptides: from molecular mechanisms to therapeutics. Br J Pharmacol 157(2):195–206. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00057.x
Opalinska JB, Gewirtz AM (2002) Nucleic-acid therapeutics: basic principles and recent applications. Nat Rev Drug Discov 1(7):503–514. doi:10.1038/nrd837
Torchilin VP (2005) Recent advances with liposomes as pharmaceutical carriers. Nat Rev Drug Discov 4(2):145–160. doi:10.1038/nrd1632
Kong HJ, Mooney DJ (2007) Microenvironmental regulation of biomacromolecular therapies. Nat Rev Drug Discov 6(6):455–463. doi:10.1038/nrd2309
Ogris M, Wagner E (2002) Targeting tumors with non-viral gene delivery systems. Drug Discov Today 7(8):479–485. doi:10.1016/s1359-6446(02)02243-2
Vives E, Brodin P, Lebleu B (1997) A truncated HIV-1 Tat protein basic domain rapidly translocates through the plasma membrane and accumulates in the cell nucleus. J Biol Chem 272(25):16010–16017. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.25.16010
Betti M, Voltan R, Marchisio M, Mantovani I, Boarini C, Nappi F, Ensoli B, Caputo A (2001) Characterization of HIV-1 Tat proteins mutated in the transactivation domain for prophylactic and therapeutic application. Vaccine 19(25–26):3408–3419. doi:10.1016/s0264-410x(01)00067-6
Tung CH, Mueller S, Weissleder R (2002) Novel branching membrane translocational peptide as gene delivery vector. Bioorg Med Chem 10(11):3609–3614. doi:10.1016/s0968-0896(02)00248-1
Kilk K, El-Andaloussi S, Jarver P, Meikas A, Valkna A, Bartfai T, Kogerman P, Metsis M, Langel U (2005) Evaluation. of transportan 10 in PEI mediated plasmid delivery assay. J Control Release 103(2):511–523. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2004.12.006
Vives E, Schmidt J, Pelegrin A (2008) Cell-penetrating and cell-targeting peptides in drug delivery. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta-Reviews on Cancer 1786(2):126–138. doi:10.1016/j.bbcan.2008.03.001
Torchilin VP (2008) Tat peptide-mediated intracellular delivery of pharmaceutical nanocarriers. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 60(4–5):548–558. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2007.10.008
Yu YY, Wang Z, Cai L, Wang G, Yang X, Wan XP, Xu XH, Li Y, Gao R (2010) Synthesis and characterization of methoxy poly(ethylene glycol)-O-chitosan-polyethylenimine for gene delivery. Carbohydr Polym 81(2):269–274. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.02.018
Park IK, Kim TH, Park YH, Shin BA, Choi ES, Chowdhury EH, Akaike T, Cho CS (2001) Galactosylated chitosan-graft-poly(ethylene glycol) as hepatocyte-targeting DNA carrier. J Control Release 76(3):349–362. doi:10.1016/s0168-3659(01)00448-5
Acknowledgments
This research has received financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 81273471, 81001357 and 30901868), the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (no. 20090181120114), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (no. 2010SCU23008), and the Science Program of the Health Office of Sichuan Province, China (no. 090342).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, B., Ma, Q., He, G. et al. Synthesis and characterization of a novel methoxy poly(ethylene glycol)-Tat peptide-chitosan copolymers. Colloid Polym Sci 291, 1319–1327 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-012-2861-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-012-2861-1